Kristinazu (Talk | contribs) |
Kristinazu (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
<img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2018/c/cc/T--Vilnius-Lithuania--Fig_1_NEW_su_uzrasu_Liposomes.png"/> | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2018/c/cc/T--Vilnius-Lithuania--Fig_1_NEW_su_uzrasu_Liposomes.png"/> | ||
<p><strong>Fig 1</strong> The composition of a liposome with encapsulated machinery for membrane protein integration. Size, membrane composition and interior composition can be easily varied.</p> | <p><strong>Fig 1</strong> The composition of a liposome with encapsulated machinery for membrane protein integration. Size, membrane composition and interior composition can be easily varied.</p> | ||
| + | </p> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 63: | Line 64: | ||
<div class="image-container"> | <div class="image-container"> | ||
<img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2018/0/0e/T--Vilnius-Lithuania--Fig2_Liposomes.png"/> | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2018/0/0e/T--Vilnius-Lithuania--Fig2_Liposomes.png"/> | ||
| − | <strong>Fig 2 a</strong>AutoCAD design for the photomask. There are 16 individual microchannel devices on a | + | <p><strong>Fig 2 a</strong>AutoCAD design for the photomask. There are 16 individual microchannel devices on a |
| − | single chip. <strong>b</strong> One device consists of three inlets, an outlet and a star-shaped junction. | + | single chip. <strong>b</strong> One device consists of three inlets, an outlet and a star-shaped junction.</p> |
</p> | </p> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 87: | Line 88: | ||
<div class="image-container"> | <div class="image-container"> | ||
<img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2018/7/7d/T--Vilnius-Lithuania--Fig3_Liposomes.png"/> | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2018/7/7d/T--Vilnius-Lithuania--Fig3_Liposomes.png"/> | ||
| − | <strong>Fig 3 </strong> Simplified scheme for microfluidic device preparation. <strong>a-b</strong> the silicon wafer is cleaned and spin-coated with photoresist; <strong>c</strong> the photomask is aligned on the sample and exposed to UV light. <strong>d</strong> sample is submerged to a developer – only the sections that were exposed to the UV light remain intact on the wafer; <strong>e</strong> PDMS is poured onto the master to create a PDMS mold and left for a bake in the oven; <strong>f</strong> the mold is then separated and prepared further by cleaning and punching inlets and outlets; <strong>e-f</strong> a microscopic slide is prepared by applying a thin layer of PDMS on top; <strong>i</strong> PDMS mold and PDMS covered microscopic slide are plasma treated and connected to each other to produce a final microfluidic chip. | + | <p><strong>Fig 3 </strong> Simplified scheme for microfluidic device preparation. <strong>a-b</strong> the silicon wafer is cleaned and spin-coated with photoresist; <strong>c</strong> the photomask is aligned on the sample and exposed to UV light. <strong>d</strong> sample is submerged to a developer – only the sections that were exposed to the UV light remain intact on the wafer; <strong>e</strong> PDMS is poured onto the master to create a PDMS mold and left for a bake in the oven; <strong>f</strong> the mold is then separated and prepared further by cleaning and punching inlets and outlets; <strong>e-f</strong> a microscopic slide is prepared by applying a thin layer of PDMS on top; <strong>i</strong> PDMS mold and PDMS covered microscopic slide are plasma treated and connected to each other to produce a final microfluidic chip.</p> |
</p> | </p> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 94: | Line 95: | ||
<div class="image-container"> | <div class="image-container"> | ||
<img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2018/7/75/T--Vilnius-Lithuania--Fig4_Liposomes.png"/> | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2018/7/75/T--Vilnius-Lithuania--Fig4_Liposomes.png"/> | ||
| − | <strong>Fig 4 </strong> Final form of Lipodrop. | + | <p><strong>Fig 4 </strong> Final form of Lipodrop.</p> |
</p> | </p> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 107: | Line 108: | ||
<div class="image-container"> | <div class="image-container"> | ||
