Kasparas12 (Talk | contribs) |
Kasparas12 (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 462: | Line 462: | ||
<ol> | <ol> | ||
<li><p>Device height was greater than our largest expected droplets, so 2D model was sufficient;</p></li> | <li><p>Device height was greater than our largest expected droplets, so 2D model was sufficient;</p></li> | ||
| − | <li>Since our devices were technically perfectly symmetrical, it was more efficient to do calculations for only half of it and mirror the results;</li> | + | <li><p>Since our devices were technically perfectly symmetrical, it was more efficient to do calculations for only half of it and mirror the results;</p></li> |
| − | <li>Usually only the first few droplets need to be analyzed, so the length of post-junction part could be decreased;</li> | + | <li><p>Usually only the first few droplets need to be analyzed, so the length of post-junction part could be decreased;</p></li> |
| − | <li>Microchannels usually contain only one phase, so their length was not crucial.</li> | + | <li><p>Microchannels usually contain only one phase, so their length was not crucial.</p></li> |
</ol> | </ol> | ||
</p> | </p> | ||
Revision as of 21:04, 4 November 2018
Modeling
Mathematical model
Mathematical models and computer simulations provide a great way to describe the function and operation of BioBrick Parts and Devices. Synthetic Biology is an engineering discipline, and part of engineering is simulation and modeling to determine the behavior of your design before you build it. Designing and simulating can be iterated many times in a computer before moving to the lab. This award is for teams who build a model of their system and use it to inform system design or simulate expected behavior in conjunction with experiments in the wetlab
Edinburgh model
The β-barrel Assembly Machinery Complex
Outer membrane proteins (OMPs) of Gram-negative bacteria are synthesized in the cytoplasm and transported across the inner membrane by SecYEG translocon into the periplasm. The survival factor A (SurA) chaperones carry the unfolded membrane proteins across the periplasm to the BAM complex, which is responsible for the insertion and assembly of OMPs into the outer membrane [1].
In E. coli BAM complex consists of a membrane protein BamA and four lipoprotein subunits BamBCDE. These subunits associate with BamA through periplasmic POTRA domains. In vitro reconstitution of the E. coli BAM complex and functional assays showed that all five subunits are required to achieve the maximum activity of BAM [1].
In theory, recruiting the BAM complex in a cell-free system could be extremely beneficial as it could integrate OmpA and lgA protease beta-domain into the membranes of liposomes from the inside without requiring any additional protein complexes. Also, this would make a cell-free system more ubiquitous, because BAM complex does not require any signal sequence for proper protein insertion. In order to ensure quick integration, BamA needs to be consistently present at high yields throughout the expression of OmpA and lgA. For this reason, it is essential to stimulate its expression by an initial addition of mRNA, ensuring rapid expression of BamA. For this reason, with the help of Edinburgh iGEM team (special thanks to Freddie Starkey), a mathematical model for BamA kinetics was created.
Mass Action Equations
First of all, to represent chemical reactions and to render a start for mechanistic modelling, Mass Action Equations were used. It is known that the laws of mass action state that the rate of a chemical reaction is directly proportional to the product of the activities or concentrations of the reactants. The mass action equations in Figure 1 can be used to represent basic protein expression:

Fig. 1 Mass Action Equations for Protein Expression
Each of these equations is used in triplicate to represent the expression of BamA, OmpA and lgA respectively and from these mass action equations a system of ordinary differential equations can be derived.
Ordinary Differential Equations
The model uses a set of differential equations:

Fig. 2 System of differential equations for BamA kinetics
Determination of the System Values
In order to solve this system it is first necessary to derive values for all the parameters used:
1. copiesBamA, copiesOmpA, copiesIgA - Relative number of plasmid copies.
It is important to consider the effect of different starting masses of DNA of BamA, OmpA, and lgA, therefore to calculate the number of plasmids from which each protein can be expressed. Assuming that we add 25-1000 ng of DNA to our system [1], a single base pair has mass of 650 Da, and the length of each plasmid is known, mass of each plasmid was calculated:
- peT2Ab with BamA - 5089.5 kDa
- pRSETb with OmpA - 2550.95 kDa
- pRSETb with lgA - 2490.8 kDa
Knowledge that 1 ng equals to 6.022∗1017 kDa, allows to calculate the number of plasmids present for a particular number of ng of DNA added (Tab. 1).
Tab. 1 Number of plasmids present for a particular number of ng of DNA added
| peT2AB with BamA | |
|---|---|
| DNA added (ng) | Number of copies |
| 25 | 2.985*1015 |
| 250 | 2.958*1016 |
| 1000 | 1.183*1017 |
| pRSETb with OmpA | |
| DNA added (ng) | Number of copies |
| 25 | 5.902*1015 |
| 250 | 5.902*1016 |
| 1000 | 2.361*1017 |
| pRSETb with IgA | |
| DNA added (ng) | Number of copies |
| 25 | 6.04415 |
| 250 | 6.04416 |
| 1000 | 2.41817 |
2. trBamA, trOmpA, trIgA - Transcription rate.
Transcription rate of T7 RNA polymerase is approximately 60 nucleotides per second [2]. Length of each gene was 2430 nucleotides for BamA, 1038 nucleotides for OmpA, and 945 nucleotides for lgA. Transcription rate per minute for each gene was calculated:
- trBamA = (60/2430)∗60 = 1.48 mRNAs per minute
- trOmpA = (60/1038)∗60 = 3.47 mRNAs per minute
- trlgA = (60/945)∗60 = 3.81 mRNAs per minute
3. degmRNA BamA, degmRNA OmpA, degmRNA IgA - mRNA degradation rate.
Degradation rate is calculable from half-life using the formula: degX = ln(2)/halflife [3], where X shows the transcript of the target gene. Average mRNA half-life approximately is 5 minutes, however we screened half-lives of 1, 5, 10, and 15 minutes for each protein in order to more precisely evaluate the variability of the results. Degradation rates per minute were calculated:
- 1 minute half-life - 0.69 mRNAs per minute
- 5 minute half-life - 0.14 mRNAs per minute
- 10 minute half-life - 0.07 mRNAs per minute
- 15 minute half-life - 0.05 mRNAs per minute
4. trlBamA, trlOmpA, trlIgA - Protein translation rate.
Translation rate is about 20 amino acids per second [2]. Lengths of target proteins are 2430 nucleotides for BamA, 1038 nucleotides for OmpA, and 945 nucleotides for lgA. Translation rates per minute were calculated:
- trlBamA = (20/810)∗60 = 1.48 proteins per minute
- trlOmpA = (20/346)∗60 = 3.47 proteins per minute
- trllgA = (20/315)∗60 = 3.81 proteins per minute
5. degBamA, degOmpA, degIgA - Protein degradation rate.
Protein half-life was determined using ProtParam Tool, which uses the N-end rule [4] to determine protein half-life. The estimates given for each of BamA, OmpA, and lgA are >10 hrs in E. coli. In order to reflect the inexact nature of these computationally derived half-lives, we screened over possible half-lives of 10, 20, and 30 hours for each of BamA, OmpA, and lgA. Applying prior used degradation rate formula degX = ln(2)/halflife [3], this yielded degradation rates per minute of:
- 10 hour half-life - 1.16∗10−3 proteins per minute
- 20 hour half-life - 5.78∗10−4 proteins per minute
- 30 hour half-life - 3.85∗10−4 proteins per minute
Starting Conditions
In order to examine the effects of higher initial mass of BamA RNA, 6 different values were screened over (Tab. 2). Assuming that addition of RNA in IVTT system is between 1 and 5 µg, the masses of sense and antisense strands of BamA in kDa [6] are 830.382 and 820.8, respectively, and conversion is 1 µg = 6.022∗1020 kDa, the number of RNA molecules added can be calculated using the formula µgadded∗(6.022∗1020/((830.382+820.8)/2)).
Tab. 2 Initial BamA mRNA| RNA added (µg) | RNA added (molecules) |
|---|---|
| 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 7.29*1017 |
| 2 | 1.46*1018 |
| 3 | 2.19*1018 |
| 4 | 2.92*10 |
| 5 | 3.65*1018 |
The primary aim of this model was to identify parameters leading to rapidly-achieved and consistently high levels of BamA under conditions of co-expression of BamA, OmpA, and lgA. Prior to this it was important to identify particular parameters leading to these conditions and to examine some general trends. The number of molecules of mRNA and protein for each average, minimum and maximum plot and each of BamA, OmpA, and lgA after 2 hours were calculated (Fig. 3) and summarized (Tab. 3).
Fig. 3.1 Fig. 3.2
Fig. 3Minimum, maximum and average levels of mRNAs and protein for BamA, OmpA and lgA Tab. 3Average, minimum and maximum number of protein molecules after 2 hours'In average, minimum, and maximum cases the protein expression of OmpA, lgA, and BamA follows the same trend which is unaffected by fluctuations of mRNA level. Each protein is expressed at a rate primarily proportional to its length and to a magnitude primarily dependent on the mass of available DNA.
Sensitivity Analysis
Fourier Amplitude Sensitivity Testing (FAST) indices represent the proportion of the output variance of the model attributable to a particular variable and its interactions. Focusing on BamA expression as the protein of interest, total order FAST sensitivity indices were calculated using the BamA protein level each 20 minutes as the model output (Fig. 4).
Fig. 4
Fig. 4 FAST sensitivity analysis of BamAAs it can be seen from the graph, number of BamA plasmid copies contributes most to output variance over the whole time span. Also, BamA mRNA degradation rate is considerably faster than BamA degradation rate - with mRNA halflife of the order of minutes and protein halflife of the order of hours - hence the greater FAST index.
Conclusions
Prior to starting the wet lab experiments, we had hypothesized that the addition of mRNA into our system would ensure that BamA folded and inserted into liposome membrane more efficiently, thus enhancing the expression of OmpA and IgA. Therefore it was decided to purify BamA mRNA and add it to the reaction mixture as a template instead of DNA as we assumed that skipping the transcription step would increase protein synthesis rate. After creating a mathematical model that calculated the necessity of mRNA addition to IVTT system, we were able to generate a more efficient transcription-translation system in which we used both the purified BamA mRNA and DNA. This model clearly revealed that using both mRNA and plasmid DNA in our system was essential as BamA mRNA did increase the rate of protein expression while this effect was proportional to the mass of initial DNA. However, after experimenting in the wet lab, we chose to use purified BamA as it was desired to reach higher expression yields of membrane proteins and it proved to be more effective as BamA mRNA degradation rate was considerably faster than BamA protein degradation rate.
References
- Gu, Y. et al. Structural basis of outer membrane protein insertion by the BAM complex. Nature 531, 64-69 (2016).
- Biolabs, N. PURExpress® In Vitro Protein Synthesis Kit | NEB. International.neb.com (2018). at < https://international.neb.com/
- Philips, R. What is faster, transcription or translation?. Book.bionumbers.org (2018). at
- Exponential decay. En.wikipedia.org (2018). Accession: at
- Bachmair, A., Finley, D. & Varshavsky, A. In vivo half-life of a protein is a function of its amino-terminal residue. Science 234, 179-186 (1986).
- RNA Molecular Weight Calculator | AAT Bioquest. Aatbio.com (2018). Accession: at
eXplaY
Background
eXplaY logo
During the past several decades, display systems have been successfully implemented in linking the genotype to phenotype of particular proteins. While some of these systems naturally occur in nature, some are artificially created in laboratory. Overall, the display systems have been widely used for protein research. For a brief overview of these systems, BBa_K2622029 click here.
One of the nearest future applications of SynDrop is liposome surface display. It stands out from the other display methods as it has fully controllable settings of an experiment such as the optimized interior composition for synthesis and adjusted exterior configuration for protein folding. Unlike cells, liposomes are free of unnecessary cross-talk and biological noise. Additionally, high-throughput production of liposomes might reduce the experimental time substantially.
To achieve this goal, we chose a prokaryotic membrane protein - OmpA (Outer membrane protein A) - it was successfully used as a membrane protein which enables the display of a fused globular protein in prokaryotes1. In our case, we wanted to demonstrate two different proteins: scFv with affinity to vaginolysin2 and camelid nanobody, capable to interact with a GFP molecule3 . These membrane proteins were chosen to mimic targets of current display systems.
In nature, OmpA surface display system flips the selective protein from the inside of the living organism to the outside of its’ surface4. By achieving this in liposomes, the bottom-up approach would allow us to understand the mechanism and relevant components of the flipping process. For this reason, we decided to model a simple system with few variables to evaluate the activity of the fusion protein containing OmpA and Anti_GFP - it seemed like a good starting point to investigate well characterized parts. This is where molecular dynamics GROMACS package came in handy. GROMACS is a powerful open-sourced tool to build simulations of protein folding and lipids interactions. With a huge help from iGEM team Groningen molecular thermodynamics model with GROMACS was built.
Setup
Sequence of particular fusion protein was built BBa_K2622029.

