| Line 91: | Line 91: | ||
<p><span>atherosclerosis</span></p> | <p><span>atherosclerosis</span></p> | ||
<h1><span> An alarming health threat: Atherosclerosis</span></h1> | <h1><span> An alarming health threat: Atherosclerosis</span></h1> | ||
| − | <p> | + | <p>Shown on the right are the cholesterol structure and pie charts of Epidemic statistics of atherosclerosis-related mortality in China</p> |
</blockquote> | </blockquote> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 104: | Line 104: | ||
<div class="span4"> | <div class="span4"> | ||
<h2><span>Pathology of Atheroscleosis</span></h2> | <h2><span>Pathology of Atheroscleosis</span></h2> | ||
| − | <p>Artery atherosclerosis refers to arteries accumulated with cholesterol resulting in blockage of blood flow. Cholesterol is the main culprit of cardio-cerebrovascular disease. In heart it | + | <p>Artery atherosclerosis refers to arteries accumulated with cholesterol resulting in blockage of blood flow. Cholesterol is the main culprit of cardio-cerebrovascular disease. In heart it causes heart attack. In brain it causes blockage stroke.</p> |
<div class="pad15"></div> | <div class="pad15"></div> | ||
<div class="hover_colour"> <a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2018/b/b0/T--UST_Beijing--bg10.jpg" data-rel="prettyPhoto[portfolio1]"> <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2018/7/75/T--UST_Beijing--bg5.jpg" alt="" /></a> </div> | <div class="hover_colour"> <a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2018/b/b0/T--UST_Beijing--bg10.jpg" data-rel="prettyPhoto[portfolio1]"> <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2018/7/75/T--UST_Beijing--bg5.jpg" alt="" /></a> </div> | ||
| Line 111: | Line 111: | ||
<div class="span4"> | <div class="span4"> | ||
<h2><span>Molecular Mechanism of Atherosclerosis Formation</span></h2> | <h2><span>Molecular Mechanism of Atherosclerosis Formation</span></h2> | ||
| − | <p>Because of | + | <p>Because of foam cell apoptosis, which is formed by macrophages overloading cholesterol, cholesterol is deposited on the inner wall of artery.</p> |
<div class="pad15"></div> | <div class="pad15"></div> | ||
<div class="hover_colour"> <a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2018/e/ed/T--UST_Beijing--bg8.jpg" data-rel="prettyPhoto[portfolio1]"> <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2018/5/5b/T--UST_Beijing--bg6.jpg" alt="" /></a> </div> | <div class="hover_colour"> <a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2018/e/ed/T--UST_Beijing--bg8.jpg" data-rel="prettyPhoto[portfolio1]"> <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2018/5/5b/T--UST_Beijing--bg6.jpg" alt="" /></a> </div> | ||
| Line 118: | Line 118: | ||
<div class="span4"> | <div class="span4"> | ||
<h2><span>Nuclear receptor LXR as therapeutic target against atherosclerosis</span></h2> | <h2><span>Nuclear receptor LXR as therapeutic target against atherosclerosis</span></h2> | ||
| − | <p>Live X receptor(LXR) functions as a | + | <p>Live X receptor(LXR) functions as a master regulation switch, which can accelerate the transport of cholesterol and prevent the formation of foam cells.</p> |
