| Line 215: | Line 215: | ||
<h3 class="heavy">IDR Conformational Sampling and Exploration</h3> | <h3 class="heavy">IDR Conformational Sampling and Exploration</h3> | ||
<p>Both the SRS and TRS methods were applied to Orthos, generating 1,000 structures each.</p> | <p>Both the SRS and TRS methods were applied to Orthos, generating 1,000 structures each.</p> | ||
| − | <p>Thanks to this large scale sampling of possible conformations, we conducted a statistical analysis studying the distance between the alpha carbon of the phenylalanine 366 and the alpha carbon of the glutamic acid 32 of the streptavidin binding site and the global RMSD of the protein.</p> | + | <p>Thanks to this large scale sampling of possible conformations, we conducted a statistical analysis studying the distance between the alpha carbon of the phenylalanine 366 and the alpha carbon of the glutamic acid 32 of the streptavidin binding site and the global Root Mean Square Deviation (RMSD) of the protein.</p> |
| + | |||
| + | <p>The RMSD calculates the sum of the geometric distances between each atom of a molecule, compared to the first frame of the simulation. Through this, we can study the variability of our protein.</p> | ||
<img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2018/2/22/T--Toulouse-INSA-UPS--Team--Callum-Model-SRS_dist_slow.gif" alt="SRS simulations GIF" /> | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2018/2/22/T--Toulouse-INSA-UPS--Team--Callum-Model-SRS_dist_slow.gif" alt="SRS simulations GIF" /> | ||
| Line 274: | Line 276: | ||
<p>The graphs indicate that this distance stays between 45 and 70 Å. This is a very satisfactory result, showing that we can design uses for our platform both with separate functions used independently and with two halves of a molecule that need to be assembled to produce a function. We had also considered using FRET to test this distance experimentally, which is now possible seeing as the distance between these two heads remain at an appropriate distance to observe interactions of that nature.</p> | <p>The graphs indicate that this distance stays between 45 and 70 Å. This is a very satisfactory result, showing that we can design uses for our platform both with separate functions used independently and with two halves of a molecule that need to be assembled to produce a function. We had also considered using FRET to test this distance experimentally, which is now possible seeing as the distance between these two heads remain at an appropriate distance to observe interactions of that nature.</p> | ||
| − | <p> | + | <p>By selecting only specific residues, we can measure the variability of certain regions of our platform through the RMSD value. </p> |
Revision as of 19:26, 16 October 2018
MOLECULAR MODELLING

Why do we want to model our platform?
Our new molecular binding platform contains three binding sites: Streptavidin (mSA2), a Carbohydrate Binding Module (CBM3a) and an unnatural amino acid, azidophenylanine (AzF). These “heads” of our Cerberus are connected by flexible regions, composed of 30-50 amino acids each. These regions called linkers are described in the literature to be highly flexible and as disordered regions 1 2.

Figure 1: General design of our Cerberus protein
For more information about our platform, visit the Description or Design pages.
As our linkers between domains are so flexible, it was possible that the CBM3a and mSA2 heads could be brought into contact. Interactions between the different molecular components of the platform could disturb its capacities to bind the target ligands. Their tertiary structures could also not be stable in the overall macromolecular assembly. In order to try to answer to all these questions, we implemented multi-step and multi-level molecular modeling strategy.
First, we built a 3D structure model of our binding platform and we assessed its stability over time. We also evaluated the distance between the different domains and its variations, which provide information about the size of the ligands that can be bound to the platform. We studied the interaction of our binding platform with target ligands. Especially, large-scale conformational sampling and exploration methods were used to assess the conformational rearrangements of these 3D structure models (the binding platform, either free or in interaction with the target ligands) over time, hopefully maintaining their binding capacities.
On this wiki page, we detail the different steps of our molecular modeling strategy and our thought process behind the solutions that we chose to use.
Strategy
To face all these challenges, we conceived a multi-level and multi-step molecular modelling workflow. Here is a graphical summary of this workflow:

Figure 2: Workflow of our molecular modelling approach
References
- Gunnoo et al., Nanoscale Engineering of Designer Cellulosomes, 2016
- E. Morag et al., Structure of a family 3a carbohydrate-binding module from the cellulosomal scaffoldin CipA of Clostridium thermocellum with flanking linkers: implications for cellulosome structure, 2013
Material and Methods
Available X-ray data
3D structures of the CBM3a and mSA2 protein domains are available on the Protein Data Bank (PDB). We chose to use 4JO5 2 and 4JNJ 3, both solved by X-ray cristallography, with a resolution of 1.98 and 1.90 Å respectively.
After obtaining these files, we faced two problems. First, the linkers connecting our heads had never been resolved by biophysics methods, due to their flexibility and length. Secondly, azidophenylalanine (AzF) had never been modelled, in its native state or covalently bonded to another molecule. This process will be detailed further on in this page.
3D structure prediction
This did however present a complex challenge for the prediction methods used. Our protein is 366 amino acids in length, containing two protein domains structurally organised in protein secondary structures (CBM, mSA2) and two peptide linkers, one connecting the CBM and SAv and the other one free on the C-terminus of the protein. The linkers are known in the literature to be highly flexible 1 2> and as Intrinsically Disordered Regions (or IDRs) and therefore their structures have never been successfully resolved by biophysics methods.
The three prediction software tools we chose to use were I-TASSER, Swiss Model and MODELLER. This allowed us to obtain a 3D structure model of our protein on which we could start calculations.
I-TASSER is an online platform hosted by the Zhang Lab (University of Michigan) that can perform 3D model protein prediction 4. It computes it by searching reference template in the PDB database through the LOMETS server, filling the unidentified regions by replica-exchange Monte Carlo Simulation. It then assemble the input structure to the 10 most probable models found on the database. It performs optimization of the structure and search for protein domain enrichment search on different databases such as Gene Ontology.
SWISS-MODEL service proposes a protein sequence homology based 3D modeling 5. It performs sequence homology research through BLAST and on the SWISS MODEL Template Library to begin the structural assembly. If there is no match on the database, the algorithm performs a Monte Carlo technique to find the best conformation.
MODELLER is an software for protein 3D structure modeling. It uses homology for template reference but also implements a structure reference based prediction of the most potent conformation 6.
Simulated Annealing
When dealing with a protein as large and complex as ours, 3D prediction approaches described above are not sufficient for obtaining an adequate structure. We then performed simulated annealing on the 3D model obtained through the previous approach. This process involves first a protein energy minimisation, then a series of heating cooling. This enables it to exit a local energy minimum and re-settle in a more global energy minimum.
Simulating Annealing was performed using sander, from the Amber16 suite. Amber is a suite of biomolecular simulation programs used both for generating parameters for molecules to be simulated and for simulating those molecules over time ⁷. It was first released in the late 1970s and is kept up to date consistently and features a large range of tutorials and forums to help users. All simulations performed with Amber16 used the ff14SB force field for topology and parameters of standard amino acids in the protein...
The minimisation phase was performed over 5,000 cycles to find the lowest energy point, holding the streptavidin and CBM3a domains fixed.
Orthos was heated for 200 picoseconds at 330K with an integration time of 2 femtoseconds, then once more at 310K with the same time parameters.
IDR Conformational Sampling and Exploration
The challenge here was the complexity of the IDRs. During the previous phase of our study, we were faced with the limitations of classic protein modelling methods. These approaches generally search for secondary structures (helices and sheets) connected by short flexible connectors (3-10 residues), but when faced with a long region lacking in secondary structures, they fail to predict an appropriate structure.
To overcome this limitation, we therefore needed to find an innovative method well-suited to predict the 3D conformation of long IDRs.
The LAAS, Laboratoire d'Analyses et d'Architecture des Systèmes, a French National Scientific Research Centre, developed original approaches for efficient large-scale molecular conformational sampling and exploration. These methods rely on a modelisation of molecular structures as polyarticulated mechanisms 8. Based on this modelisation, efficient algorithms derived from robotics have been adapted to explore molecular rearrangements. These algorithms allow avoiding expensive molecular modeling methods and accessing macromolecular rearrangements, thus overcoming limitations of traditional approaches.
These methods have recently been extended to explore IDRs and generate realistic conformational ensembles, and are integrated into the Psf-Amc library developed at LAAS. By disregarding secondary structure and seeking simply the angles between amino acids in an IDR, their approach builds protein chains incrementally from N- to C-termini. A database of experimentally-determined angles between tripeptides is sampled for each step, and the angle selected in this manner is added to the chain, then checked for collisions.
Two strategies can be used. The first, Single Residue Sampling (SRS), considers each amino acid individually to find appropriate angles, ignoring the residues flanking it (except if it is followed by a proline). The second, Triple Residue Sampling (TRS), takes the neighbouring amino acids into account when selecting the angles to add to the chain. This does require additional constraints applied onto the selection, to respect the angles found when adding the previous amino acid. The TRS strategy requires more calculation time, but is better at finding partially structured regions in the protein chain 8.
AzF Building and Parameterization
Incorporating an unnatural amino acid into a protein is a complex task not just for molecular biologists, but also for molecular modellers. Most protein prediction and modelling algorithms use predefined force field parameters for the 20 canonical amino acids, which simplify parameterization. Using AzF meant building the 3D structure and then generating specific parameters for it. Rather than go through this whole pipeline multiple times, we opted to construct it bonded with the DBCO-Fluorescein, the fluorophore that we were using in the wetlab. This proved harder to accomplish than originally planned.
A first 3D structure was built using Avogadro, an advanced molecular editor and visualiser 9, from a 2D model of AzF-DBCO-fluorescein molecule generated by ChemDraw. Next, the parameters of the molecule were generated using the GAFF force field 10 and different modules (antechamber, LeAP, parmchk) of the AMBER biomolecular software suite. The main difficulty here was to incorporate the functionalised AzF residue as a part of the main protein, which involves creating covalent bonds to the neighbouring amino acids.
