Kristinazu (Talk | contribs) |
Kristinazu (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
<div class="image-container"> | <div class="image-container"> | ||
<img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2018/c/cc/T--Vilnius-Lithuania--Fig_1_NEW_su_uzrasu_Liposomes.png"/> | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2018/c/cc/T--Vilnius-Lithuania--Fig_1_NEW_su_uzrasu_Liposomes.png"/> | ||
| − | + | <p><strong>Fig 1</strong> The composition of a liposome with encapsulated machinery for membrane protein integration. Size, membrane composition and interior composition can be easily varied.</p> | |
| − | + | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
Revision as of 00:51, 18 October 2018
Design and Results
Results
Cell-free, synthetic biology systems open new horizons in engineering biomolecular systems which feature complex, cell-like behaviors in the absence of living entities. Having no superior genetic control, user-controllable mechanisms to regulate gene expression are necessary to successfully operate these systems. We have created a small collection of synthetic RNA thermometers that enable temperature-dependent translation of membrane proteins, work well in cells and display great potential to be transferred to any in vitro protein synthesis system.
Liposomes
Liposomes as closed containers for bottom up research
At the core of SynDrop lays a liposome. Liposomes are essentially synthetic vesicles, artificially synthesized droplets of liquid, separated from the environment by a lipid bilayer (Fig.1). They act as containers that encapsulate purified transcriptional and translational machinery and other vital elements that enable complex circuitry design. They have become increasingly popular due to various applications such as being carriers for medicinal drugs1, closed environments for protein engineering2 and characterization of RNAs3, as biosensors4 and molecular diagnostic tools5. The growing perspectives of liposomes as scaffolds for synthetic circuitry and membrane protein research are compelling as they have a multitude of different parameters that can be controlled. These include size, composition of a lipid membrane and interior composition.

Fig 1 The composition of a liposome with encapsulated machinery for membrane protein integration. Size, membrane composition and interior composition can be easily varied.
Requirements for liposomes
There are many different ways to synthesize liposomes, resulting in a vast range of diverse outputs. For our project, we set particular requirements to suit our scientific design. Ideally, our liposomes must be stable, cell-sized, monodisperse, have a single bilayered membrane and demonstrate excellent encapsulation efficiency. The only approach to optimally combine these attributes proved to be microfluidics. In recent years, droplet-based microfluidic techniques have proved to achieve a robust control over physical parameters of the final product, therefore showing superiority compared to the macroscale bulk methods6. We successfully customized and integrated a novel octanol-assisted liposome assembly (OLA)7 method for high-throughput production of our liposomes.
AutoCAD design for creating photomasks
The first step we had to take towards the production of liposomes was to design, fabricate and prepare a unique microfluidic device. A microfluidic channel design was created with the AutoCAD platform. The prototype acts as a photomask during the photolithography to create a master for the fabrication of microfluidic chips. Our design consists of an array of 16 separate microfluidic channel devices distributed parallelly in groups of four on a single chip (Fig. 2). The dimensions of the microchannels limit the size range of the synthesized liposomes. To dig deeper into the details of how the dimensions of the microfluidic channels influence liposome size we created a phase-field based SynFlow model with COMSOL Multiphysics. Auxiliary parametric sweeps were performed that defined the dimensions needed to attain cell – sized liposomes, a range from 5 µm to 30 µm. The final design can be downloaded here and used by anyone interested in the synthesis of liposomes.
 Fig 2 aAutoCAD design for the photomask. There are 16 individual microchannel devices on a
single chip. b One device consists of three inlets, an outlet and a star-shaped junction.
Fig 2 aAutoCAD design for the photomask. There are 16 individual microchannel devices on a
single chip. b One device consists of three inlets, an outlet and a star-shaped junction.
Photolithography as a tool for microfluidic chip fabrication
After calculating the exact parameters for microfluidic channels and receiving a printed photomask, photolithography is performed to create a master for microfluidic chip preparation. After completing this step, PDMS (polydimethylsiloxane) is poured on to the master left in a thermostat overnight. Inlets and outlets are punched with a biopsy puncher, and the PDMS is cleaned and plasma treated before attaching it to the PDMS coated microscope glass slides. Fig. 3 presents a simplified scheme demonstrating photolithography and other +6steps towards creating a microfluidic chip. To learn more details about the fabrication process, refer to our Protocols. We called our chip LipoDrop. The final form of LipoDrop is shown in Fig. 4.
 Fig 3 Simplified scheme for microfluidic device preparation. a-b the silicon wafer is cleaned and spin-coated with photoresist; c the photomask is aligned on the sample and exposed to UV light. d sample is submerged to a developer – only the sections that were exposed to the UV light remain intact on the wafer; e PDMS is poured onto the master to create a PDMS mold and left for a bake in the oven; f the mold is then separated and prepared further by cleaning and punching inlets and outlets; e-f a microscopic slide is prepared by applying a thin layer of PDMS on top; i PDMS mold and PDMS covered microscopic slide are plasma treated and connected to each other to produce a final microfluidic chip.
Fig 3 Simplified scheme for microfluidic device preparation. a-b the silicon wafer is cleaned and spin-coated with photoresist; c the photomask is aligned on the sample and exposed to UV light. d sample is submerged to a developer – only the sections that were exposed to the UV light remain intact on the wafer; e PDMS is poured onto the master to create a PDMS mold and left for a bake in the oven; f the mold is then separated and prepared further by cleaning and punching inlets and outlets; e-f a microscopic slide is prepared by applying a thin layer of PDMS on top; i PDMS mold and PDMS covered microscopic slide are plasma treated and connected to each other to produce a final microfluidic chip.
 Fig 4 Final form of Lipodrop.
Fig 4 Final form of Lipodrop.