Fig 1 Sequence scheme of Lpp_OmpA and Anti_GFP nanobody fusion protein.
Next, the fusion protein was constructed. The sequences of OmpA and anti-GFP (PDB: 3OGO) were joined exactly where they will be fused according to the DNA sequence using PyMOL (Fig. 2). To start, the structure of OmpA (PDB: 1QJP) had to be reconstructed as parts of it are missing in the crystal structure. This was achieved using the “modeler” software, a python module for homology modeling. The same structure was used as the reference structure and so the filled in structure only serves to complete the molecule.
Then the fusion protein was coarse grained by the martinize script, producing a well calibrated coarse grained bead mapping for the fusion protein in the MARTINI 2 forcefield. The fusion protein was then inserted in a DOPC bilayer constructed by the insane.py script.
GFP was also coarse grained using martinize and inserted in the system containing the fusion protein and the DOPC bilayer, after which the system was solvated with regular water beads. 150mM equivalence of NaCl was added to neutralize the system. For both coarse grained structures, an elastic network was applied with a cutoff of 0.5nm such that the beta-barrels of the proteins are maintained.

Fig 2 The molecular system. Left image represents the fused Lpp_OmpA+anti_GFP inserted to a DOPC lipid bilayer while the coarse grained structure of GFP is presented on the right.
To set up a calculation, the system having the simplest and least variables containing configuration was chosen:
- Lipid membrane, containing DOPC lipids only
- GFP molecules surrounding the membrane
- Lpp_OmpA+Anti_GFP (transmembrane protein + globular protein with affinity to GFP)
Common parameters for martini were used for minimization and equilibration, and the model was setup to run for about 10 microseconds with berendsen temperature coupling and Parrinello-Rahman pressure coupling. The system runs at 300 K and a pressure of 1 bar.
The building process is documented on the project’s github page
Results
Binding between anti-GFP and GFP was visualized over time in Fig. 3 to validate that the model functions as expected. Fig. 3 shows that binding occurs after roughly 1 ms and is quite strong as expected.

Fig 3 Distance between GFP and anti-GFP measured over time. Strong binding occurs over roughly 1 ms of simulation.
The Root Mean Square Deviation (RMSD) was computed over time using GROMACS and plotted in Fig. 4 to show OmpA unfolding over time. The entire event takes place over a time scale of roughly 1 ms.

Fig 4 OmpA unfolding visualized over time by computing the Root Mean Square Deviation from the starting conformation. Unfolding occurs roughly over a time scale of 1 ms.
Due to a strong tendency to shield charged residues within the remaining barrel structure from interacting with apolar lipids tails, a part of the transmembrane OmpA stays anchored in the lipid bilayer Fig. 5. The figure shows clearly that red and blue (charged) side chains are kept within the remnants of the beta barrel and only apolar and slightly polar side chains are exposed to the lipid environment.
Another observation is that the end of the unfolded beta-barrel is sticking out of the membrane, and contains many charged side chains as well, while the boundary between this part and the transmembrane domain is quite apolar. Overall this structure gives the impression to be still highly stable, but perhaps less stable than the native beta-barrel, anchored in the lipid bilayer.