<img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2018/2/29/T--Vilnius-Lithuania--Fig5_Liposomes.png"/> | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2018/2/29/T--Vilnius-Lithuania--Fig5_Liposomes.png"/> | ||
| − | <strong>Fig 5 </strong> A schematic representation of the interphase of air and PVA at the star shaped junction of LipoDrop. | + | <p><strong>Fig 5 </strong> A schematic representation of the interphase of air and PVA at the star shaped junction of LipoDrop.</p> |
</p> | </p> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 124: | Line 125: | ||
<div class="image-container"> | <div class="image-container"> | ||
<img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2018/7/77/T--Vilnius-Lithuania--Fig6_Liposomes.png"/> | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2018/7/77/T--Vilnius-Lithuania--Fig6_Liposomes.png"/> | ||
| − | <strong>Fig 6 </strong> A close-up of the phase interface during liposome synthesis; <strong>IA</strong> phase contains elements required for the synthesis | + | <p><strong>Fig 6 </strong> A close-up of the phase interface during liposome synthesis; <strong>IA</strong> phase contains elements required for the synthesis |
and integration of membrane proteins; <strong>LO</strong> phase consists of octanol and lipids that form a lipid bilayer; OA solution | and integration of membrane proteins; <strong>LO</strong> phase consists of octanol and lipids that form a lipid bilayer; OA solution | ||
| − | carries surfactants that stabilize the initial formation and propagation of the droplets along the microfluidic device. | + | carries surfactants that stabilize the initial formation and propagation of the droplets along the microfluidic device.</p> |
</p> | </p> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 138: | Line 139: | ||
<div class="image-container"> | <div class="image-container"> | ||
<img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2018/f/fc/T--Vilnius-Lithuania--Fig7_Liposomes_formation_video.mp4"/> | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2018/f/fc/T--Vilnius-Lithuania--Fig7_Liposomes_formation_video.mp4"/> | ||
| − | <strong>Fig 7 </strong> High throughput formation of cell-sized liposomes. The video is 60x slowed down | + | <p><strong>Fig 7 </strong> High throughput formation of cell-sized liposomes. The video is 60x slowed down </p> |
</p> | </p> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 149: | Line 150: | ||
<div class="image-container"> | <div class="image-container"> | ||
<img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2018/4/4e/T--Vilnius-Lithuania--Fig8_Liposomes.png"/> | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2018/4/4e/T--Vilnius-Lithuania--Fig8_Liposomes.png"/> | ||
| − | <strong>Fig 8 </strong> An automatic detection of droplets with SpotCaliper: the droplets are marked with teal colored circles and the | + | <p><strong>Fig 8 </strong> An automatic detection of droplets with SpotCaliper: the droplets are marked with teal colored circles and the |
diameter of each is measured; <strong>b</strong> size frequency distribution histogram fitted to Gaussian distribution (teal fit) proves | diameter of each is measured; <strong>b</strong> size frequency distribution histogram fitted to Gaussian distribution (teal fit) proves | ||
| − | the homogeneity of the liposomes; μ=11.853 >µm±0.017 >µm ; SD=0.442 µm ±0.017 µm. | + | the homogeneity of the liposomes; μ=11.853 >µm±0.017 >µm ; SD=0.442 µm ±0.017 µm. <p></p> |
</p> | </p> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 169: | Line 170: | ||
scale bar is 10 µm; <strong>b</strong> liposomes imaged with FITC: fluorescence confirms that transcription and translation | scale bar is 10 µm; <strong>b</strong> liposomes imaged with FITC: fluorescence confirms that transcription and translation | ||
reactions occur inside them; scale bar is 10 µm; <strong>c</strong> liposomes containing purified GFP protein: all the | reactions occur inside them; scale bar is 10 µm; <strong>c</strong> liposomes containing purified GFP protein: all the | ||
| − | liposomes exhibit fluorescence validating excellent encapsulation efficiency; scale bar is 20 µm. | + | liposomes exhibit fluorescence validating excellent encapsulation efficiency; scale bar is 20 µm.</p> |
</p> | </p> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 189: | Line 190: | ||