Coating LipoDrop with PVA
Final and critical step in preparing the chip is the selective coating of post-junction channels with PVA (Polyvinyl alcohol) to render them hydrophilic. It is required to prevent the lipid/octanol solution from wetting the inherently hydrophobic inner channel surface of the device. Without this additional coating, liposomes are unable to form. To coat only a part of microfluidic channels is a challenge: PVA must only remain in post-junction channels without any leakage to the other side. To counter the spreading of PVA to pre-junction channels, air is introduced from separate inlets. A correct interphase between air and PVA must form and stay stable for at least several minutes to let the PVA molecules adhere to the surface (Fig. 5). Any PVA contamination to the opposite side makes the whole device unusable. Not only is this process time consuming (at least 15-20 minutes for each microfluidic device) and requires constant supervision, the procedure quite often fails due to human error while controlling the infusion rates of air and PVA.
 Fig 5 A schematic representation of the interphase of air and PVA at the star shaped junction of LipoDrop.
Fig 5 A schematic representation of the interphase of air and PVA at the star shaped junction of LipoDrop.
Lipovision software for fully automated microfluidic experiments
In pursuit to substantially reduce the manual effort in performing coating procedure, we have designed a software called LipoVision. LipoVision software reduces human labor down to the bare minimum and optimizes the coating procedure entirely. It uses an open standard computer library OpenCV at its’ core, detects the events at the interphase and controls the pumps for the accurate infusion rates according to the situation. The LipoVision software is based on Go and available on all operating systems and is accessible to any custom microfluidic experiment. Eventually, we are planning to apply this software for the fully automated synthesis of the liposomes. To learn more about LipoVision, refer to Software.
The synthesis of liposomes
After successfully coating the chips, the devices are finally ready for liposome synthesis. An experiment is conducted utilizing an octanol-assisted liposome assembly (OLA) method. Liposomes are formed when three unique phases (solutions - OA phase, LO phase and IA phase) form a correct interphase at the junction (Fig. 6). The IA phase (inner aqueous) occupies the inner part of the liposome and contains an IVTT transcription/translation system, DNA, membrane protein integration machinery, chaperones and salts needed for protein synthesis and integration into the membrane of the liposome. The LO phase contains lipids (i.e. DOPC, Cholesterol) and organic solvent (i.e. 2-octanol); it can also contain fluorescent lipids, such as Rh PE, for imaging. This phase introduces all of the components that will form the liposomes’ membrane. Octanol acts as an organic solvent for phospholipids. In the OLA method, initially double emulsions are formed; the excess octanol and lipids dewet and separate from the droplet leaving double-layered liposomes. Octanol removal from liposomes is crucial as the correct bilayer cannot form in excess organic solvent. Lastly, the OA phase (outer aqueous) contains surfactants that help stabilize the droplets at the initial formation and propagation through the microfluidic channels.
 Fig 6 A close-up of the phase interface during liposome synthesis; IA phase contains elements required for the synthesis
and integration of membrane proteins; LO phase consists of octanol and lipids that form a lipid bilayer; OA solution
carries surfactants that stabilize the initial formation and propagation of the droplets along the microfluidic device.
Fig 6 A close-up of the phase interface during liposome synthesis; IA phase contains elements required for the synthesis
and integration of membrane proteins; LO phase consists of octanol and lipids that form a lipid bilayer; OA solution
carries surfactants that stabilize the initial formation and propagation of the droplets along the microfluidic device.
Optimized flow rates for high throughput synthesis
With this method, we effectively produce monodisperse bilayered liposomes with high throughput. It is important to note that together with the microchannel dimensions, the infusion rates of the different phases also have an impact on the size of the droplets. Additionally, the infusion rates regulate the throughput of liposome production. The already mentioned SynFlow model determines the optimized flow rates for the most stable and highest frequency synthesis. With the right dimensions and flow rates we reach the production rate that is up to 2000 Hz. The results suggest that this method could be successfully adapted for mass production of liposomes. Fig. 7 reveals the slowed down process of droplet formation.
 Fig 7 High throughput formation of cell-sized liposomes. The video is 60x slowed down
Fig 7 High throughput formation of cell-sized liposomes. The video is 60x slowed down
A simple liposome size frequency distribution was determined with an image analysis software ImageJ. A plugin SpotCaliper was utilized to identify circular objects and measure their diameters (Fig. 8a). Gaussian distribution was fitted to the frequency histogram. Results verify that the size of the liposomes follows the Gaussian distribution (Fig. 8b). It proves that the droplets are highly homogeneous. Average diameter of a liposome (results from a single batch experiment) is around 12 µm, with standard deviation of 0.4 µm which fits our requirements very well.
 Fig 8 An automatic detection of droplets with SpotCaliper: the droplets are marked with teal colored circles and the
diameter of each is measured; b size frequency distribution histogram fitted to Gaussian distribution (teal fit) proves
the homogeneity of the liposomes; μ=11.853 >µm±0.017 >µm ; SD=0.442 µm ±0.017 µm.
Fig 8 An automatic detection of droplets with SpotCaliper: the droplets are marked with teal colored circles and the
diameter of each is measured; b size frequency distribution histogram fitted to Gaussian distribution (teal fit) proves
the homogeneity of the liposomes; μ=11.853 >µm±0.017 >µm ; SD=0.442 µm ±0.017 µm.
Characterization: encapsulation efficiency and internal synthesis
To prove the encapsulation efficiency and test whether protein synthesis and folding are feasible within the liposomes we employed green fluorescent protein (GFP). First, plasmid DNA coding GFP (3.0 ng/µL) was encapsulated together with PUREfrex 2.0 transcription translation system. The total reaction mixture was 40 µL. The microtubes were kept on ice during the production and collection of the liposomes. After all the reaction mixture was used up, the collected suspension was incubated in 37℃ for six hours. During the incubation time, negative and positive controls were prepared. The negative control contained the same reaction mixture as previously, excluding the DNA. Positive control, on the other hand, contained purified GFP proteins and no included DNA. The outer solution of all samples contained RNAse to ensure that no synthesis occurred outside the droplets (in case some liposomes erupted and released DNA to the outside). After the incubation period, fluorescent microscopy was utilized to reveal the results. Excitation and emission wavelengths of GFP are 488 nm and 510 nm, respectfully, therefore a suitable FITC filter was used.
