| Line 469: | Line 469: | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<div class="service-text"> | <div class="service-text"> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | |||
<div class="row services-list block-1-2 block-tab-full"> | <div class="row services-list block-1-2 block-tab-full"> | ||
Revision as of 12:29, 17 October 2018
Alternative Roots
Naringenin Operon Assembly Results
Results
Introduction
Guided by the successful chemotaxis results, proving that 50µM naringenin attracts the nitrogen fixing bacteria A. brasilense and H. seropedicae, we aimed to engineer a naturally colonising endophyte Pseudomonas sp. (CT 364) to produce naringenin. For proof of concept the production of naringenin would first need to be demonstrated in E. coli before being tested in Pseudomonas sp., our final chassis organism.
Naringenin biosynthesis is achieved through the expression of an operon containing four genes encoding the enzymes that constitute the naringenin biosynthetic pathway (Figure 1). This operon was previously assembled and submitted to the iGEM registry by TU Darmstadt 2014 iGEM team BBa_K1497016 and is a composite of the following four genes, each with the strong RBS (BBa_B0034):
- 4-Coumaryl ligase - 4CL (BBa_K1033001)
- Tyrosine ammonia lyase - TAL (BBa_K1033000)
- Chalcone isomerase - CHI (BBa_K1497000)
- Chalcone synthase - CHS (BBa_K1497001)
Alongside this, in an attempt to optimise naringenin production, a new design of the naringenin operon was made in Benchling. This was based on the pathway modelling results and was constructed to show how BG28 and BG51 dual E. coli-Pseudomonas promoters with a 10-fold difference in strength could increase naringenin production.

Figure 1: The naringenin synthesis pathway from L-tyrosine.
Results
Experimental Work
Plasmid Design
The initial plasmid design for naringenin biosynthesis was based on TU Darmstadt’s design but with a codon optimised tyrosine ammonia lyase. We used pSB1C3 as a backbone, into which we would clone each of the four necessary genes downstream of a strong ribosome binding site (BBa_B0034). This construct was under the control of a strong Anderson promoter (J23100) to allow for constitutive expression of the operon (Figure 2). Once biosynthesis under the control of J23100 is achieved, future experiments will test this under the strong constitutive T7 promoter in E. coli (Figure 3). Parts for biosynthesis in root-colonising Pseudomonas sp., will be implemented into a plasmid backbone more suitable for its uptake. .
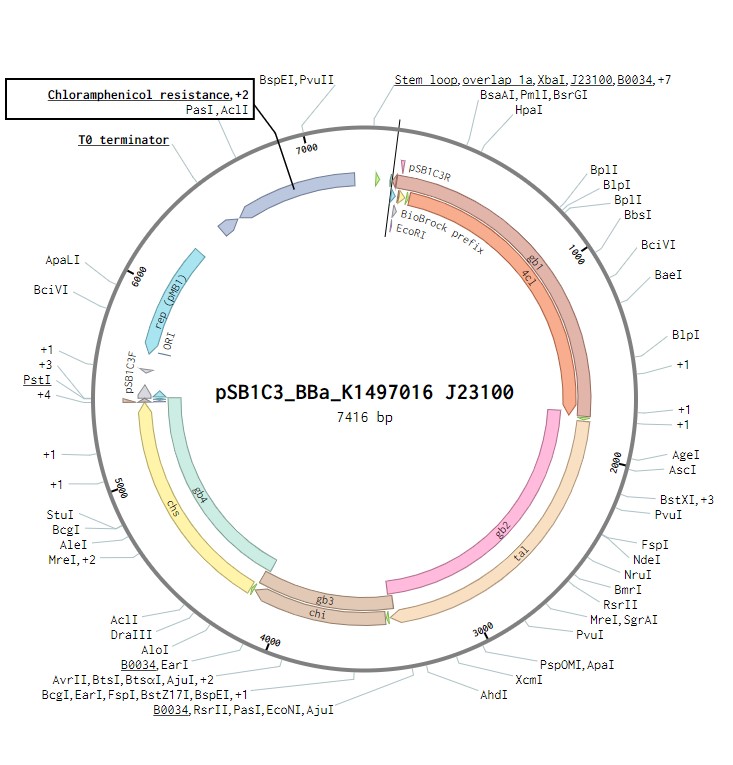
Figure 2:The naringenin biosynthetic operon under control of a J23100 promoter created in Benchling.

Figure 3:The naringenin biosynthetic operon under control of a T7 promoter created in Benchling.

Figure 4:The naringenin biosynthetic operon construct under control of a J23100 promoter created in SBOL.

Figure 5: The naringenin biosynthetic operon contruct under control of a T7 promoter created in SBOL.
Naringenin pathway modelling influenced design
Results of the naringenin pathway modelling demonstrated that weaker expression of the first two genes and 10-fold stronger expression of the last two genes would reduce the build-up of malonyl CoA and optimise naringenin synthesis. As a result of this, two synthetic promoters (BG28 and BG51) (Figure 7) were selected and an additional E. coli his operon terminator that was placed after the first two genes (Figure 6). These changes to the operon design could allow enhanced naringenin production in future experiments. More information about the pathway can be found here.
Figure 6:The naringenin biosynthetic operon under control of synthetic promoters BG28 and BG51 created in Benchling.

Figure 7: A close up of the synthetic promoters BG28 and BG51 placement in the operon, created in Benchling.