<div class="image-container"> | <div class="image-container"> | ||
<img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2018/3/34/T--Vilnius-Lithuania--Fig10_Liposomes.png"/> | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2018/3/34/T--Vilnius-Lithuania--Fig10_Liposomes.png"/> | ||
| − | <strong>Fig 10 a</strong> concentrated calcein encapsulated within liposomes: the outer solution fluoresces as some of the liposomes | + | <p><strong>Fig 10 a</strong> concentrated calcein encapsulated within liposomes: the outer solution fluoresces as some of the liposomes |
inevitably burst releasing calcein into the outside; <strong>b</strong> box plot comparison of the control (without α-hemolysin) and | inevitably burst releasing calcein into the outside; <strong>b</strong> box plot comparison of the control (without α-hemolysin) and | ||
a group with inserted α-hemolysin; nonparametrical Mann-Whitney U test was used for the statistical evaluation: | a group with inserted α-hemolysin; nonparametrical Mann-Whitney U test was used for the statistical evaluation: | ||
| − | the group with α-hemolysin shows statistically significant (p < 0.0001) increase in fluorescence | + | the group with α-hemolysin shows statistically significant (p < 0.0001) increase in fluorescence</p> |
</p> | </p> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
Revision as of 00:57, 18 October 2018
Design and Results
Results
Cell-free, synthetic biology systems open new horizons in engineering biomolecular systems which feature complex, cell-like behaviors in the absence of living entities. Having no superior genetic control, user-controllable mechanisms to regulate gene expression are necessary to successfully operate these systems. We have created a small collection of synthetic RNA thermometers that enable temperature-dependent translation of membrane proteins, work well in cells and display great potential to be transferred to any in vitro protein synthesis system.










 Fig 9 brightfield image of the liposomes that contain IVTT system and plasmid GFP DNA (after incubation);
scale bar is 10 µm; b liposomes imaged with FITC: fluorescence confirms that transcription and translation
reactions occur inside them; scale bar is 10 µm; c liposomes containing purified GFP protein: all the
liposomes exhibit fluorescence validating excellent encapsulation efficiency; scale bar is 20 µm.
Fig 9 brightfield image of the liposomes that contain IVTT system and plasmid GFP DNA (after incubation);
scale bar is 10 µm; b liposomes imaged with FITC: fluorescence confirms that transcription and translation
reactions occur inside them; scale bar is 10 µm; c liposomes containing purified GFP protein: all the
liposomes exhibit fluorescence validating excellent encapsulation efficiency; scale bar is 20 µm.

 Fig. 1 Principle of ribosome attachment to the liposome membrane. The ribosome exit tunnel is localized near the membrane, resulting in transmembrane domains of newly synthesized peptides interacting with the membrane, reducing aggregation
Fig. 1 Principle of ribosome attachment to the liposome membrane. The ribosome exit tunnel is localized near the membrane, resulting in transmembrane domains of newly synthesized peptides interacting with the membrane, reducing aggregation
 Fig. 2 Scheme of the genome modification process:
Fig. 2 Scheme of the genome modification process:
 Fig.3 Example of a constructed donor sequence. The sequence of the selected tag is present in primer used for the PCR of the homology arm that encompasses the target subunit. As a result, the tag sequence is fused to the ribosomal subunit gene.
Fig.3 Example of a constructed donor sequence. The sequence of the selected tag is present in primer used for the PCR of the homology arm that encompasses the target subunit. As a result, the tag sequence is fused to the ribosomal subunit gene.
 Fig. 4 PCR of homology arms, and antibiotic resistance genes
Fig. 4 PCR of homology arms, and antibiotic resistance genes
 Fig. 5 Constructed donor DNA sequences. The L29 donor DNA was not further revisited due to time constraints
Fig. 5 Constructed donor DNA sequences. The L29 donor DNA was not further revisited due to time constraints

 Fig. 2 Electrophoresis gel of PCR products: 6 - Sw2, 7 - Sw3, 8 - Sw6, 9 - Sw7, 10 - Sw9, 11 - Sw11.