Brightfield images of the synthesized liposomes are presented in Fig. 9a. The same area was then imaged under the FITC filter Fig. 9b, showing prominent fluorescence. It confirms that the liposomes are biocompatible, and synthesis occurs within them successfully . These results, together with positive control (Fig. 9c) validated that the encapsulation efficiency is immensely effective, as all the liposomes exhibit fluorescence signal. Negative control exhibited no measurable fluorescence with FITC filter, as expected (data not shown), confirming that no contamination was present to distort the results.
 Fig 9 brightfield image of the liposomes that contain IVTT system and plasmid GFP DNA (after incubation);
scale bar is 10 µm; b liposomes imaged with FITC: fluorescence confirms that transcription and translation
reactions occur inside them; scale bar is 10 µm; c liposomes containing purified GFP protein: all the
liposomes exhibit fluorescence validating excellent encapsulation efficiency; scale bar is 20 µm.
Fig 9 brightfield image of the liposomes that contain IVTT system and plasmid GFP DNA (after incubation);
scale bar is 10 µm; b liposomes imaged with FITC: fluorescence confirms that transcription and translation
reactions occur inside them; scale bar is 10 µm; c liposomes containing purified GFP protein: all the
liposomes exhibit fluorescence validating excellent encapsulation efficiency; scale bar is 20 µm.
Characterization: unilamellarity validation using α-hemolysin protein pores
Most membrane proteins insert, fold and function properly only in unilamellar membranes, therefore unilamellarity is an absolutely critical parameter for studying MPs. To validate that our synthesized liposomes are truly unilamellar, we recruited the pore forming membrane protein α-hemolysin (2 mM) from Staphylococcus aureus. Monomers of α-hemolysin self-assemble to form mushroom-shaped heptameric 1.5 nm wide pores in the phospholipid bilayer. The integration of these proteins make the bilayer selectively permeable to small molecules sized 2 kDa or less8. This protein pore was chosen as it can perforate into only one bilayer, therefore a multilamellar membrane would not allow the internal content of the liposome to escape9.
To test the incorporation of α-hemolysin into the liposome membrane we used a membrane-impermeable fluorescent probe calcein. Calcein is a self quenching fluorophore - a unique molecule that exhibits fluorescence only after it is diluted. That means that if we encapsulate concentrated calcein solution inside of our liposomes, we should observe that while looking through a fluorescence filter they appear darker than the outer solution (Fig. 10a). That happens because a small fraction of liposomes inevitably falls apart, releasing calcein into the outside, thus diluting it and therefore we measure the fluorescence in the outer solution. Hypothetically, inserting α-hemolysin into the liposome membrane will increase the fluorescence of the outer solution to a much greater degree, as the calcein molecules can now leave the liposomes via the α-hemolysin pore.
To test this hypothesis, we prepared two sets of liposomes. Lipid composition of liposomes was composed of DOPC and Cholesterol (cholesterol is necessary for the integration of α-hemolysin). Both sets of liposomes were prepared from the same batch microfluidic experiment. The same volume of liposomes was transferred into a solution with α-hemolysin and to an identical solution without the protein. Plate-reader measurements of fluorescence were then recorded, and results analyzed. As expected, in the absence of α-hemolysin (control), some background fluorescence was observed. However, in the solution where α-hemolysin was included, the measured fluorescence was significantly stronger (p < 0.0001 Fig. 10b) compared to the control group. That confirms the successful integration of α-hemolysin pore into the liposome membrane, explaining the increased fluorescence of the measured outer solution.
 Fig 10 a concentrated calcein encapsulated within liposomes: the outer solution fluoresces as some of the liposomes
inevitably burst releasing calcein into the outside; b box plot comparison of the control (without α-hemolysin) and
a group with inserted α-hemolysin; nonparametrical Mann-Whitney U test was used for the statistical evaluation:
the group with α-hemolysin shows statistically significant (p < 0.0001) increase in fluorescence
Fig 10 a concentrated calcein encapsulated within liposomes: the outer solution fluoresces as some of the liposomes
inevitably burst releasing calcein into the outside; b box plot comparison of the control (without α-hemolysin) and
a group with inserted α-hemolysin; nonparametrical Mann-Whitney U test was used for the statistical evaluation:
the group with α-hemolysin shows statistically significant (p < 0.0001) increase in fluorescence
References
- Torchilin, V. P. Recent advances with liposomes as pharmaceutical carriers. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 4, 145–160 (2005).
- Shin, J. & Noireaux, V. An E. coli cell-free expression toolbox: Application to synthetic gene circuits and artificial cells. ACS Synth. Biol. 1, 29–41 (2012).
- Kapoor, M., Burgess, D. J. & Patil, S. D. Physicochemical characterization techniques for lipid based delivery systems for siRNA. Int. J. Pharm. 427, 35–57 (2012).
- Michener, J. K., Thodey, K., Liang, J. C. & Smolke, C. D. Applications of genetically-encoded biosensors for the construction and control of biosynthetic pathways. Metab. Eng. 14, 212–222 (2012).
- Pardee, K. et al. Paper-based synthetic gene networks. Cell 159, 940–954 (2014).
- Carugo, D., Bottaro, E., Owen, J., Stride, E. & Nastruzzi, C. Liposome production by microfluidics: Potential and limiting factors. Sci. Rep. 6, (2016).
- Deshpande, S., Caspi, Y., Meijering, A. E. C. & Dekker, C. Octanol-assisted liposome assembly on chip. Nat. Commun. 7, 1–9 (2016).
- Noireaux, V. & Libchaber, A. A vesicle bioreactor as a step toward an artificial cell assembly. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 101, 17669–17674 (2004).
- Lu, L., Schertzer, J. W. & Chiarot, P. R. Continuous microfluidic fabrication of synthetic asymmetric vesicles. Lab Chip 15, 3591–3599 (2015).
Ribosome modifications
Background
Insertion of many membrane proteins in prokaryotes as well as the endoplasmic reticulum of eukaryotes is facilitated by various translocons. These complexes interact with the ribosome during protein synthesis and direct the newly forming peptide into the translocon pore, or directly into the membrane. However, for the translocon to function properly, it requires many auxiliary components (signalling sequence, chaperones, insertion mechanism), which would be far too many for our system to remain stable. Since we could not simply transfer the entire translocation system into SynDrop, we hypothesized that some of its functionality could be emulated in different ways.