<div class="pad15"></div> | <div class="pad15"></div> | ||
<div class="hover_colour"> <a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2018/4/4d/T--UST_Beijing--bg9.jpg" data-rel="prettyPhoto[portfolio1]"> <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2018/f/fc/T--UST_Beijing--bg7.jpg" alt="" /></a> </div> | <div class="hover_colour"> <a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2018/4/4d/T--UST_Beijing--bg9.jpg" data-rel="prettyPhoto[portfolio1]"> <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2018/f/fc/T--UST_Beijing--bg7.jpg" alt="" /></a> </div> | ||
| Line 125: | Line 125: | ||
<div class="pad15"></div> | <div class="pad15"></div> | ||
<div class="row"> | <div class="row"> | ||
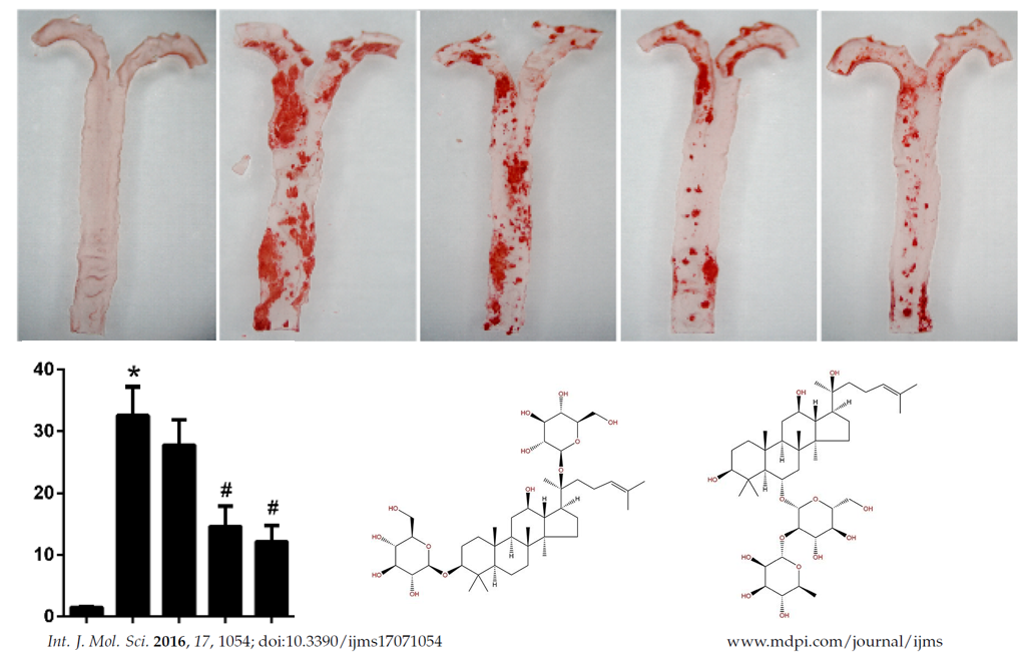
| − | <blockquote><p>Ginseng | + | <blockquote><p>Ginseng triterpenes' structure is similar to that of cholesterol, that is to say, it has the potential of regulating LXRs. |
| − | LXRs | + | LXRs is a typical nuclear receptor. In the presence of co-activators, regulated by agonists (such as ginsenoside), LXRs could binds |
| − | So to sum up, | + | special site on target gene promoter region to repress or active the transcription of the target gene. |
| + | So to sum up, ginsenosides could regulate the metabolism of cholesterol. We devote to finding a better way to solve the two remaining problems. | ||
Here is the foothold of our project postulates.</p></blockquote> | Here is the foothold of our project postulates.</p></blockquote> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
Revision as of 00:57, 11 October 2018
Cholesterol
an essential component of membrane structure, but gradually accumulates in arteries of human body, which results in the number one killer mechanism of human life:
atherosclerosis
An alarming health threat: Atherosclerosis
Shown on the right are the cholesterol structure and pie charts of Epidemic statistics of atherosclerosis-related mortality in China
Pathology of Atheroscleosis
Artery atherosclerosis refers to arteries accumulated with cholesterol resulting in blockage of blood flow. Cholesterol is the main culprit of cardio-cerebrovascular disease. In heart it causes heart attack. In brain it causes blockage stroke.
Molecular Mechanism of Atherosclerosis Formation
Because of foam cell apoptosis, which is formed by macrophages overloading cholesterol, cholesterol is deposited on the inner wall of artery.
Ginseng triterpenes' structure is similar to that of cholesterol, that is to say, it has the potential of regulating LXRs. LXRs is a typical nuclear receptor. In the presence of co-activators, regulated by agonists (such as ginsenoside), LXRs could binds special site on target gene promoter region to repress or active the transcription of the target gene. So to sum up, ginsenosides could regulate the metabolism of cholesterol. We devote to finding a better way to solve the two remaining problems. Here is the foothold of our project postulates.