| Line 56: | Line 56: | ||
width: 120px !important; | width: 120px !important; | ||
} | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | .homeheight { | ||
| + | height: calc(100vh - 80px); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | .nextheight{ | ||
| + | height:250px; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | .hold{margin-top:-28px;} | ||
| + | .center{text-align:center;} | ||
| + | ._center{padding-left:20px;text-align:center;} | ||
| + | p{line-height: 30px; font-family: Georgia; font-size:17px;} | ||
| + | h2{font-family:thin;font-size:60px;color:#ffffff} | ||
| + | .blu{background-color:#4da2dc!important; | ||
| + | box-shadow: 0px 3px 1px #4da2dc} | ||
| + | .card{min-height:450px;} | ||
</style> | </style> | ||
<header> | <header> | ||
| − | <nav class=" | + | <nav class="blu"> |
<div class="nav-wrapper"> | <div class="nav-wrapper"> | ||
| − | <a href="#" class="brand-logo"> | + | <a href="#" class="brand-logo"></a> |
<a href="#" data-target="mobile-demo" class="sidenav-trigger"><i class="material-icons">menu</i></a> | <a href="#" data-target="mobile-demo" class="sidenav-trigger"><i class="material-icons">menu</i></a> | ||
<ul class="right hide-on-med-and-down"> | <ul class="right hide-on-med-and-down"> | ||
| Line 196: | Line 212: | ||
</ul> | </ul> | ||
</header> | </header> | ||
| + | <div class="section hold"></div> | ||
| − | <div | + | <div STYLE="position:absolute;top=20;width:100%"> |
| − | + | <div class="row container"> | |
| − | <h2 class="header"> | + | <br/><br/><br/><br/><br/><br/><br/><br/><br/><br/> |
| + | <h2 class="header center">NEU-China-A</h3> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| − | <div class="parallax-container"> | + | |
| − | + | <div class="homeheight"> | |
| − | + | <div class="parallax-container homeheight"> | |
| − | + | <div class="parallax"> | |
| + | <img class="responsive-img" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2018/d/d6/T--NEU_China_A--home1.jpg"> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | |||
</div> | </div> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
<div class="section white"> | <div class="section white"> | ||
<div class="row container"> | <div class="row container"> | ||
| − | <h3 class="header"> | + | <h3 class="header center">Overview</h3> |
</div> | </div> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| − | <div class="container row"> | + | |
| − | <img class="responsive-img" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2018/ | + | <div class="container row " > |
| + | <img class="responsive-img" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2018/c/cb/T--NEU_China_A--homepage-pic2-img.png" alt="Overview" onscroll="Materialize.fadeInImage('#image-test')"/> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="container row"> | <div class="container row"> | ||
| − | <p class=" | + | <p class="card-panel hoverable"> |
| − | + | The goal of NEU_China_A this year is to design a biological system aiming to alleviate intestinal inflammatory diseases and prevent potential colorectal cancer. We chose E. coli Nissle 1917 as our chassis, a probiotic that is safe for humans. On the one hand, when it senses an inflammatory signal in the intestine, it releases an anti-inflammatory drug (interleukin-10) to put out the fire in the intestines. On the other hand, it can release myrosinase to convert the glucosinolate contained in cruciferous vegetables into sulforaphane. The sulforaphane can both alleviate inflammation in the intestine and prevent colorectal cancer induced by chronic inflammation. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
</p> | </p> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
</div> | </div> | ||
| − | <div class="section white"> | + | <br/><br/> |
| − | + | <!-- first--> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | <!--<div class="row"> | |
| + | <div class="section white"> | ||
| + | <div class="row container"> | ||
| + | <h3 class="header center">Intestinal homeostasis</h3> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| − | <div class=" | + | <div class="row "> |
| − | <img class="responsive-img" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2018/ | + | <div class="col m7 pull-s5"> |
| + | <div class="_center"> | ||
| + | <img class="responsive-img" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2018/1/1a/T--NEU_China_A--fig1.png" alt="Intestinal homeostasis" /> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | <div class="col m5 pull-s7"> | ||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | <p class="card-panel hoverable"> | ||
| + | There are a lot of microorganisms living in the intestines. The intestinal villi and the underlying tissueshave | ||
| + | the largest immune cell population in the human body. Harmonious coexistence between the intestinalflora and | ||
| + | the immune cells is critical to human health. Consequently, the intestine has evolved severalmechanisms. | ||
| + | </p> | ||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| − | <div class=" | + | --> |
| − | + | <div class="row"> | |
| − | + | <div class="light-blue lighten-3"> | |
| − | + | ||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | <div class="row container"> | ||