Nickel-chelating lipids and polyhistidine tags as potential solution
Specifically to localize the ribosomes near the membrane and reduce the exposure of MP transmembrane domains to the aqueous environment, we eventually chose a method that has already been successfully used to attach other proteins to membranes - via a his-tag to nickel ions, chelated by specific lipids composing membrane1,2. Our reasoning for this was threefold. Firstly, this would have allowed ribosomes to be correctly positioned. If the ribosomes were localized near the membrane, but the peptide exit tunnel hadn’t been consistently pointed towards the membrane, the entire benefit of reducing MP aggregation would be lost. By being able to create his-tagged fusion proteins specifically of the ribosomal subunits localized near the exit tunnel, we guaranteed that the exit tunnel could never point away from the membrane. Secondly, general protein synthesis should be the least impeded, compared to alternatives, such as introducing a lipid anchor via an enzyme, or creating a fusion protein with a self inserting MP. These latter methods would completely immobilize the ribosome onto the membrane, removing degrees of freedom. With the polyhistidine-nickel interaction the ribosome would simply exhibit a much greater affinity towards the membrane, while still being able to detach and reattach as needed. Lastly, the simplicity for this method seemed to be the greatest, as only modified ribosomes as well as the incorporation of nickel-chelating lipids during liposome synthesis was needed - this was far more important than it can appear, because it was vital for our overall system to be as robust as possible.
 Fig. 1 Principle of ribosome attachment to the liposome membrane. The ribosome exit tunnel is localized near the membrane, resulting in transmembrane domains of newly synthesized peptides interacting with the membrane, reducing aggregation
Fig. 1 Principle of ribosome attachment to the liposome membrane. The ribosome exit tunnel is localized near the membrane, resulting in transmembrane domains of newly synthesized peptides interacting with the membrane, reducing aggregation
Results
Designing the modifications
The basic procedure we designed to obtain our modified ribosomes is as follows: first, using CRISPR-Cas9, we modify the genome of E. coli (native strain MG1655) to incorporate his-tags onto the ribosomal subunits, as well as a Strep-tag onto the L12 subunit for ease of purification3. In literature a his-tag was described to aid purification when fused to subunit L12, however we exchanged it for a Strep tag, as it is also short in sequence and while being biologically does not interfere with the functionality of other his-tags. The subunits localized near the exit tunnel we chose as potential targets, in order of priority, were L24, L23, and L29. These subunits were chosen as they had free, unfolded C ends exposed to the surface at nearest proximity to the exit tunnel. These subunits are also not integral to the overall function of the ribosome, meaning that our modifications would have little to no impact on peptide synthesis4,5,6,7. After the E. coli genome is successfully modified, the ribosomes are purified with the help of the previously incorporated Strep tag, and the final product is used for IVTT reactions.
Modification procedure
CRISPR-Cas9 was utilized via pCas9 and pTargetF plasmids 8. pCas9 constitutively expresses Cas9, which induces a double-strand DNA break at a specific target sequence, that is complementary to the guide RNA. The guide RNA sequences for our targets were introduced via reverse PCR into the pTargetF plasmid series, which then supplies it to Cas9. After the double stranded break occurs, the HDR (homology directed repair) mechanism is activated, which repairs the genome according to a supplied donor sequence. This process is highly efficient with the assistance λ-red proteins, expressed from pCas9. The donor sequence has ~300 bp length homology arms and the insertion sequence that can include either the His or Strep tag to be fused with the chosen ribosomal subunit C’-end, as well as an in frame selection marker (select antibiotic resistance genes). pCas9 expresses a gRNA targeting the ori of pTargetF, therefore the cells are automatically cured from pTargetF after each modification. Additionally, pCas9 has a temperature-sensitive ori, it is cured by growing the cells at 37 oC.
 Fig. 2 Scheme of the genome modification process:
Fig. 2 Scheme of the genome modification process:
- 1. pCas9 is introduced into the target cells
- 2. pTargetF and the according donor DNA are electroporated into the cells
- 3. Cas9 and our custom gRNA form a complex that cuts the genome DNA at the target. The genome is repaired via HDR according to our donor DNA sequence - X1 (homology arm of target ribosomal subunit) with fused tag, X3 (antibiotic resistance gene) and X2 (second homology arm).
- 4. pTargetF is cured and the process can be repeated with a new target.
When the homology arm and marker gene pcr products are restricted and ligated, the end result is a single sequence with an antibiotic resistance gene flanked on either side by ~300 bp homology arms, in addition to the according tag fused to the selected subunit’s gene. The entire linear DNA product was amplified via PCR using primers that annealed to the ends of the strand. Large amounts of nonspecific product was present even after performing PCR of the whole ligated sequence, therefore gel purification was necessary after each amplification (Fig. 5).
 Fig.3 Example of a constructed donor sequence. The sequence of the selected tag is present in primer used for the PCR of the homology arm that encompasses the target subunit. As a result, the tag sequence is fused to the ribosomal subunit gene.
Fig.3 Example of a constructed donor sequence. The sequence of the selected tag is present in primer used for the PCR of the homology arm that encompasses the target subunit. As a result, the tag sequence is fused to the ribosomal subunit gene.
 Fig. 4 PCR of homology arms, and antibiotic resistance genes
Fig. 4 PCR of homology arms, and antibiotic resistance genes
 Fig. 5 Constructed donor DNA sequences. The L29 donor DNA was not further revisited due to time constraints
Fig. 5 Constructed donor DNA sequences. The L29 donor DNA was not further revisited due to time constraints
The genome modifications were then carried according to Protocols our protocol. Although cPCR gave us mixed results, we could not verify any colonies that afterwards grew on our selected marker antibiotics, and thus could not continue our experiments with them. It appears most likely that the genome modifications were not entirely successful, due to the somewhat unstable nature of the ligated linear DNA used for the donor sequence.