Here, we needed to align the structure of our AzF residue with that of the phenylalanine near the end of the C-ter linker, remove the phenylalanine then add the AzF with all the correct bonds (and none of the wrong ones).
Biotin is a well known case study of ligand - receptor, so building and parameterizing it was easier to perform. Additionally, this did not require any new bonds in our protein, as the interaction is not covalent. Again, we used the antechamber force field of AMBER18 to create the necessary files. Placing it into the correct position in the streptavidin binding site was used by aligning our streptavidin domain with the X-ray structure of the streptavidin-biotin complex (PDB: 4JNJ 3).
Explicit Solvent Model
To consider the protein as it behaves in its environment, we decided to simulate our platform explicitly in its solvent. This means adding a great number of water molecules around it, using the TIP3P model, and calculating values for all of these new interactions, instead of simply simulating the general physical and chemical conditions of the solvent. Due to the great flexibility of our linkers, we needed to generate the box large enough to accommodate the full length of our Cerberus protein when these linkers are fully stretched out. We therefore left a minimum distance of 20 Å around our protein when generating the water box to contain it, in the shape of a truncated octahedron.
In total, this amounted to over 40,000 water molecules in our model, and 127,995 atoms with the protein. Incorporating this number of new atoms into out model meant adding millions, maybe even billions of new interactions.
The equilibration phase decreases the temperature of the protein and its solvent to allow it to settle back down into a local medium, usually a lower one than the previous minimum attained.
5 Na+ ions were also added to neutralise the protein.
This model represents the full Cerberus system. It features the unnatural amino acid incorporated into the C-terminal linker, functions added onto the two binding sites that we wished to explore and characterise and a complete simulation environment containing water molecules and sodium ions. We were then ready to prepare it for the molecular dynamics phase.
Molecular Dynamics
Preparation of molecular dynamics simulations consisted of initial minimization steps (steepest descent and conjugate gradient methods) where atomic positions of solute were first restrained using a harmonic potential. The force constant was then progressively diminished along the minimization procedure until a final unrestrained minimization step. We first minimised our system over 5,000 steps with restraints on the whole protein to minimise the solvent and ions, then reduced the restraints gradually over five minimisation cycles, for 1,000 steps each cycle. One final minimisation was performed with no restraints for 10,000 steps.
The minimization procedure was then followed by a slow heating to 310 K over a period of 0.1ns, with a moderate restraint placed on the protein. At the final required temperature, the system was equilibrated for 100 ps using constant temperature (310 K) and pressure (1 bar) conditions via the Berendsen algorithm with a coupling constant of 0.2 ps for both parameters. Along the equilibration, the restraints on the protein were gradually diminished. Electrostatic interactions were calculated using the Particle-mesh Ewald method with a nonbonded cutoff of 10 A. All bonds involving hydrogen were constrained with the SHAKE algorithm, permitting the use of 2 fs time steps to integrate the equations of motions.
Next came the production phase, where we can observe how the model behaves over a large period of time. Depending on the size of the system and the resources available, this phase can last from a few nanoseconds up to a few hundred ns. Due to the explicit solvent in our model and the size of our platform, we needed vast amounts of processing power to simulate it for a long time.
Thanks to CALMIP, a regional high performance calculation mesocentre, we were able to model our platform for a sufficient period and obtain useable results. We used 100,000 CPU hours on their servers for our simulations, generating over 85GB of data.
Two separate production phases were performed. The first involved our Cerberus protein in its water box, with no constraints on any region of the system. It ran for 120ns. The second featured a distance constraint between the sulfur atom of the biotin molecule and the alpha carbon of the nearby glycine 14 residue, to keep it within range of its associated binding site. This one ran for 80ns.
Both simulations were performed at constant temperature (310K) and pressure (1 bar) and with an integration time step of 2fs.
NAMD is a parallel molecular dynamics code designed for high-performance simulation for large systems 11. NAMD was developed by the Theoretical and Computational Biophysics Group in the Beckman Institute for Advanced Science and Technology at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. It is based on Charm++ parallel object, and scales well on up to thousands of cores for the largest simulations. NAMD is compatible with the Amber force fields generated during the previous phases, it was therefore easy to reuse these parameters.
Simulations were performed on Amber16 for the minimisation, heating and equilibration phases of the dynamics workflow, and NAMD for the production phase due to its higher multiprocessor capacities. The first three steps were run on 80 processors in parallel, whereas production was performed on 1000.
References
- Gunnoo et al., Nanoscale Engineering of Designer Cellulosomes, 2016
- E. Morag et al., Structure of a family 3a carbohydrate-binding module from the cellulosomal scaffoldin CipA of Clostridium thermocellum with flanking linkers: implications for cellulosome structure, 2013
- D. Demonte et al. , Structure-based engineering of streptavidin monomer with a reduced biotin dissociation rate, 2013
- J Yang et al. , The I-TASSER Suite: Protein structure and function prediction, 2015
- A. Waterhouse et al., SWISS-MODEL: homology modelling of protein structures and complexes, 2018
- B. Webb, A. Sali, Comparative Protein Structure Modeling Using Modeller, 2016
- R. Salomon-Ferrer, D.A. Case, R.C. Walker, An overview of the Amber biomolecular simulation package, 2013.
- A. Estana, N. Sibille, E. Delaforge, M. Vaisset, J. Cortes, P. Bernado, Realistic ensemble models of intrinsically disordered proteins using a structure-encoding coil database, in press (submitted Sep 2018).
- M. Hanwell et al., Avogadro: An advanced semantic chemical editor, visualization, and analysis platform, 2012
- J. Wang, Development and Testing of a General Amber Force Field, 2004
- James C. Phillips et al., Scalable molecular dynamics with NAMD, 2005
Results
3D Structure Prediction
Only Modeller provided us with a satisfactory structure, most likely due to its improved de novo prediction capacities and the usage of restraints on the final model. The other two algorithms struggled to suitably resolve the position of the linkers.