| + | <h3 class="header center">Intestinal homeostasis</h3> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | <div class="container"> | ||
| + | <p class="card-panel hoverable caption center-align"> | ||
| + | There are a lot of microorganisms living in the intestines. The intestinal villi and the underlying tissueshave | ||
| + | the largest immune cell population in the human body. Harmonious coexistence between the intestinalflora and | ||
| + | the immune cells is critical to human health. Consequently, the intestine has evolved severalmechanisms. | ||
| + | </p> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | <div class="container row"> | ||
| + | <img class="responsive-img" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2018/1/1a/T--NEU_China_A--fig1.png" alt="Intestinal homeostasis" /> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | <div class="container row"> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div class="col s4"> | ||
| + | <div class="card"> | ||
| + | <div class="card-content"> | ||
| + | <p>In the crypt, the goblet cells secrete mucus covering the surface of the intestinal villi and Paneth cells | ||
| + | secrete antibacterial peptides to inhibit bacterial invasion. In addition, the basal stem cells continue to | ||
| + | proliferate and differentiate to renew the intestinal epithelium. | ||
| + | </p> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | <div class="col s4"> | ||
| + | <div class="card"> | ||
| + | <div class="card-content"> | ||
| + | <p>Peyer’s patch contains a large amount of lymphoid tissues, which is the key to regulating the immune | ||
| + | system's response to pathogens, and is tolerant to harmless microorganisms and food. Dendritic cells in the | ||
| + | Peyer’s patch can extend dendrites among epithelial cells, collecting antigen and decomposing it, by which | ||
| + | to activate the tolerability of lymphoid cells.</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | <div class="col s4"> | ||
| + | <div class="card"> | ||
| + | <div class="card-content"> | ||
| + | <p>Regulatory T cells secrete IL-10 in the lamina propria, inhibit the immune cells of the lamina propria and | ||
| + | epithelial layers, preventing vigorous immunoreaction along with unnecessary inflammation. Once the | ||
| + | imbalance of homeostasis in the immune system occurs, it can cause intestinal disease. When this condition | ||
| + | persists without intervention, it can lead to inflammatory bowel disease.</p> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| + | <br/><br/> | ||
| + | <div class="parallax-container nextheight"> | ||
| + | <div class="parallax"> | ||
| + | <img class="responsive-img" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2018/d/d6/T--NEU_China_A--home1.jpg"> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <!-- second --> | ||
| + | |||
<script type="text/javascript"> | <script type="text/javascript"> | ||
// 初始化navBar | // 初始化navBar | ||
| Line 262: | Line 346: | ||
$('.parallax').parallax(); | $('.parallax').parallax(); | ||
}); | }); | ||
| + | var instance = M.Tabs.init(el, options); | ||
| + | |||
| + | // Or with jQuery | ||
| + | |||
</script> | </script> | ||
</html> | </html> | ||
Revision as of 04:18, 16 October 2018
NEU-China-A

Overview
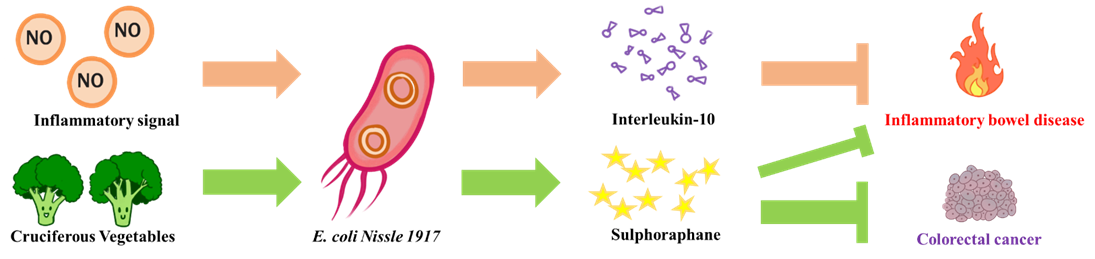
The goal of NEU_China_A this year is to design a biological system aiming to alleviate intestinal inflammatory diseases and prevent potential colorectal cancer. We chose E. coli Nissle 1917 as our chassis, a probiotic that is safe for humans. On the one hand, when it senses an inflammatory signal in the intestine, it releases an anti-inflammatory drug (interleukin-10) to put out the fire in the intestines. On the other hand, it can release myrosinase to convert the glucosinolate contained in cruciferous vegetables into sulforaphane. The sulforaphane can both alleviate inflammation in the intestine and prevent colorectal cancer induced by chronic inflammation.
Intestinal homeostasis
There are a lot of microorganisms living in the intestines. The intestinal villi and the underlying tissueshave the largest immune cell population in the human body. Harmonious coexistence between the intestinalflora and the immune cells is critical to human health. Consequently, the intestine has evolved severalmechanisms.

In the crypt, the goblet cells secrete mucus covering the surface of the intestinal villi and Paneth cells secrete antibacterial peptides to inhibit bacterial invasion. In addition, the basal stem cells continue to proliferate and differentiate to renew the intestinal epithelium.
Peyer’s patch contains a large amount of lymphoid tissues, which is the key to regulating the immune system's response to pathogens, and is tolerant to harmless microorganisms and food. Dendritic cells in the Peyer’s patch can extend dendrites among epithelial cells, collecting antigen and decomposing it, by which to activate the tolerability of lymphoid cells.
Regulatory T cells secrete IL-10 in the lamina propria, inhibit the immune cells of the lamina propria and epithelial layers, preventing vigorous immunoreaction along with unnecessary inflammation. Once the imbalance of homeostasis in the immune system occurs, it can cause intestinal disease. When this condition persists without intervention, it can lead to inflammatory bowel disease.