Conclusion and Discussion
Although well described and planned in theory, our ribosome attachment system did not yield desired results. We hypothesize, that the underlying cause may include a flawed implementation of the CRISPR-Cas9 system: in our case we were forced to incorporate selection markers due to the functionality of the specific expression plasmids we used, which lead to the construction of unstable donor sequences. While this is unfortunate, we are still confident that our idea is worth further investigation: as we could not reproduce genome modifications on the subunit that has already been reportedly modified in a similar manner, it does not suggest that our primary concept is unworkable. Moving forward, we will most likely move to an alternative CRISPR-Cas9 expression system that would allow for optimized modifications, such as removing the requirement for a selection marker, which in turn would allow us to construct more robust donor sequences. Nonetheless, herein we provide a concept and initial tools for ribosome engineering. This demonstrates great potential in synthetic biology, especially in cell-free biomolecular systems like SynDrop.
References
- 1.Chikh, G., Li, W., Schutze-Redelmeier, M., Meunier, J. & Bally, M. Attaching histidine-tagged peptides and proteins to lipid-based carriers through use of metal-ion-chelating lipids. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes 1567, 204-212 (2002).
- 2.Blanchette, C., Fischer, N., Corzett, M., Bench, G. & Hoeprich, P. Kinetic Analysis of His-Tagged Protein Binding to Nickel-Chelating Nanolipoprotein Particles. Bioconjugate Chemistry 21, 1321-1330 (2010).
- 3.Ederth, J., Mandava, C., Dasgupta, S. & Sanyal, S. A single-step method for purification of active His-tagged ribosomes from a genetically engineered Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Research 37, e15-e15 (2008).
- 4.Spillmann, S. & Nierhaus, K. The ribosomal protein L24 of Escherichia coli is an assembly protein. Journal of Biological Chemistry (1978). at http://www.jbc.org/content/253/19/7047.long
- 5.GU, S. The signal recognition particle binds to protein L23 at the peptide exit of the Escherichia coli ribosome. RNA 9, 566-573 (2003).
- 6.STOFFLER-MEILICKE, M., DABBS, E., ALBRECHT-EHRLICH, R. & STOFFLER, G. A mutant from Escherichia coli which lacks ribosomal proteins S17 and L29 used to localize these two proteins on the ribosomal surface. European Journal of Biochemistry 150, 485-490 (1985).
- 7.Noeske, J. et al. Synergy of Streptogramin Antibiotics Occurs Independently of Their Effects on Translation. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 58, 5269-5279 (2014).
- 8.Jiang, Y. et al. Multigene Editing in the Escherichia coli Genome via the CRISPR-Cas9 System. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 81, 2506-2514 (2015)
BAM complex
RNA Thermoswitches

Fig. 1 A simplified mechanism of action of RNA thermometers. At lower temperatures the secondary messenger RNA (mRNA) stem-loop masks the ribosome binding site (RBS). Higher temperature induces melting of the hairpin which reveals the RBS to allow ribosome binding and initiation of translation.
Background
RNA thermometers are RNA-based genetic control tools that react to temperature changes1. Low temperatures keep the mRNA at a conformation that masks the ribosome binding site within the 5’ end untranslated region (UTR). Masking of the Shine-Dalgarno (SD) sequence restricts ribosome binding and subsequent protein-translation. Higher temperatures melt the hairpins of RNA secondary structure allowing the ribosomes to access SD sequence to initiate translation 1. In terms of applicability of RNA thermometers in in vitro systems, they display certain advantages over ribo- or toehold switches: they do not require binding of a ligand, metabolite or trigger RNA to induce the conformational change2,3, therefore are especially compatible with our liposome IVTT system. Keeping that in mind we have explored literature 1,4 and found five different RNA thermoswitches that we decided to test and build into our system in order to delay the translation of fusion construct bearing beta-barrel membrane protein. Furthermore, understanding the importance of expanding the library of well characterized and widely-applicable biobricks, we have de novo designed () six completely unique heat-inducible RNA thermometers.
Results
With custom IDT primers with overhangs bearing thermoswitch sequences we performed a PCR from a GFP gene containing plasmid and inserted RNA thermometers GJx (link: BBa_K2622010, BBa_K2622011, BBa_K2622012, BBa_K2622013, BBa_K2622014) upstream the GFP gene. Another set of primers was used to produce RNA thermometers Swx (link: BBa_K2622016, BBa_K2622017, BBa_K2622018, BBa_K2622019, BBa_K2622020, BBa_K2622021). PCR was successful and all products were the same size as expected for Swx constructs ~76 bp (Fig. 2). DNA gel electrophoresis was not performed for GJx constructs, because whole plasmid was multiplied and only 40-60 bp were inserted.
 Fig. 2 Electrophoresis gel of PCR products: 6 - Sw2, 7 - Sw3, 8 - Sw6, 9 - Sw7, 10 - Sw9, 11 - Sw11.
Fig. 2 Electrophoresis gel of PCR products: 6 - Sw2, 7 - Sw3, 8 - Sw6, 9 - Sw7, 10 - Sw9, 11 - Sw11.
pRSET plasmid and Swx PCR products were digested with restriction enzymes and ligated, while GJx PCR products were phosphorylated and ligated to produce plasmids from linear products. DH5α competent cells were transformed and plated on lysogeny broth (LB) media with ampicillin (Amp) and grown for 16 hours. Positive colonies were selected by colony PCR or restriction analysis (Fig. 3 and Fig. 4) and grown in 5 mL LB media. Plasmids were purified and BL21 competent cells were transformed. Three tubes of every construct plus plasmid with GFP without RNA thermometer were grown till OD600 reached 0.4. Control samples were taken and protein expression was induced with Isopropyl β-D-1-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG). One tube of every construct was grown in 24 ˚C, 30 ˚C, and 37 ˚C. Samples were taken after 1 and 2 hours. SDS-PAGE was run (for elaborate protocol see Notebook/Protocols). Fig. 5, Fig 6 and Fig. 7 depicts GFP expression at different temperatures. Although our RNA thermometers were designed to melt at 37 ˚C, some displayed leakiness to different extent. GJ3 (link:BBa_K2622011) RNA thermometer was the leakeast and allowed for GFP translation at lower temperatures. On the other hand, when grown at 37 ˚C, it unlocked the translation of GFP to highest yields. GJ2 (link:BBa_K2622010) was less leaky, but inhibited protein translation more strictly when grown at 37 ˚C. GJ6 (link: BBa_K2622012), GJ9 (link:BBa_K2622013), and GJ10 (link: BBa_K2622014) suppressed GFP production at 24 ˚C and 30 ˚C at similar level. They also inhibited translation to some extent at higher temperatures, meaning their melting temperature was not reached. Altogether these results prove, that our synthetic thermoswitches are temperature-responsive and act in physiological temperature range needed for IVTT reaction and also for BamA folding and membrane insertion.