Figure 3: 3D structure of Orthos obtained from Modeller
We can see that the linkers seem to tangle together quite significantly.
Simulated Annealing
After completing these phases, we obtained this structure:

Figure 4: 3D structure of Orthos obtained after simulated annealing
We can see that once again, the linkers are considerably tangled. We wanted to investigate the possibilities further, which is why we continued the strategy with the robotics inspired methods.
IDR Conformational Sampling and Exploration
Both the SRS and TRS methods were applied to Orthos, generating 1,000 structures each.
Thanks to this large scale sampling of possible conformations, we conducted a statistical analysis studying the distance between the alpha carbon of the phenylalanine 366 and the alpha carbon of the glutamic acid 32 of the streptavidin binding site and the global Root Mean Square Deviation (RMSD) of the protein.
The RMSD calculates the sum of the geometric distances between each atom of a molecule, compared to the first frame of the simulation. Through this, we can study the variability of our protein.

Figure 5: Various positions of the mSA2 domain (in red) in relation to the CBM3a (in green) as calculated by the SRS strategy developped by the LAAS, showing the distance between the mSA2 binding site and AzF alpha carbon (dotted line, distance in Å)


Figure 6: Various positions of the mSA2 domain (in blue or red) in relation to the CBM3a (in green) as calculated by the SRS strategy (left) and the TRS strategy (right)


Figure 7: Distribution of the mSA2 binding site - AzF distance for each conformation calculated by the SRS strategy (left) and TRS strategy (right)


Figure 8: Distrubtion of the global RMSD for each conformation calculated by the SRS strategy (left) and TRS strategy (right)
The figures shown directly above were generated by loading 5 different structures calculated by the LAAS, then aligning the CBM3a domain of each of them. As you seen on the figures, both of these simulations show the range of positions that the streptavidin head can take in relation to the CBM3a, also demonstrating the high flexibility of the linkers.
We selected the most represented overall conformation of our protein, and therefore the most probable, by analysing these parameters to continue our strategy.
Molecular Dynamics

