Contents
Polymers
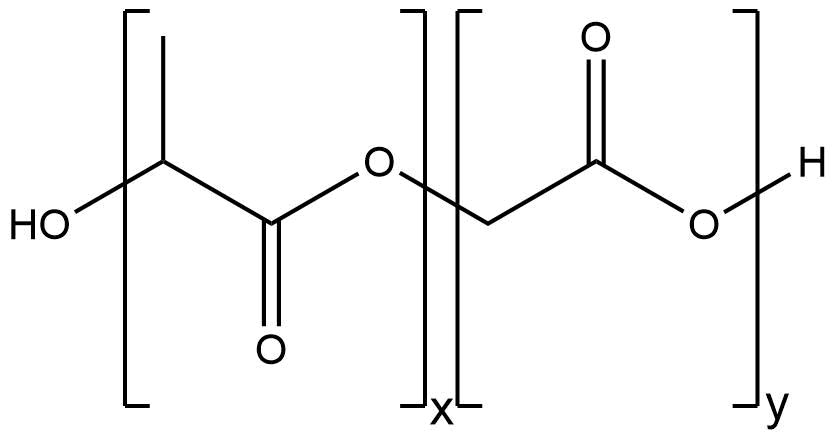
PLGA
There are two major methods for the synthesis of PLGA. The first method is the polycondensation reaction[1]. The second approach that we chose for our synthesis is the anionic ring opening polymerization (ROP). If the synthesis is performed using ROP we need a combination of an initiator and co-initiator to start a living polymerization.
This has the advantage of producing higher molecular weights than the previous method, due to there is no release of water as a couple product. High molecular weights are important for our desired application. The downside of the ROP is that it can be killed by low amounts of impurities like present water. The reaction therefore has to be carried out under an inert gas atmosphere and impurities have to be removed before the reaction by applying a strong vacuum on the reaction vessel. This can be easily achieved by using a schlenk. The Polymer is later analyzed via gel permeation chromatography (GPC) and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy[1].
For more information visit the PLGA page.
Figure 1: Structure of PLGA
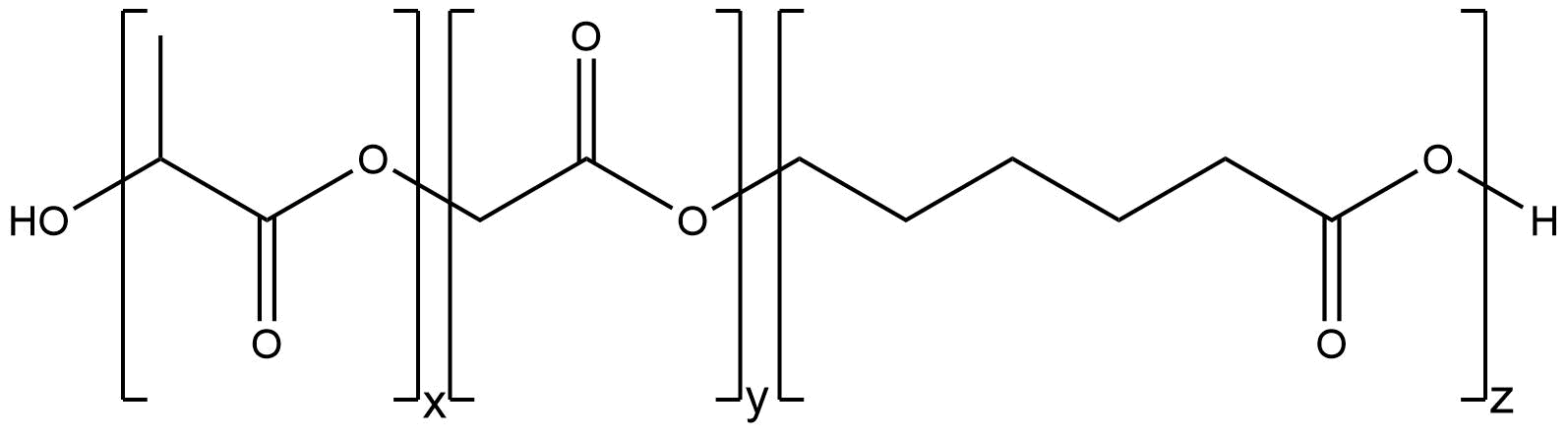
PLGC
Due to the fact, that Poly(Lactide-co-Glycolide-co-Caprolactone) (PLGC) is similar constructed to PLGA, the way of manufacturing is the same. PLGC is also synthesized via an anionic ring-opening polymerization. Both, the mechanism and the problems during the synthesis are identical. The essential difference lies in both the mechanical characteristics, which is explained in the background section, and the degradation behaviors of both polymers. The degradation behavior is an important polymer characteristic for all applications of PLGA and PLGC. Therefore we will focus on the structural difference, which leads to different characteristics. To analyze the synthesized PLGC, we also use GPC and NMR-spectroscopy. After that we used our purified polymer to manufacture PLGC nanospheres.
For more information visit the PLGC page
Figure 2: Structure of PLGC
Characterization & Analysis
To characterize and analyze our polymers, we used gel permeation chromatography (GPC) and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR). To analyze the nanospheres, we used dynamic light scattering spectroscopy (DLS), confocal microscopy and transmission electron microscopy (TEM).
For more information visit the Analysis page
Applications
The PLA co-polymers are biodegradable and can be used as wrapping materials, surgery supplies like suture stitches, or drug delivery systems for therapeutics.
We also put a focus on the manufacturing of nanospheres as a delivery system.
For more information visit the Application page
Team
Group picture of the "Chemistry" team
From left to right: Maurice Knebl, Felicitas Gülzow, Anies Rösch and Jonathan Funk