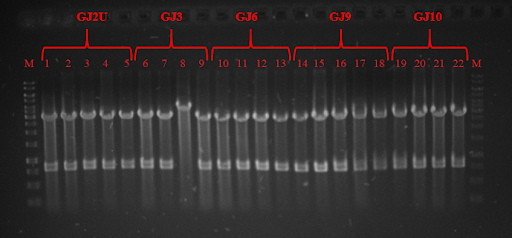 Fig. 3 Restriction analysis of GJx constructs
Fig. 3 Restriction analysis of GJx constructs
 Fig. 4 Colony PCR of RNA thermometers in pSB1C3 plasmid.
Fig. 4 Colony PCR of RNA thermometers in pSB1C3 plasmid.
 Fig. 5 expression at 24 ˚C. On the right you can see GFP expression without RNA thermometer./>
Fig. 5 expression at 24 ˚C. On the right you can see GFP expression without RNA thermometer./>
 Fig. 6 GFP expression at 30 ˚C. On the right you can see GFP expression without RNA thermometer./>
Fig. 6 GFP expression at 30 ˚C. On the right you can see GFP expression without RNA thermometer./>
 Fig. 7 GFP expression in 37 ˚C. On the right you can see GFP expression without RNA thermometer./>
Fig. 7 GFP expression in 37 ˚C. On the right you can see GFP expression without RNA thermometer./>
Discussion
As described in other sections of the Design and results page , beta-barrel bearing proteins are assembled into the membrane by the BAM protein complex machinery. The key protein BamA is itself a membrane protein, whose folding and insertion into membrane where it helps assemble target proteins, last up to two hours. In order to prevent the aggregation of our fusion proteins after encapsulating their gene-bearing plasmids and purified BamA mRNA into liposomes, we needed to develop a modulatory regulatory tool to lock the translation of our membrane proteins to allow enough time for the encapsulated BamA to fold and insert into the liposome membrane.
 Fig. 8 Associational scheme of thermoswitches’ action in the SynDrop system. Not locking the concomitant translation of our target protein and BamA results in target protein aggregation due to insufficient membrane insertion and assembling potential of BamA.
Fig. 8 Associational scheme of thermoswitches’ action in the SynDrop system. Not locking the concomitant translation of our target protein and BamA results in target protein aggregation due to insufficient membrane insertion and assembling potential of BamA.
 Fig. 9 Associational scheme of thermoswitches’ action in the SynDrop system. Locking up translation gives time for proper folding and insertion of BamA and prevents undesirable aggregation of target membrane proteins.
Fig. 9 Associational scheme of thermoswitches’ action in the SynDrop system. Locking up translation gives time for proper folding and insertion of BamA and prevents undesirable aggregation of target membrane proteins.
Additionally, while creating SynDrop, we have considered various options on how to make our complex cell-free system more user-controllable and predictable. Cell-free systems are becoming an attractive platform for in vitro compartmentalization and protein research, and although usually compositionally sensitive, they also offer a platform for building synthetic genetic regulatory tools or logic gates. Both the need to control the translation time of target genes and desire to provide more modularity for our synthetic system, led us to exploring RNA thermometers as a viable option to perform these tasks. They have minimal molecular burden and are easy to modulate. These properties encouraged us to developed a library of synthetic RNA thermometers suitable to translationally regulate the expression of our fusion constructs in bacteria with a further possibility to transfer them to IVTT systems. All of the RNA thermometers including those we found in literature and our de novo modelled ones were optimized for best performance at 37oC, bearing in mind their future transition to IVTT system, whose optimum performance temperature is also 37oC. Consequently, our experiments showed that our synthetic RNA thermometers, despite their simplistic structures compared to naturally occurring ones, efficiently triggered the expression of target constructs at 37oC, and successfully locked it at lower temperatures having made them an ideal complement to our liposome IVTT system. All of our thermoswitches unlocked the expression to similarly high levels at 37oC, but differed in terms of leakiness and success at inhibiting translation at lower temperatures.
Conclusions
We proved that herein described synthetic RNA thermometers enable high-yield expression of our constructs in an inducible temperature range. What is more important, this spectrum of temperature is compatible with currently used in vitro transcription and translation systems. Synthetic Thermoswitches allow the user-controllable and responsive protein translation for custom experiments. Finally, we introduced six de novo designed RNA thermoswitches which will have been used by future iGEM teams having to work both with cell-free and in vivo synthetic biology systems.
References
- 1. Neupert J, Karcher D, Bock R. Design of simple synthetic RNA thermometers for temperature-controlled gene expression in Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. Oxford University Press; (2008); 36:e124–e124.
- 2. Narberhaus F, Waldminghaus T, Chowdhury S. RNA thermometers. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. Wiley/Blackwell (10.1111); (2006); 30:3–16.
- 3. Storz G. An RNA thermometer. Genes Dev. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; (1999); 13:633–6.
- 4. Sen S, Apurva D, Satija R, Siegal D, Murray RM. Design of a Toolbox of RNA Thermometers. ACS Synth. Biol. (2017); 6:1461–70.
