Garten Choi (Talk | contribs) |
Hannah9743 (Talk | contribs) |
||
| (7 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
<br><br><br> | <br><br><br> | ||
<center><h4><font size = 6.5><strong>B</strong>acterial <strong>E</strong>volutionary <strong>G</strong>ame <strong>S</strong>imulation (<strong>BEGS</strong>)</font><br><font size = 3><i>for Snowdrift, Harmony, Stag Hunt and Prisoner's Dilemma Games</i></font></h4> | <center><h4><font size = 6.5><strong>B</strong>acterial <strong>E</strong>volutionary <strong>G</strong>ame <strong>S</strong>imulation (<strong>BEGS</strong>)</font><br><font size = 3><i>for Snowdrift, Harmony, Stag Hunt and Prisoner's Dilemma Games</i></font></h4> | ||
| − | <br><br> | + | <br><br> |
| − | <p><img src="// | + | |
| + | <p><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2018/c/c2/T--KUAS_Korea--description.jpg" height = "480px"style="max-width:100%"/></p> | ||
<li>Producer strain (“cooperator”): display of β-glucosidase on the cell surface</li> | <li>Producer strain (“cooperator”): display of β-glucosidase on the cell surface</li> | ||
| Line 36: | Line 37: | ||
<div class="row"> | <div class="row"> | ||
<div class="col-12"> | <div class="col-12"> | ||
| − | < | + | <br><br> |
| − | < | + | <ol><h4><strong>Mechanisms</strong></h4> |
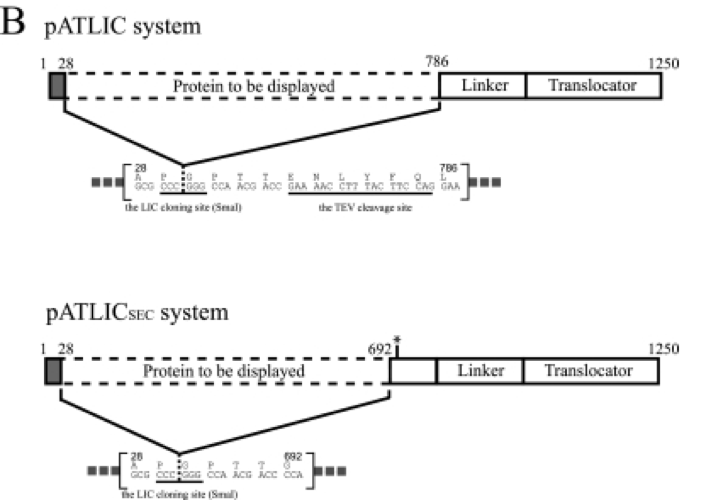
| − | < | + | <strong>1. Constitutive expression vector for both cheater and cooperator<ul></strong> |
| + | |||
<li>Using the plasmid containing BBa_J23106 showing high-level constitutive expression, the constitutive expression vector applicable to ligation independent cloning including SwaI restriction site at the LIC site was constructed. Parts J23100 through J23119 are a family of constitutive promoter parts isolated from a small combinatorial library. The resultant LIC vector was designated as ‘pCELIC’.</li> | <li>Using the plasmid containing BBa_J23106 showing high-level constitutive expression, the constitutive expression vector applicable to ligation independent cloning including SwaI restriction site at the LIC site was constructed. Parts J23100 through J23119 are a family of constitutive promoter parts isolated from a small combinatorial library. The resultant LIC vector was designated as ‘pCELIC’.</li> | ||
<li>Bgl1A of S. degradans was subcloned into a pATLIC vector as a previously report for the autodisplay (Ko et al., 2012) and was amplified by LA-taq polymerase by PCR. GFPuv also was amplified using α-taq polymerase by PCR. Amplified products were mixed with the linear LIC ready pCELIC vector at 1 1:4 molar ratios before transforming into DH5α.</li> | <li>Bgl1A of S. degradans was subcloned into a pATLIC vector as a previously report for the autodisplay (Ko et al., 2012) and was amplified by LA-taq polymerase by PCR. GFPuv also was amplified using α-taq polymerase by PCR. Amplified products were mixed with the linear LIC ready pCELIC vector at 1 1:4 molar ratios before transforming into DH5α.</li> | ||
<li>BBa_J23106 Part-only sequence (35 bp)</li> | <li>BBa_J23106 Part-only sequence (35 bp)</li> | ||
| − | <li>tttacggctagctcagtcctaggtatagtgctagc< | + | <li>tttacggctagctcagtcctaggtatagtgctagc<br><br> |
| − | + | ||
| − | [Figure 1. pATLIC display system for the designed vector] | + | <center><img src="//2018.igem.org/wiki/images/b/b7/T--KUAS_Korea--design_figure_4.png" style="max-width:80%"/><br> |
| + | [Figure 1. pATLIC display system for the designed vector]</li><br> | ||
</ul> | </ul> | ||
| − | <li>E.coli BW25113 as an expression host </ | + | </li><br><br> |