Fig. 2 Electrophoresis gel of PCR products: 6 - Sw2, 7 - Sw3, 8 - Sw6, 9 - Sw7, 10 - Sw9, 11 - Sw11.
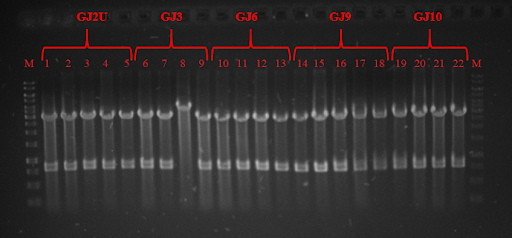 Fig. 3 Restriction analysis of GJx constructs
Fig. 3 Restriction analysis of GJx constructs
 Fig. 4 Colony PCR of RNA thermometers in pSB1C3 plasmid.
Fig. 4 Colony PCR of RNA thermometers in pSB1C3 plasmid.
 Fig. 5 expression at 24 ˚C. On the right you can see GFP expression without RNA thermometer./>
Fig. 5 expression at 24 ˚C. On the right you can see GFP expression without RNA thermometer./>
 Fig. 6 GFP expression at 30 ˚C. On the right you can see GFP expression without RNA thermometer./>
Fig. 6 GFP expression at 30 ˚C. On the right you can see GFP expression without RNA thermometer./>
 Fig. 7 GFP expression in 37 ˚C. On the right you can see GFP expression without RNA thermometer./>
Fig. 7 GFP expression in 37 ˚C. On the right you can see GFP expression without RNA thermometer./>
 Fig. 8 Associational scheme of thermoswitches’ action in the SynDrop system. Not locking the concomitant translation of our target protein and BamA results in target protein aggregation due to insufficient membrane insertion and assembling potential of BamA.
Fig. 8 Associational scheme of thermoswitches’ action in the SynDrop system. Not locking the concomitant translation of our target protein and BamA results in target protein aggregation due to insufficient membrane insertion and assembling potential of BamA.
 Fig. 9 Associational scheme of thermoswitches’ action in the SynDrop system. Locking up translation gives time for proper folding and insertion of BamA and prevents undesirable aggregation of target membrane proteins.
Fig. 9 Associational scheme of thermoswitches’ action in the SynDrop system. Locking up translation gives time for proper folding and insertion of BamA and prevents undesirable aggregation of target membrane proteins.




 Fig. 1 Simplified structure of scFv Antibody
Fig. 1 Simplified structure of scFv Antibody
 Fig. 2 Scheme of scFv_antiVLY and VLY interaction. Left- scFv_antiVLY binds to VLY, erythrocytes stay intact, Right- scFv_antiVLY does not bind and VLY lyse erythrocytes.
Fig. 2 Scheme of scFv_antiVLY and VLY interaction. Left- scFv_antiVLY binds to VLY, erythrocytes stay intact, Right- scFv_antiVLY does not bind and VLY lyse erythrocytes.
 Fig. 3 SDS-PAGE of scFv. GFP is used as positive control, C- chaperone DnaK.
Fig. 3 SDS-PAGE of scFv. GFP is used as positive control, C- chaperone DnaK.
 Fig. 4 Percentage of erythrocyte lysis at different +/-scFv dilutions.
Fig. 4 Percentage of erythrocyte lysis at different +/-scFv dilutions.
 Fig. 5 A- MstX-scFv_antiVLY expression in Escherichia coli. B- scFv_antiVLY and MstX-scFv_antiVLY expression in cell-free system.
Fig. 5 A- MstX-scFv_antiVLY expression in Escherichia coli. B- scFv_antiVLY and MstX-scFv_antiVLY expression in cell-free system.
 Fig. 6 Fig 6. Percentage of erythrocyte lysis at different scFv/MstX-scFv dilutions.
Fig. 6 Fig 6. Percentage of erythrocyte lysis at different scFv/MstX-scFv dilutions.