Mistic fusion protein
Mistic Fusion Protein
Self-inserting Bacillus subtilis protein called Mistic (MstX) is originally involved in biofilm formation1. It is thought that MstX might directly chaperon the membrane insertion of potassium ion channel YugO. Together these proteins create a positive autoregulatory feedback loop that assists biofilm assembly in a population of cells and is mediated by a pathway involving potassium ion efflux2.
MstX comprises 110 residues that are arranged into a four-helix bundle exposing numerous polar and charged amino acids (Fig. 1). This α-helical protein is characterized by an uncommonly hydrophilic surface. Until this day there is a great debate on how MstX is able to autonomously associate with a lipid bilayer despite its hydrophilic surface 2. It is known that three of the four MstX helices are much shorter than transmembrane helices of canonical integral MPs. In general, the four helices of this protein show no apparent differences in hydrophobicity or charge distribution among each other.

Fig. 1 NMR structure of Mistic (MstX). Protein is comprised of four ɑ-helices with a polar lipid-facing surface. Topology measurements have shown that both C-terminus and N-terminus of MstX are exposed at the same side. Adapted by Yarnell, 2005
MstX was identified back in 2005 by Rooslid and colleagues. Interestingly, until this day little is known about how MstX promotes integral protein targeting to the membrane3. Recently it has found a novel application as a fusion tag supporting the recombinant production and bilayer insertion of other membrane proteins (MPs)1. MstX, when fused to the N-terminus of integral MPs, enables the cargo proteins to fold into their native conformations in the membrane, thus yielding high-level expression. It is known that MstX autonomously targets proteins to the membrane bypassing the canonical secretory apparatus, like Sec translocon. In addition to this, it was indirectly presumed that MstX lacks any recognizable signal sequence 2.
According to this, we have decided to implement the advantages of MstX into our project. In order to boost protein expression yield MstX was fused with target integral membrane protein Outer membrane protein A (OmpA). Prior using these recombinant proteins in cell-free system, it has to be ensured that proteins are expressed in bacteria. To do so, E. coli BL21 stain cells were transformed and induced for 2 and 4 hours with isopropyl β-D-1-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG). Results were analyzed by sodium dodecyl sulphate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE). This experiment was conducted in order to detect if there are any differences in protein production yield comparing native and MstX-fused proteins.
First of all, it was concluded that MstX-OmpA-X and OmpA-X (X - additional part of the construct) are expressed in cells (Fig. 2).

Fig. 2 OmpA-X and MstX-OmpA-X (X - additional part of the construct; shown with arrows) expression in E. coli; SDS-PAGE after induction with IPTG for 2 hours and 4 hours; K - control, M - protein ladder

Fig. 3 IgA, IgA-MstX, and X-IgA-MstX (X - additional part of the construct; shown with arrows) expression in E. coli; SDS-PAGE; U4-2 - samples affected with 8M urea, S2-4 - samples affected with protein denaturation dye, K - control, M - protein ladder
Analyzing electrophoresis gel, differences of native IgA protein and recombinant IgA fused with MstX can be observed. It is extremely important that MstX in this case ensures higher-level yield of integral membrane proteins in E. coli as well.
According to these results, we validated that chosen integral membrane proteins are expressed in cells. In addition to this, their expression in cell-free system could be also expected. Moreover, MstX increases these MPs yield by functioning as a chaperone and enabling our target proteins to fold into their native conformations in the membrane even more efficiently.
Using MstX in cell-free systems is extremely advantageous as it allows effortless protein research without any need for additional protein purification step. Also, this fusion tag is universal as MstX it is compatible with different kinds of membrane proteins. In addition to this, the final task was to refine our cell-free system with MstX in order to make system more efficient and even more suitable for protein research.
To demonstrate that MstX is beneficial to cell-free system not only for membrane protein expression, it was fused with single-chain variable fragment (scFv; Fig. 3). It was decided to do so as scFvs are usually prone to form aggregates and lose their function in vitro. We thought that MstX could stabilize scFvs and prevent aggregation. As a result, we observed that MstX fusion could enhance scFv solubility allowing it to use in cell-free systems.

Fig. 4 Single-chain variable fragment (scFv) expression in IVTT system; SDS-PAGE. M - protein ladder, + - positive control DHFR, 1 - scFv, 2 - MstX-scFv, - negative control (without template DNA)
Analyzing the reaction samples, sediments in scFv were observed, which meant that scFv aggregated. However, in MstX-scFv sample there were no sediments. By analysing electrophoresis results (Fig. 4) it can be seen that MstX prevented formation of the aggregates which resulted in higher scFv expression yield.
References
- 1. Broecker, J., Fiedler, S., Gimpl, K. & Keller, S. Polar Interactions Trump Hydrophobicity in Stabilizing the Self-Inserting Membrane Protein Mistic. Journal of the American Chemical Society 136, 13761-13768 (2014).
- 2. Textor., M. Reconstitution and Membrane Topology of Mistic from Bacillus subtilis (Doctoral dissertation). University of Kaiserslautern. Retrieved from https://kluedo.ub.uni-kl.de
- 3. Lundberg, M. E. Biochemical and functional characterization of MISTIC. (Doctoral dissertation). UC San Diego. Retrieved from https://escholarship.org/uc/item/5b594287 (2013).
Surface display system
ScFv Antibody
Background
scFv consists of a minimal functional antigen-binding domain of an antibody (~30 kDa) (Fig. 1) , in which the heavy variable chain (VH) and light variable chain (VL) are connected by Ser and Gly rich flexible linker. [1] In most cases scFv is expressed in bacteria, where it is produced in cytoplasm, a reducing environment, in which disulfide bonds are not able to form and protein is quickly degraded or aggregated. Although poor solubility and affinity limit scFvs’ applications, their stability can be improved by merging with other proteins. [2] When expressed in cell free system, scFv should form disulfide bonds with the help of additional molecules. Merging to a membrane protein would provide additional stability and would display scFv on liposome membrane, where its activity could be detected. These improved qualities make ScFv recombinant proteins a perfect tool to evaluate, if SynDrop system acts in an anticipated manner. Of all possible scFvs we decided to use scFv-anti vaginolysin, which binds and neutralizes toxin vaginolysin (VLY). Its main advantage is rapid (< 1 h) and cheap detection of activity by inhibition of erythrocyte lysis (Fig. 2). Looking into future applications, scFvs are also attractive targets of molecular evolution, because one round of evolution would last less than one day thus generating a and wide range of different scFv mutants. Those displaying the highest affinity for antigens could be selected and used as drugs or drug carriers.