Figure 9: Restrained biotin simulation, showing the distance between the mSA2 binding site and the AzF alpha carbon (dotted line, distance in Å)
Above, you can see a video generated from the structural data generated by taking snapshots every 0.5ns along our simulation. By observing its general structure, we can see that the linker sections are indeed very flexible but seem to adopt some preferred positions.
For example, the N-terminal linkers sticks to one side of the CBM3a domain due to hydrogen interactions. We can also see the biotin molecule exiting its binding site after around 15ns.
We also tracked the distance between the alpha carbon of the azidophenylalanine residue and the glutamic acid 32 residue. Extracting the raw numbers for each frame displayed allowed us to study its evolution closely, as you can see on these plots:

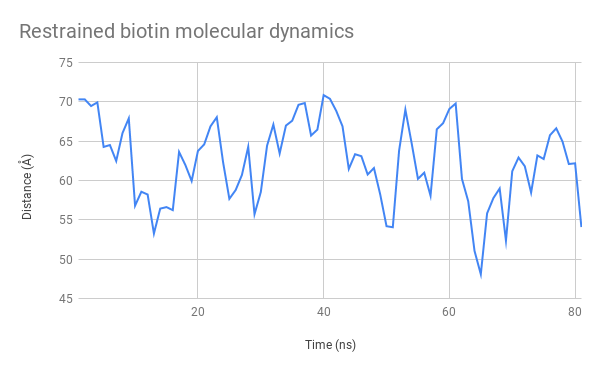
Figure 10: Evolution over time of the distance between the mSA2 binding site and AzF alpha carbon for the free biotin (left) and restrained biotin (right) simulations
The graphs indicate that this distance stays between 45 and 70 Å. This is a very satisfactory result, showing that we can design uses for our platform both with separate functions used independently and with two halves of a molecule that need to be assembled to produce a function. We had also considered using FRET to test this distance experimentally, which is now possible seeing as the distance between these two heads remain at an appropriate distance to observe interactions of that nature.
By selecting only specific residues, we can measure the variability of certain regions of our platform through the RMSD value.

Figure 11: Evolution of the RMSD of the different domains of our Cerberus protein over time: N-terminal linker in yellow, mSA2 in red and CBM3a in green
The structured domains keep their stability over time, with the RMSD of the CBM3a staying at around 2 Å throughout the simulation, and the streptavidin at around 4 Å.
The N-terminal linker however shows great flexibility, never keeping the same position during the time period studied here, with an RMSD peaking at close to 60 Å. The C-terminal linker presents a similar behaviour, with peaks at around 40 Å, it is not shown here for clarity’s sake.
Conclusion
Thanks to these results, we are able to determine through multiple methods that out molecular binding platform behaves as planned when we designed it. Using the LAAS’ innovative robotics inspired methods, we overcame the challenge presented by the Intrinsically Disordered Regions. This novel approach circumvented the limitations that classic modelling software encounters and allowed us to progress in our project.
By measuring the RMSD of each domain of our protein and following their positions over the duration of our simulations, we can confirm that our linker regions are too flexible to resolve a definite conformation. Despite this extreme variability, we never observed entanglement between them, nor did we see them bring the binding sites of our domains into contact. With this information, we can also be sure that the linkers shouldn't adopt a conformation where these binding sites become unavailable to their ligands.
Although we observe that the biotin molecule exits the streptavidin docking site during the molecular dynamics simulation, this occurs quite often in protein molecular modelling and is not a great source of concern for the viability of our platform. It is important to remember that all of these data are obtained through mathematical approximations, and that it is important to verify them in situ.
Finally, tracking the distance between the two distal heads showed that we could indeed attach medium to large functional molecules to these heads without risking too many unwanted interactions. However, due to the fact that they remain within 100 Å of each other, we could still imagine placing functions on the heads designed to interact with each other, for example to subunits of a protein that meet and activate under certain conditions.
No dogs were harmed over the course of this iGEM project.
The whole Toulouse INSA-UPS team wants to thank our sponsors, especially:









And many more. For futher information about our sponsors, please consult our Sponsors page.
The content provided on this website is the fruit of the work of the Toulouse INSA-UPS iGEM Team. As a deliverable for the iGEM Competition, it falls under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0. Thus, all content on this wiki is available under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 license (or any later version). For futher information, please consult the official website of Creative Commons.
This website was designed with Bootstrap (4.1.3). Bootstrap is a front-end library of component for html, css and javascript. It relies on both Popper and jQuery. For further information, please consult the official website of Bootstrap.



