Met differ
Data format
We design a data format, .met format, to simply describe a metabolic network. .met format is easy to read and write.
If a line starts with ‘##’, this line indicates a new subgraph. Follows the ‘##’ is the name of the subgraph. And the next lines are this subgraph.
If a line starts with ‘#’, this line is a metabolite. In this line, there should be metabolite ID, name and other information like SMILES.
If a line starts without any symbol, it indicates a reaction. Reaction ID, reactors and products should be included. And if exists, enzyme information should be included as well.
If a line starts with ‘##’, this line indicates a new subgraph. Follows the ‘##’ is the name of the subgraph. And the next lines are this subgraph.
If a line starts with ‘#’, this line is a metabolite. In this line, there should be metabolite ID, name and other information like SMILES.
If a line starts without any symbol, it indicates a reaction. Reaction ID, reactors and products should be included. And if exists, enzyme information should be included as well.

Algorithm
In this part, we use merge-and-mine method. First, we merge the pathway graph and the network graph into one graph called align graph, according to the similarity coefficient of nodes. Then the nodes in the align graph are lined according to topology structure. Finally, we search for maximal connected subgraph as the alignment result.
Similarity coefficient
When we align the pathway to the network, similarity should be qualified. We use similarity coefficient to value the similarity between the pathway and the network. Here we consider the similarity from two aspects, node and topology structure.

NodeThere are two kinds of nodes in the metabolic network, metabolites and reactions. We consider them separately.
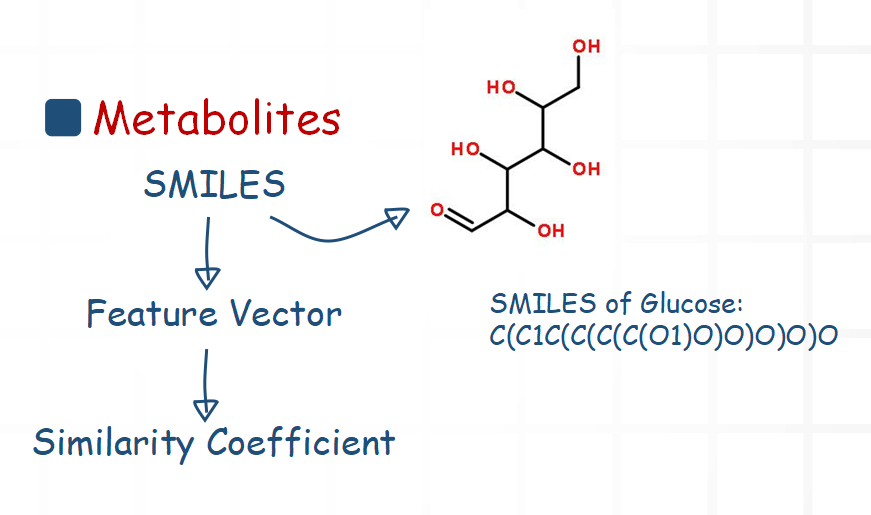
For metabolites, we mainly compare their structure information. Chemical structural formula can be described with SMILES. So we use a software package to extract a feature vector from the SMILES. Then we calculate the similarity coefficient of two feature vectors.

For reactions, we mainly consider the enzyme information. For each enzyme has an EC number, we can simply regularize the EC number to be the enzyme’s feature vector. For those reactions without an EC number, we use their reactors’ and products’ information to be the reaction’s information.
Topology structureAfter merging the pathway and the network into an align graph, we add edges to the align graph according to topology structure. We define the pathway as graph X, the network as graph Y, the align graph as Z. And x1, x2 are two nodes from X; y1, y2 are nodes from Y. x1, y1 are similar enough to be merged into a node z1 in Z, and x2, y2 are similar enough to be merged into a node z2. If node pairs (x1,x2) and (y1,y2) are both connected, and the edges have the same direction, we give the edge (z1,z2) a high weight; if the edge (x1,x2) is opposite to (y1,y2), we give the edge (z1,z2) a lower weight; if there is no edge (x1,x2) or (y1,y2), we give the edge (z1,z2) the lowest weight.

Now the weight is not accurate enough to evaluate the edges, so we calculate ELI(extended local interactome) between each pair of nodes. ELI is a coefficient to evaluate the connection between two nodes and the surrounding nodes. The calculation of ELI is as follows:
1. Calculate Ek(x): The set of paths connecting node x and its neighbors at distance k.
2. Calculate Sk(x,y):


3. Calculate ELI(x,y):


Met differ
Data format
We design a data format, .met format, to simply describe a metabolic network. .met format is easy to read and write.
If a line starts with ‘##’, this line indicates a new subgraph. Follows the ‘##’ is the name of the subgraph. And the next lines are this subgraph.
If a line starts with ‘#’, this line is a metabolite. In this line, there should be metabolite ID, name and other information like SMILES.
If a line starts without any symbol, it indicates a reaction. Reaction ID, reactors and products should be included. And if exists, enzyme information should be included as well.
If a line starts with ‘##’, this line indicates a new subgraph. Follows the ‘##’ is the name of the subgraph. And the next lines are this subgraph.
If a line starts with ‘#’, this line is a metabolite. In this line, there should be metabolite ID, name and other information like SMILES.
If a line starts without any symbol, it indicates a reaction. Reaction ID, reactors and products should be included. And if exists, enzyme information should be included as well.