| − | <li>As E.coli BW25113 is used as an display and expression host. In our experiment, cooperator expresses beta-glucosidase on its cell surface and degrades cellobiose into glucose. It is done by a surface display system using the autotransporter YfaL protein. < | + | <strong>2. E.coli BW25113 as an expression host<ul></strong> |
| + | <li>As E.coli BW25113 is used as an display and expression host. In our experiment, cooperator expresses beta-glucosidase on its cell surface and degrades cellobiose into glucose. It is done by a surface display system using the autotransporter YfaL protein.<br><br> | ||
| − | [Figure 2. Schematic diagrams for the domain organization of autotransporter] | + | <center><img src="//2018.igem.org/wiki/images/3/3a/T--KUAS_Korea--Design_figure_3.png" style="max-width:60%"/><br> |
| − | + | [Figure 2. Schematic diagrams for the domain organization of autotransporter]<br> | |
| − | [Figure 3. Autotransporter protein structure] | + | <br><br> |
| − | + | <center><img src="//2018.igem.org/wiki/images/c/c3/T--KUAS_Korea--design_figure_2.png" style="max-width:60%"/><br> | |
| − | < | + | [Figure 3. Autotransporter protein structure]</li><br> |
| + | |||
| + | <h4><strong>References</strong></h4> | ||
<li>Baba, T., Ara, T., Hasegawa, M., Takai, Y., Okumura, Y., Baba, M., . . . Mori, H. (2006). Construction of Escherichia coli K-12 in-frame, single-gene knockout mutants: The Keio collection. Molecular Systems Biology, 2. doi:10.1038/msb4100050</li> | <li>Baba, T., Ara, T., Hasegawa, M., Takai, Y., Okumura, Y., Baba, M., . . . Mori, H. (2006). Construction of Escherichia coli K-12 in-frame, single-gene knockout mutants: The Keio collection. Molecular Systems Biology, 2. doi:10.1038/msb4100050</li> | ||
<li>Ko, H., Park, E., Song, J., Yang, T. H., Lee, H. J., Kim, K. H., & Choi, I. (2012). Functional Cell Surface Display and Controlled Secretion of Diverse Agarolytic Enzymes by Escherichia coli with a Novel Ligation-Independent Cloning Vector Based on the Autotransporter YfaL. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 78(9), 3051-3058. doi:10.1128/aem.07004-11</li> | <li>Ko, H., Park, E., Song, J., Yang, T. H., Lee, H. J., Kim, K. H., & Choi, I. (2012). Functional Cell Surface Display and Controlled Secretion of Diverse Agarolytic Enzymes by Escherichia coli with a Novel Ligation-Independent Cloning Vector Based on the Autotransporter YfaL. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 78(9), 3051-3058. doi:10.1128/aem.07004-11</li> | ||
<li>https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Autotransporter-protein-structure-and-secretion-Autotransporter-proteins-have-modular_fig1_51233167</li> | <li>https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Autotransporter-protein-structure-and-secretion-Autotransporter-proteins-have-modular_fig1_51233167</li> | ||
</ul> | </ul> | ||
| − | </ | + | </li> |
| + | </ol> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
Latest revision as of 18:08, 17 October 2018
Design |
Bacterial Evolutionary Game Simulation (BEGS)
for Snowdrift, Harmony, Stag Hunt and Prisoner's Dilemma Games

- The mechanism is as follows.
- The producer (cooperator) constitutively expresses beta-glucosidase on its surface and degrades the cellobiose.
- The cooperator and the cheater take them as energy source and the cheater expresses GFPuv as a reporter gene when it takes up the glucose.
- As the ratio between the cheater and cooperator changes, the total number of cooperator and cheater changes at the end.