Fig 5 Van der Waals representation of the side chains of OmpA in the membrane. The membrane is represented by dashed lines. The protein backbone is colored in magenta. White beads represent non-polar side chains, green beads represent polar side chains (of varying polarity, there are 5 different levels of polarity in Martini and they are all colored green), blue beads represent positively charged side chains and red beads represent negatively charged side chains.
As this large scale conformational change should have a large effect on the behaviour of the protein, the angle between OmpA and the membrane normal was measured over time. To visualize trends in the data, a running average was calculated with a window of 100 frames. Fig 6. shows that this angle oscillates stably around 84.9 degrees. However after 10 ms of simulation, the angle suddenly shifts to 84 degrees. This could be an indication that the usual right-angle of OmpA is perhaps not so stable in the new conformation this fusion protein adopts.

Fig 6 Angle between OmpA and membrane normal, running average over time. The angle oscillates stably around 84.9 then suddenly drops to 84.
Under the assumption that the fusion protein indeed retains this conformation, the unfolding beta-barrel and subsequent stable anchoring in the membrane is a novel insight. As the system is meant to function as a display mechanism for soluble proteins binding to it, it is likely that this change in conformation contributes to this mechanism. It is hypothesized that the protein-ligand complex flips across the lipid bilayer entirely to function as a display system, generally assisted by chaperone proteins. Since the angle between OmpA and the membrane normal becomes more acute over the time scale of the simulation, unfolding of the beta-barrel structure may contribute to OmpA flipping over the lipid bilayer to display its ligand.

Fig 7 A. OmpA-anti-GFP fusion structure at the start of the simulation represented on the left. OmpA is colored in green, anti-GFP is colored in red. Martini elastic bonds are colored in orange. Membrane position is indicated with dashed lines. B. Fusion protein after 10ms of simulation. GFP is colored in blue.
Conclusions
In conclusion, it seems that the system is working as intended, as the OmpA-anti-GFP fusion protein stays anchored in the lipid bilayer and remains able to strongly bind GFP as expected. Whether this is the real situation is however impossible to know as the fusion abolishes some beta-sheets in OmpA that are important for beta-barrel formation.
Discussion
It is always difficult when modeling these kinds of processes to predict the time scale of the whole event. The current model helps us to predict that the flipping process is very slow or unfeasible at all. The latter hypothesis might be reasonable enough and it would allow us to predict that the surface display system requires additional machinery which is found in living organisms. Therefore, it is unlikely to achieve a more accurate model without extra experimental information.
In eXplaY we model a system in a pure DOPC bilayer, which is also a simplified version of natural systems. Original E. coli lipids composition can make a huge impact to the model and its’ results as well.
Potential of mean force(PMF) simulations on pulling the anti-GFP across the membrane needs to be made in order to prove that the energy barrier is really high and the process can not occur naturally. Additionally, to observe flipping in a modeled system, higher temperature (37°C) might be a promising solution.
References
- Freudl, R. Insertion of peptides into cell-surface-exposed areas of the Escherichia coli OmpA protein does not interfere with export and membrane assembly. Gene 82, 229-236, doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-1119(89)90048-6 (1989).
- Pleckaityte, M., Mistiniene, E., Lasickiene, R., Zvirblis, G. & Zvirbliene, A. Generation of recombinant single-chain antibodies neutralizing the cytolytic activity of vaginolysin, the main virulence factor of Gardnerella vaginalis. BMC biotechnology 11, 100, doi:10.1186/1472-6750-11-100 (2011).
- Twair, A., Al-Okla, S., Zarkawi, M. & Abbady, A. Q. Characterization of camel nanobodies specific for superfolder GFP fusion proteins. Molecular biology reports 41, 6887-6898, doi:10.1007/s11033-014-3575-x (2014).
- Benhar, I. Biotechnological applications of phage and cell display. Biotechnology Advances 19, 1-33, doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/S0734-9750(00)00054-9 (2001).
COMSOL model
Background
Phase-field modeling overview
Phase-field models are mathematical models used for solving interfacial problems. They are based on the generalized free-energy functional approach (lattice Boltzmann), meaning that the system evolution is driven by the minimisation of free energy. Important thing to note is that sharp fluid interfaces in the models are replaced by a thin transition region where the interfacial forces are distributed in a smooth manner. This provides model an easy treatment of topological variations at the interface1. In order to describe phases in numerical form, equations use phase variables ϕ. In three-phase systems, phase variables are described as ϕi , where i = A, B, C, and the variable is equal to 1 in the phase i and 0 outside.
Typically used phase-field models for two and three phase fluid systems couple fourth order nonlinear advection-diffusion equations, called Cahn-Hilliard equations, which represent the evolution of the phase variables with the Navier-Stokes equations for the fluid motion 2 . Equations (1), (2) and (3) form the traditional Cahn-Hilliard equation, and Eq. (4) is Navier-Stokes equation - both of them are used in our calculations on COMSOL
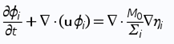



M0 is the mobility tuning parameter that determines the relaxation time of interface and the time scale of diffusion in C-H equation. It should be noted, that interfacial diffusion (the Gibbs-Thomson effect) is inevitable in phase phase field method because the diffusion term is used in the right side of Eq. (1). Due to this, prolonged simulations of our system result in spheres diffusing and constantly changing their size (Fig. 1.). Because of that, we have chosen to analyze only the first few spheres formed in every simulation as their size proved to be most accurate.
ϵ (interface thickness parameter) is also an important parameter as it defines the width of transition between phases and affects both the surface tension force and the relaxation time of interface. Usually it is compared to the characteristic length of the system and must be chosen small enough to depict interface changes accurately, yet too small of a thickness shall cause instabilities in calculations.
Most of the time the model can be described with several dimensionless parameters, such as capillary number calculated for the continuous phase, Ca =μcvc/γ, the Reynolds number Re =ρvcL/μc, the viscosity ratio λ=μd/μc, and the flow rate ratio Q=vd/vc 3. In our model Reynolds number is small (Re < 1) and does not influence droplet size, so we mainly focus on Ca, λ and Q and consider the influence of the latter two on the liposome formation.