 Fig. 1 Simplified structure of scFv Antibody
Fig. 1 Simplified structure of scFv Antibody
 Fig. 2 Scheme of scFv_antiVLY and VLY interaction. Left- scFv_antiVLY binds to VLY, erythrocytes stay intact, Right- scFv_antiVLY does not bind and VLY lyse erythrocytes.
Fig. 2 Scheme of scFv_antiVLY and VLY interaction. Left- scFv_antiVLY binds to VLY, erythrocytes stay intact, Right- scFv_antiVLY does not bind and VLY lyse erythrocytes.
Results
scFv constructs were created BBa_K2622004. and checked by colony PCR and DNA sequencing. scFv synthesis was performed in a cell free system. Validation of protein expression was done by running a sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE), see (Fig. 3)
 Fig. 3 SDS-PAGE of scFv. GFP is used as positive control, C- chaperone DnaK.
Fig. 3 SDS-PAGE of scFv. GFP is used as positive control, C- chaperone DnaK.
Red arrows in the photo indicate scFv anti-vaginolysin (~27 kDa). As successful synthesis was confirmed, the next step was to check if protein folded correctly and was able to bind its antigen - vaginolysin. We examined this by erythrocyte-lysis test, which was performed by comparing erythrocytes incubated with VLY (erythrocytes burst open) and erythrocytes incubated with VLY that was previously incubated with scFv anti-vaginolysin (less or no erythrocyte lysis). Results revealed that scFv binded to vaginolysin and inhibited cell lysis. Graph in (Fig. 4) demonstrates that scFv indeed attenuated the lysis of erythrocytes. These result prove scFv activity in IVTT system.
 Fig. 4 Percentage of erythrocyte lysis at different +/-scFv dilutions.
Fig. 4 Percentage of erythrocyte lysis at different +/-scFv dilutions.
We then went one step further and constructed MstX-scFv_antiVLY BBa_2622038, fusion protein, aiming to increase the stability of scFv having in mind future applications and experiments of exposing it on liposome surface. Fusion protein was expressed in E.coli cells; yellow to red arrows in (Fig. 5A) indicate MstX-scFv expression after induction with IPTG.
Finally, we expressed the protein in a cell free system (Fig. 5B) along with scFv in order to compare how well scFv accomplishes its function alone or binded to other protein. In this case MstX-scFv_antiVLY fusion did not show superior activity than scFv_antiVLY alone (Fig. 6). These results also reveal that scFv_antiVLY is very sensitive and loses its activity with time. Ist and IInd attempts were separated by 1-2 hours. This amount of time is enough to measure decreasing activity. This must be taken into account when performing future experiments.
 Fig. 5 A- MstX-scFv_antiVLY expression in Escherichia coli. B- scFv_antiVLY and MstX-scFv_antiVLY expression in cell-free system.
Fig. 5 A- MstX-scFv_antiVLY expression in Escherichia coli. B- scFv_antiVLY and MstX-scFv_antiVLY expression in cell-free system.
 Fig. 6 Fig 6. Percentage of erythrocyte lysis at different scFv/MstX-scFv dilutions.
Fig. 6 Fig 6. Percentage of erythrocyte lysis at different scFv/MstX-scFv dilutions.
Conclusions
We successfully expressed scFv_antiVLY antibody and MstX-scFv_antiVLY construct in E.coli cells as well as in a cell free system. We demonstrated that our scFv anti-vaginolysin can bind to its target antigen vaginolysin and inhibit erythrocyte-lysis reaction. Based in scFv general properties in IVTT activity, we conclude that scFvs are an elegant addition to SynDrop liposome display system.
Discussion
Small size of scFv makes it a widely researched antibody. It’s ability to penetrate deeply into tissues and trait to elicit low to none organism’s immune response, makes scFv the one of the best candidates for medical, diagnostic, and research applications [3]. Efficient and fast method for scFv generation is in demand. SynDrop liposome display system offers an ability to produce scFv in IVTT system and display them on membranes to facilitate rapid antigen binding. scFv on the other hand can also help us prove that our system work either cost efficiently or with extreme precision. scFv surface display is compatible with using fluorescence assisted cell sorting (FACS) to detect well functioning liposomes. [4] This would reduce amount of time needed for mutant sorting compared with enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Second, scFv display is compatible with the experiments described in this section. We have performed erythrocyte-lysis tests to prove the functional activity of scFv anti-vaginolysin that was synthesized in the IVTT system. Not all experiments with VLY indicated positive antibody activity. We hypothesized that proteins could have aggregated very quickly after IVTT expression and the amount of active antibody left in the solution was not enough to inhibit VLY in quantities, what would have been detectable. This hypothesis was further supported by several experiments, which revealed decreasing scFv antibody’s functional activity with time. Moreover, not every experiment was done just after IVTT reaction completed and spend few hours in +4 ˚C. Another option to test scFv, single or displayed on liposomes to gain most reliable results, is an ELISA test. It requires specific antibodies and tags (His-6x or Strep-tag) on scFv or MstX-scFv.
Refferences
- Monnier, P., Vigouroux, R. & Tassew, N. In Vivo Applications of Single Chain Fv (Variable Domain) (scFv) Fragments. Antibodies 2, 193-208 (2013).
- Wang, R. et al. Engineering production of functional scFv antibody in E. coli by co-expressing the molecule chaperone Skp. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology 3, (2013).
- Ahmad, Z. et al. scFv Antibody: Principles and Clinical Application. Clinical and Developmental Immunology 2012, 1-15 (2012).
- Vorauer-Uhl, K., Wagner, A., Borth, N. & Katinger, H. Determination of liposome size distribution by flow cytometry. Cytometry 39, 166 (2000).