- Using the plasmid containing BBa_J23106 showing high-level constitutive expression, the constitutive expression vector applicable to ligation independent cloning including SwaI restriction site at the LIC site was constructed. Parts J23100 through J23119 are a family of constitutive promoter parts isolated from a small combinatorial library. The resultant LIC vector was designated as ‘pCELIC’.
- Bgl1A of S. degradans was subcloned into a pATLIC vector as a previously report for the autodisplay (Ko et al., 2012) and was amplified by LA-taq polymerase by PCR. GFPuv also was amplified using α-taq polymerase by PCR. Amplified products were mixed with the linear LIC ready pCELIC vector at 1 1:4 molar ratios before transforming into DH5α.
- BBa_J23106 Part-only sequence (35 bp)
- tttacggctagctcagtcctaggtatagtgctagc
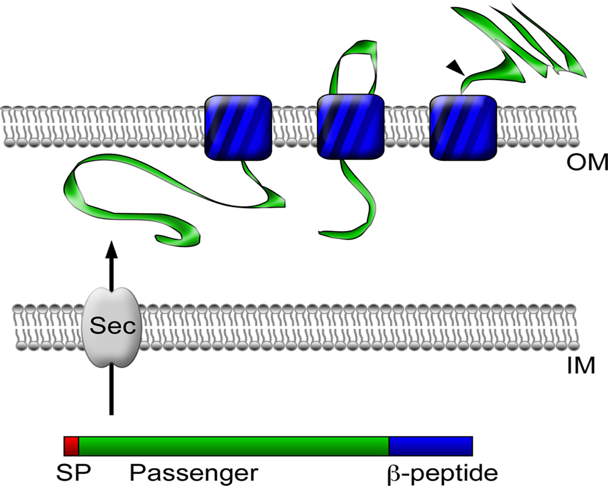
[Figure 1. pATLIC display system for the designed vector] - As E.coli BW25113 is used as an display and expression host. In our experiment, cooperator expresses beta-glucosidase on its cell surface and degrades cellobiose into glucose. It is done by a surface display system using the autotransporter YfaL protein.
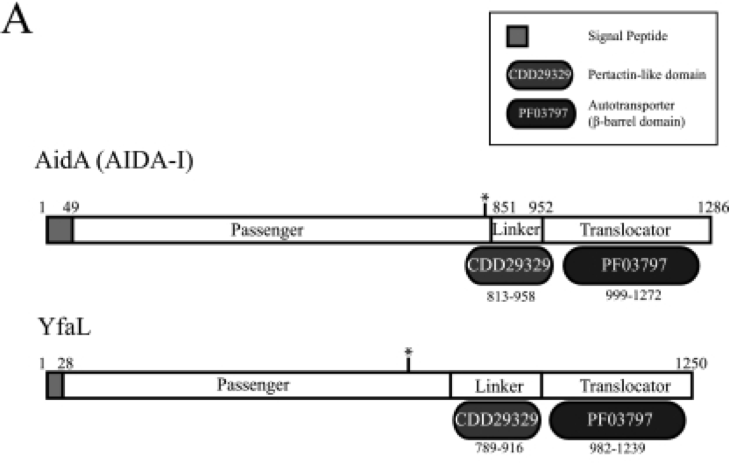
[Figure 2. Schematic diagrams for the domain organization of autotransporter]
[Figure 3. Autotransporter protein structure] - Baba, T., Ara, T., Hasegawa, M., Takai, Y., Okumura, Y., Baba, M., . . . Mori, H. (2006). Construction of Escherichia coli K-12 in-frame, single-gene knockout mutants: The Keio collection. Molecular Systems Biology, 2. doi:10.1038/msb4100050
- Ko, H., Park, E., Song, J., Yang, T. H., Lee, H. J., Kim, K. H., & Choi, I. (2012). Functional Cell Surface Display and Controlled Secretion of Diverse Agarolytic Enzymes by Escherichia coli with a Novel Ligation-Independent Cloning Vector Based on the Autotransporter YfaL. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 78(9), 3051-3058. doi:10.1128/aem.07004-11
- https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Autotransporter-protein-structure-and-secretion-Autotransporter-proteins-have-modular_fig1_51233167
Mechanisms
1. Constitutive expression vector for both cheater and cooperator2. E.coli BW25113 as an expression host
References
Sponsors