Geometry
Since the microfluidic devices were designed by ourselves, we were able to extract the exact geometry from the CAD file. The part that interested us was the junction at which all of three phases contacted and started forming droplets (Fig. 2). However, we then proceeded to minimize the geometry (Fig. 3) in order to reduce the computation times and improve solution qualities:
Device height was greater than our largest expected droplets, so 2D model was sufficient;
Since our devices were technically perfectly symmetrical, it was more efficient to do calculations for only half of it and mirror the results;
Usually only the first few droplets need to be analyzed, so the length of post-junction part could be decreased;
Microchannels usually contain only one phase, so their length was not crucial.


Mesh
For solving the model we used finite element method, which divides geometry into small mesh elements, where partial differential equations are solved. Interface capturing method incorporated in it keeps the mesh fixed and the boundary discontinuities are smeared out over the finite width ϵ 3,4. To successfully capture interface movement between different phases, mesh size should be small enough, but not too small, as every single element adds more time to computing and quality of the results stops improving substantially at a certain point.
Most of the time we only control the size of mesh elements. For our channel domains a predefined normal sized mesh was used, as they only contained one phase and interface problems did not occur there. For junction and post-junction parts, a predefined extra fine mesh was used with maximum element size value set to 1µm, which is 1/10 size of a smallest expected droplet and also 1/10 of our characteristic length, which has been chosen to be the width of horizontal IA channel (Fig. 4)
Fig. 4 Generated mesh used in all simulations. Refined grid in junction and post-junction helps with realistic interface capturing.Materials
Our system consists of three different fluids: OA (Outer Aqueous), IA (Inner Aqueous) and LO (Lipid carrying organic) phases. It should be noted that experiments have been carried with fluids of many different compositions, but here we use only one for each. IA and OA phases are quite similar so for simplicity, we set the same densities for both of them. It has a negligible influence on the results since in most microfluidic configurations buoyancy-driven speeds are much smaller than the actual flow speeds 3. Parameters and compositions of materials are shown in Tab. 1.
Tab. 1Main parameters of our fluid system. To simplify the system and approximate the viscosity closest to reality, only the content of glycerol, octanol and water was taken into account.| Phase | Density ρ(kg/m3) | Dynamic viscosity µ (Pa*s) | Real composition |
|---|---|---|---|
| OA | 1000 | 0.00119 | Purefrex custom buffer and surfactant (treated as 7% glycerol and 93% water) |
| IA | 1000 | 0.00115 | Purefrex IVTT reaction mixture (treated as 6% glycerol and 94% water) |
| LO | 830 | 0.00736 | 98% octanol 2% lipids |
Description of the System
Fig. 3 shows our flow focusing model configuration with boundaries specified. There is one main inlet for IA phase, and two for each LO and OA phases on the left side. On the right side, there is an outlet with outflow pressure set to p = 0. For laminar flow, wall condition is set to no slip, which states that the flow velocity at the walls is always v = 0 and it gives a good approximation of the whole system.
In experimental set-up, we coat the OA channels, junction and post-junction with PVA to make it hydrophilic, contrary to hydrophobic PDMS, which is the material of which the microfluidic devices are made. This provides a good setting for liposome formation5, and we take that into account by adjusting contact angles at the wetted walls for ternary phase field node. With respect to model limitations (nukreipia į skiltį limitations), all the contact angles in IA and LO channels are set to 90 degrees. In the coated side, we assume phase OA has a perfect wetting condition on the channel walls against both IA and LO phases, while the contact angle between the latter two is set at 30 degrees.
The aforementioned interface thickness parameter ϵ is set to 1.4 µm as it is the lowest stable value regarding our mesh and mobility tuning parameter, though it is more than enough to accurately depict the results of simulations. Surface tension is another important aspect to be considered and it is set to σ = 0.0085 N/m, which is an interfacial tension between octanol and water 6, for all three interfaces between phases (See Limitations).
In order to make our model as realistic as possible, several other parameters are taken from a single baseline wet lab experiment with similar materials and geometry as mentioned before.
Flow rates are transformed into flow velocities for COMSOL and calculated as described in Tab. 2.
Tab. 2 Specifications of baseline set-up fluid flows.| Channel | Inlet area(µm2) ρ(kg/m3) | Flow rate(µL/h) | Flow velocity (m/s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| OA | 273 | 240 | 0.244 |
| LO | 157 | 14.57 | 0.0258 |
| IA | 193 | 11.36 | 0.0164 |
Mobility parameter in this model is crucial. As its value becomes higher, droplet size in micro-channel increases. This can be explained by the parameters’ mathematical function - raising values causes the increase in interface relaxation time, meaning the diffusion gets stronger as well 1>. So we have compared the numerical and experimental results of liposome synthesis (Fig. 5) and approximated our characteristic mobility tuning parameter to be M0 = 2E-12 m3>/s. The diameter of the droplet with this value was 12.1µm, which is a close match to the real size.