Figure 8: The naringenin biosynthetic operon contruct under control of a BG28 and BG51 promoters and an additional his operon terminator created in SBOL.
Primers were designed for amplification of the backbone and the 4 gBlocks (Table 1). These were designed in Benchling. The primers were used to prevent running out of the gBlocks synthesised by IDT and to detect the specific genes from the operon that could be present in transformed cells.
Table 1: Primers designed in Benchling for amplification of the 4 gblocks and the pSB1C3 backbone.
| Primer name | Sequence | Tm | Ta Q5 | Amplified product(bp) | Shown to work | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pSB1C3F | tactagtagcggccgctgc | 70 | 71 | 2070 | 6/8/18 | To amplify pSB1C3 backbone |
| pSB1C3R | ctctagaagcggccgcga | 70 | 71 | 2070 | 6/8/18 | To amplify pSB1C3 backbone |
| 4CLF | ccaaatcgccgccaattttc | 59 | 56 | 1686 | 6/9/18 | To amplify 4CL part |
| 4CLR | cgtcgtcgttttgaagtggt | 59.07 | 56 | 1686 | 28/9/18 | To amplify 4CL part |
| TALF | gaatgtccgaacgctacagg | 58.72 | 55 | 1649 | 28/9/18 | To amplify TAL part |
| TALR | tcggaattgagcaggtcgat | 59.18 | 56 | 1649 | 28/9/18 | To amplify TAL part |
| CHIF | ctgggcatagaggtctggag | 58.95 | 56 | 726 | 28/9/18 | To amplify CHI part |
| CHIR | caccttctccgagtactgct | 58.82 | 56 | 726 | 28/9/18 | To amplify CHI part |
| CHSF | aagacgtgcctgggttgata | 59.02 | 56 | 1197 | 28/9/18 | To amplify CHS part |
| CHSR | gcttctcctccttcaaccct | 59.01 | 56 | 1197 | 6/9/18 | To amplify CHS part |
| gb1F | ctggaattcgcggccgct | 72 | 54 | 1686 | 20/9/18 | To amplify 4CL part |
| gb1R | ttacaatccatttgctag | 53 | 54 | 1686 | 20/9/18 | To amplify 4CL part |
| gb2F | ggcaaaactagcaaatgg | 59 | 59 | 1649 | 20/9/18 | To amplify TAL part |
| gb2R | ttatcagacgggagattg | 58 | 59 | 1649 | 20/9/18 | To amplify TAL part |
| gb3F | cttgcagcaatctcccgt | 65 | 59 | 726 | 20/9/18 | To amplify CHI part |
| gb3R | ctagactccaatcactgg | 58 | 59 | 726 | 20/9/18 | To amplify CHI part |
| gb4F | tactattccagtgattgg | 54 | 55 | 1197 | 20/9/18 | To amplify CHS part |
| gb4R | cggactgcagcggccgct | 78 | 55 | 1197 | 20/9/18 | To amplify CHS part |
Backbone amplification
The pSB1C3 backbone was amplified, purified and quantified in preparation for Gibson assembly of the naringenin operon. Amplification was performed by PCR using Q5 ® High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase and primers pSB1C3F and pSB1C3R. The resultant PCR product was analysed by agarose gel electrophoresis and showed a band at 2kb that corresponded to the size of the plasmid. The backbone was then purified using Qiagen QIAquick PCR Purification Kit. The DNA concentration was quantified using a Qubit fluorometer and was determined to be 3.58 µg/ml. As this concentration was far too low for Gibson assembly the backbone was amplified and purified again using the same techniques resulting in a brighter band at 2kb than before (Figure 9) and a stock concentration of 26.2 µg/ml.
Protocol Details found hereGibson Assemblies
A positive control of the Gibson assembly was conducted. The NEBuilder® HiFi DNA Assembly Cloning Kit was used. A positive control reagent supplied with the kit contained two overlapping dsDNA fragments and the pUC19 plasmid. The positive control was conducted to check the assembly mix was working, the protocols for transformation were correct and that the cells prepared previously were competent.
The results of the positive control showed that the E. coli DH5α cells had successfully been made competent as they were able to take up the three-part assembly of the two overlapping fragments and the pUC19 backbone (Figure 10). Furthermore the reagents and protocols used in the Gibson assemblies were shown to have worked proving their viability for use in future experiments. No colonies grew on the negative control plates (Figure 10), verifying that E. coli DH5α cells are not ordinarily resistant to amplicillin and that no contamination had occurred.

Figure 1.0; Schematic of a standard USB cable. [1]

Figure 1.1: Above is 4 exposed wires. Red is power, black is ground,white and green are the data lines. [1]

Figure 1.0; Schematic of a standard USB cable. [1]

Figure 1.1: Above is 4 exposed wires. Red is power, black is ground,white and green are the data lines. [1]

Results
Conclusions
Two colonies from Gibson transformations resulted in a 7kb band, corresponding to the size of the operon and plasmid backbone. However sequencing was inconclusive therefore this operon could not be classified as a working part. Future experimentation should attempt to assemble the gblocks one by one into the plasmid backbone and gain sequencing results that show full alignment. Following this the 7kb plasmid should be transformed into BL21 expression cells to produce naringenin, to be extracted using ethyl acetate and measured through HPLC. HPLC of stock naringenin should be conducted for comparison. Observing the expression of the operon using T7 promoters instead of the J23100 constitutive promoter, to see if naringenin production is enhanced. This could be implemented using T7 primers and Q5 site directed mutagenesis in E. coli.