Results
Parametric sweeps and example of liposome radius calculation
In order to investigate how our system depends on certain parameters, we have performed parametric sweeps on every one of these parameters separately. By doing so, COMSOL Multiphysics resolved our model with every parametric value specified automatically and stored the results under a single node. To find out the size of the liposomes, the first fully formed droplet was taken and 2D cut line data set was created going through the middle of the sphere in y-axis direction (Fig. 6). Next, the variation of phase variable C (which stands for our IA phase) was extracted from the data set and results were depicted in graphs. The exact point of phase edge for all studies performed has been assumed as ϕc = 0.5.

Liposome size dependence on viscosity ratio λ
First of all, the impact of IA and OA phase viscosity ratio ( λ = µIA/µOA) was investigated. Studies suggest, that increasing λ also increases the generated droplet size 7. Though the changes are more significant in high capillary numbers, where droplet formation is driven by viscosity. In our case, the capillary number was relatively small (Ca ≈ 0.034), so the flow was more surface tension-dominated. The simulation was run with a set of different OA phase dynamic viscosity values (Tab. 3.) and results are presented in Fig. 7 and Fig. 8.
Tab. 3 Values of OA phase dynamic viscosity used for parametric sweep; µIA = 0.00115 Pa*s.| No. | OA dynamic viscosity µOA (Pa*s) | Viscosity ratio λ |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.00050 | 2.300 |
| 2 | 0.00119 | 0.966 |
| 3 | 0.00130 | 0.885 |
| 4 | 0.00150 | 0.767 |
| 5 | 0.00200 | 0.575 |
| 6 | 0.00300 | 0.383 |
| 7 | 0.00800 | 0.144 |


As we see, droplet size increases almost linearly up to λ = 0.996, meaning that increasing viscosity of OA phase leads to formation of smaller liposomes. However, it should be noted that by increasing viscosity in real life, we may encounter other problems, such as impeded droplet formation or liposomes bursting due to differences in osmotic pressure between inside and outside environments. Given these limitations, we can still effectively control our liposome size in about 1µm range. Thus, we can conclude that viscosity ratio, while having a moderate effect, is still not a decisive parameter in vesicle size determination.
Liposome size dependency on velocity ratio V
Flow rates of our fluids were easiest and fastest to control as a parameter, so they certainly needed to be studied more deeply. The flow of the continuous phase here was fixed, so the Capillary number could be considered as a constant. Thus, only the flow rate of disperse IA phase was varied and the effect of flow rate ratio (Q = QIAIA/QOA) could be assessed. The simulation was run with a set of different IA phase flow velocity values (Tab. 4.) and results are presented in Fig. 9 and Fig. 10.
Tab. 4 Values of IA phase flow velocities used for parametric sweep and reference flow rates and ratios; vOA= 0.244 m/s, QOA= 240µl/h.| No. | IA flow velocity vIA (m/s) | IA flow rate QIA(µl/h) | Flow rate ratio Q |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.0050 | 3.46 | 0.014 |
| 2 | 0.0100 | 6.93 | 0.029 |
| 3 | 0.0164 | 11.36 | 0.047 |
| 4 | 0.0500 | 34.63 | 0.144 |
| 5 | 0.0750 | 51.95 | 0.216 |
| 6 | 0.1000 | 69.27 | 0.289 |
| 7 | 0.2000 | 138.54 | 0.577 |


Relying on the results we can safely assume, that liposome size depends directly on IA phase flow rate. However studies suggest that this dependency is not linearly proportional because the droplet formation process is also affected by the surface tension force and the dynamic energy equilibrium1. This seems to be true considering given data.
In contrary to dynamic viscosity ratio variation, flow rate ratio can be experimentally modified in a broad range of values, meaning we can effectively synthesize liposomes from 12 µm to around 17 µm with our current set-up. Nevertheless, we have found that when Q = 0.7, spheres cannot form anymore, as the OA phase cannot cut the stream of IA phase and it transforms into a continuous flow (Fig. 11). Therefore, Q = 0.7 is the critical value for liposome synthesis in our system. In conclusion, the regulation of IA phase flow rate gives us an effective and fast method to vary the size of our liposomes in a range of few micrometers.

Liposome size dependency on IA channel width w
While our goal has always been to attain cell-sized liposomes, which stretch from 5 µm to 30 µm, theoretically we had yet only managed to produce 10 µm to around 17 µm sized vesicles by modifying dynamic viscosity and flow rates of our fluids. It became clear that in order to expand this range, we had to start from the microfluidics device design. Possibilities of the design are virtually infinite, but here we focused on the width of IA phase channel, which we assumed to have the biggest impact on sphere size.
In our model configuration, we have added an additional parameter wy, which is the width expansion of the device parallel to the symmetry axis (See Geometry). The simulation was run with a set of different wy values (Tab. 5.) and results are present in Fig. 12 and Fig. 13
Tab. 5 Values of wy used for parametric sweep, the width of channels with parameter applied and IA phase inflow velocities, which were varied in order to keep the flow rate constant.| No. | wy(µm) | IA channel width (µm) | IA flow velocity vIA(m/s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 10 | 0.0164 |
| 2 | 0.5 | 11 | 0.0148 |
| 3 | 1 | 12 | 0.0135 |
| 4 | 1.5 | 13 | 0.0125 |
| 5 | 2 | 14 | 0.0116 |
| 6 | 2.5 | 15 | 0.0108 |


As we can see, channel width has a huge impact on the size of liposomes. Even by keeping flow rates of all phases the same, droplet radius variations depend solely on channel dimensions. We have tested channels from 10 µm to 15 µm, but other widths should also comply with given results and the only limit on minimal channel dimensions could be the quality of photolithography used in production of microfluidic devices.Using given results we can now calculate the required width of the channel in order to produce liposomes of needed size as well as synthesize them in whole range of 5-30 µm.
Conclusion
From the simulations we’ve gained much invaluable information about liposome size determination in silico, which led us to saving some of our most expensive reagents, such as Purefrex IVTT system. Also, we could conclude that the system worked just as expected and it matched real life experiments surprisingly well. All of the studied parameters affected liposome size to some extent, IA channel-junction width being the most sensitive and effective, flow rate ratio being easiest to control for fine adjustments, while dynamic viscosity ratio tuning may be used in tandem with flow rate regulation.
Discussion
Although we can choose from a vast selection of different parameter values to achieve needed results, there are consequences to every change since microfluidics’ experiments are so delicate. For this reason, parameters for every experiment should be properly evaluated in order to evade failed attempts and wasted materials. For example, proper junction between all three phases sometimes might be so sensitive, that even slight variations can disrupt the flow. In this case, it might be wiser to avoid extreme flow rate changes and design devices with a bit different channel dimensions at first. Moreover, liposome velocity increases with IA phase flow rate, so by colliding with each other in post-junction, risk of them bursting also increases. This is also the case with viscosity changes because it may sometimes be hard to regulate dynamic viscosity ratio without disrupting osmotic pressure. To conclude, every experiment should begin with selection of the right channel design, while flow rate and viscosity regulation should only be used for fine-tuning
Model Limitations
Our model has some limitations. Due to the nature of phase-field model and minimal free energy principle, it proved to be an invidious task to model liposomes exactly like in the real life. Since we cannot characterize lipids and surfactants inside our materials to act as in reality, LO phase just forms a distinct sphere outside of junction instead of surrounding the IA phase.
However, LO phase doesn’t impact the size of liposomes in any meaningful way and just needs to barely reach the junction to subsequently form a pocket for inner fluid. So, in order to mimic the reality as best as possible, we have made a few adjustments:
- The surface tension between IA and OA phases was set the same as LO and OA, to depict the interface movement correctly.
- The surface tension between IA and OA phases was set the same as LO and OA, to depict the interface movement correctly.
References
- Bai, F., He, X., Yang, X., Zhou, R. & Wang, C. Three dimensional phase-field investigation of droplet formation in microfluidic flow focusing devices with experimental validation. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 93, 130–141 (2017).
- Kim, J. Phase-Field Models for Multi-Component Fluid Flows. Commun. Comput. Phys. 12, 613–661 (2012).
- De Menech, M., Garstecki, P., Jousse, F. & Stone, H. A. Transition from squeezing to dripping in a microfluidic T-shaped junction. J. Fluid Mech. 595, (2008).
- Boyer, F., Lapuerta, C., Minjeaud, S., Piar, B. & Quintard, M. Cahn–Hilliard/Navier–Stokes Model for the Simulation of Three-Phase Flows. Transp. Porous Media 82, 463–483 (2010).
- Deshpande, S., Caspi, Y., Meijering, A. E. C. & Dekker, C. Octanol-assisted liposome assembly on chip. Nat. Commun. 7, 10447 (2016).
- Demond, A. H. & Lindner, A. S. Estimation of interfacial tension between organic liquids and water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 27, 2318–2331 (1993).
- Nekouei, M. & Vanapalli, S. A. Volume-of-fluid simulations in microfluidic T-junction devices: Influence of viscosity ratio on droplet size. Phys. Fluids 29, 032007 (2017).
Thermo Switches model
Background
RNA thermometers are RNA-based genetic control tools that react to temperature changes 1. Low temperatures keep the mRNA at a conformation that masks the ribosome binding site within the 5’ end untranslated region (UTR). Masking of the Shine-Dalgarno (SD) sequence restricts ribosome binding and subsequent protein-translation. Higher temperatures melt the hairpins of RNA secondary structure allowing the ribosomes to access SD sequence to initiate translation 1. In terms of applicability of RNA thermometers in in vitro systems, they display certain advantages over ribo- or toehold switches: they do not require binding of a ligand, metabolite or trigger RNA to induce the conformational change 2,3, therefore are especially compatible with liposome IVTT system.
Although some acquirable and already tested thermoswitches can be found in literature 1,4, the field is still particularly underexplored. Possibility to design countless synthetic thermoswitches corresponding to different temperatures and of varying structure, is facilitated by computational models and RNA bioinformatics approaches. Together with two pioneers in this field from Vienna University (see Attributions), we have de novo designed six heat-inducible RNA thermometers previously never mentioned in any paper or literature review. Not only did they complement SynDrop, but also helped expanding the library of well characterized and widely-applicable biobricks.
Concept of the Model
We have optimized the opening energy of the ribosome docking site, which is a stretch of 30 nucleotides starting at the beginning of the Shine-Dalgarno (SD) sequence downstream into the coding sequence. This region corresponds to the binding footprint of the assembled initiation ribosome and must be unfolded prior to the assembly of the ribosome machinery. The model optimized for that region to have a high opening energy (meaning low translation efficiency) at low temperatures and a low opening energy (high translation efficiency) at high temperatures. Opening energies were calibrated around the mean value of opening energies observed for all protein coding genes in E. coli. When designing custom synthetic RNA thermometers, it was important to take into account the upstream and downstream sequences of our constructs and to model different structures and sequences in order to select only the best ones for practical implementation. Therefore 10 designs for each construct was designed (see figures below) out of which only 1 was selected based on the computed plots of translation efficiency vs. temperature.
Results
the model computed total 40 different thermoswitches for our composite parts, 10 for each:
- Mstx-OmpA-GFP Nanobody;
- GFP Nanobody-Iga-Mstx;
- Mstx-OmpA-His;
- His-Iga-Mstx.
Only 1 design was selected based on the computed plots of translation efficiency vs. temperature.
Fig. 1 Plots of translation efficiency vs. temperature. On the left hand side: plots of 10 modelled thermoswitches for Mstx-OmpA-GFP Nanobody. On the right hand side: plot of the selected thermoswitch to use with Mstx-OmpA-GFP Nanobody. RNA thermometer termed sw_6 displayed no artifacts, with near control-identical translation efficiency at high temperature and low efficiency at < 25 C.
Fig. 2 Plots of translation efficiency vs temperature. On the left hand side: plots of 10 modelled thermoswitches for GFP Nanobody-Iga-Mstx. On the right hand side: plot of the selected thermoswitch to use with GFP Nanobody-Iga-Mstx. RNA thermometer termed sw_5 displayed no artifacts, with relatively high translation efficiency at high temperature and largely lower efficiency at < 25 C.
Fig. 3 Plots of translation efficiency vs. temperature. On the left hand side: plots of 10 modelled thermoswitches for Mstx-OmpA-His. On the right hand side: plot of the selected thermoswitch to use with Mstx-OmpA-His. RNA thermometer termed sw_8 displayed no artifacts, with near control-identical translation efficiency at high temperature and low efficiency at < 25 C.
Fig. 4 Plots of translation efficiency vs temperature. On the left hand side: plots of 10 modelled thermoswitches for His-Iga-Mstx. On the right hand side: plot of the selected thermoswitch to use with His-Iga-Mstx. RNA thermometer termed sw_4 displayed no artifacts, with relatively high translation efficiency at high temperature and largely lower efficiency at < 25 C.
Thermoswitches were initially designed to appropriately melt and function at 37 C. Comparing the first curve in each plot which resembles the original sequence of our constructs without incorporated thermoswitch (control), it can be seen that novel designs show much stronger temperature dependence. However, they did not manage to achieve quite exact 37 C and displayed marginally lower translation efficiency than controls. Some sequences displayed artifacts that showed up as jumps in the efficiency plots. The believed reason was the usage of different SD sequences at low and high temperatures. For in vivo testing we selected designs that did not exhibit such jumps. Another interesting finding was that all thermoswitches designed for Iga protease bearing constructs showed a considerably lower efficiency of translation even at higher temperatures compared to OmpA bearing constructs, meaning that this characteristic was probably attributed to membrane protein structure and would be needed to be addressed in the future.
The model was also applied to check the activity of thermoswitches that we have acquired from literature (see Design and Results/RNA Thermoswitches). Our model predicted fair, but viable switching effects for thermoswitch-GFP designs, which were later supported by in vivo measurements.
Fig. 5 Plots of translation efficiency vs. temperature of the “GJ” thermoswithes-GFP constructs. Thermoswitches GJ2, GJ3, GJ9, GJ10 display similarly fair translation efficiency at 37 C, except for GJ6, which displays notably higher translation efficiency. GJ thermoswitches significantly differ in their activity at lower temperatures, with GJ9 locking the transcription most tightly and GJ3 being the leakiest of all tested designs.
Model
A simple in-silico translation-initiation potential model5 to quantify the likelihood of in vitro translation of a given mRNA sequence from a series of interaction energy parameters at constant temperatures was developed. The model defines the translation-initiation potential σ as:
Fig. 6
where R is the Boltzmann constant, T the temperature, ΔESD the hybridization energy between the SD and anti-SD sequences, ΔEtRNA the hybridization energy of the start codon and its respective anti-codon (i.e, the tRNAMet), and ΔEopen the energy required to unfold the 30-nucleotide-long RDS. Here, ΔESD and ΔEtRNA are constant since neither the SD nor the start codon are altered. Consequently, variations in σ are exclusively determined by ΔEopen. Applying the model to the plasmids with our constructs bearing thermoswitches, enabled us to rationalize translation events, as translatable constructs consistently scored higher σ, or lower ΔEopen, than non-translatable ones.
References
- Neupert J, Karcher D, Bock R. Design of simple synthetic RNA thermometers for temperature-controlled gene expression in Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. [Internet]. Oxford University Press; 2008; 36:e124–e124.
- Narberhaus F, Waldminghaus T, Chowdhury S. RNA thermometers. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. [Internet]. Wiley/Blackwell (10.1111); 2006; 30:3–16.
- Storz G. An RNA thermometer. Genes Dev. [Internet]. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 1999; 13:633–6.
- Sen S, Apurva D, Satija R, Siegal D, Murray RM. Design of a Toolbox of RNA Thermometers. ACS Synth. Biol. [Internet]. 2017; 6:1461–70.
- Zayni S, Damiati S, Moreno-Flores S, Amman F, Hofacker I, Ehmoser EK. Enhancing the cell-free expression of native membrane proteins by in-silico optimization of the coding sequence – an experimental study of the human voltage-dependent anion channel.ioRxiv [Internet]. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory; 2018; 411694.

