Results
The goal of our project was to find stress using mammalian synthetic biology. And we found it.




Figure 1. The image on the top left corner shows the induction of MT1 construct by H2O2. The image on the top right shows the induction of MT1 construct by CuSo4.
the image on the bottom left shows the Michaelis-Menten fit for the induction of MT1 construct by H2O2.the image on the bottom right shows the Michaelis-Menten fit for the induction of MT1 construct by H2O2.
[1] “Copper Fact Sheet.” Archive.epa.gov, US EPA, archive.epa.gov/pesticides/reregistration/web/pdf/copper_red_fs.pdf.
“Copper Sulfate.” Copper Sulfate, EXTOXNET, pmep.cce.cornell.edu/profiles/extoxnet/carbaryl-dicrotophos/copper-sulfate-ext.html.
“CDC - COPPER SULFATE (Anhydrous) - International Chemical Safety Cards - NIOSH.” Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, www.cdc.gov/niosh/ipcsneng/neng0751.html.
Nakamura, Jun, et al. “Micromolar Concentrations of Hydrogen Peroxide Induce Oxidative DNA Lesions More Efficiently than Millimolar Concentrations in Mammalian Cells.” Nucleic Acids Research, Oxford University Press, 15 Mar. 2003, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC152865/.
“Hydrogen Peroxide.” Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 11 Apr. 2016, www.cdc.gov/niosh/npg/npgd0335.html.
Eagles-Smith, C.A., and B.L. Johnson, 2012, Contaminants in the Klamath Basin: Historical patterns, current distribution, and data gap identification: U.S. Geological Survey Administrative Report, 88 p.
Santos, Anderson K. et al. "Expression System Based on An MtIIa Promoter to Produce Hpsa In Mammalian Cell Cultures". Frontiers in Microbiology, vol 7, 2016. Frontiers Media SA, doi:10.3389/fmicb.2016.01280.
Peterson CW, Narula SS, Armitage IM. "3D solution structure of copper and silver-substituted yeast metallothioneins". FEBS Lett. 379 (1): 85–93, 1996. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(95)01492-6. PMID 8566237.
t.
From our processed data, we found that Metallothionein 1 (MT1) had a high quality induction curves, so we selected this construct as our proof of concept. From the induction curve of copper sulfate against Metallothionein 1, we can see a well defined induction curve. We took this data and fit it into our Michaelis-Menten model of saturation kinetics to determine the sensitivity of our promoter constructs.
After maximum expression, as concentration of copper sulfate increases, expression decreases. We hypothesize that this is due to the cells dying at higher concentrations of chemical of concern.
From literature review, we found that the relevant cytotoxicological dose for copper sulfate is less than 1.3 parts per million, which is equivalent to 6.25 uM [1].
First, allow us to define some parameters from our model: Kstimulus is our michaelis-menten constant, which for our project is used as a measure of the sensitivity of our promoters. Vmax is the maximum reaction velocity, and in the context of our project, Vmax gives us maximum EGFP expression. Kstimulus is the concentration at which EGFP expression is one half of maximum expression.
From our curve-fit data, we found our Kstimulus value to be 0.2784 uM. This implies that our promoter construct is approximately 23 times more sensitive to the chemical than the threshold of the cytotoxicological limit defined in literature. From our curve fit, we also found that Vmax value occurs at a copper sulfate concentration of 5 uM. As defined by the EPA, the relevant dose is 6.25 uM. Because our Vmax is very close to the EPA defined value, it implies that our promoter operates within the range defined by the EPA to be of interest.
The data that is displayed on the wiki is data that was found twelve hours after induction in the cell line, CHO-DG44.

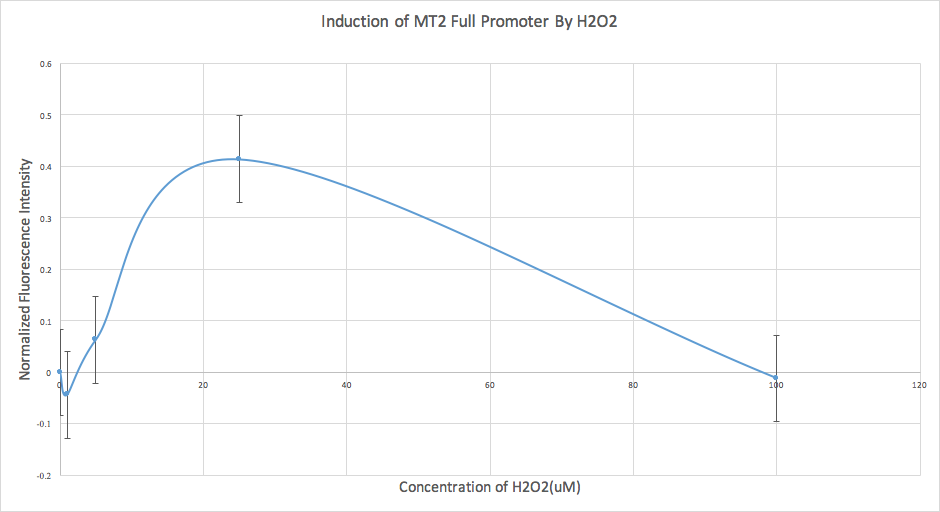
We also conducted an analysis of our data for our MT2 construct. However, we found that the error was too high, and therefore we determined that it wasn’t sensitive enough at this time, and further experiments are required.
Our transgenic (MT1) mammalian cells proved to be much more sensitive to copper sulfate than the defined EPA range of concern. This indicates that the metallothionein 1 gene is being expressed in the cell when exposed to these concentrations of copper sulfate. This gene is typically activated as part of heavy metal induced stress pathways and has been implicated as a chelator of heavy metals in yeast. This suggests it is possible that similar stress pathways are stimulated in human cells at similar concentrations-- concentrations approximately 400 times lower than the EPA cytotoxicological level. Further experiments are required to examine this finding, and investigate what it means for human health.
After maximum expression, as concentration of copper sulfate increases, expression decreases. We hypothesize that this is due to the cells dying at higher concentrations of chemical of concern.
From literature review, we found that the relevant cytotoxicological dose for copper sulfate is less than 1.3 parts per million, which is equivalent to 6.25 uM [1].
First, allow us to define some parameters from our model: Kstimulus is our michaelis-menten constant, which for our project is used as a measure of the sensitivity of our promoters. Vmax is the maximum reaction velocity, and in the context of our project, Vmax gives us maximum EGFP expression. Kstimulus is the concentration at which EGFP expression is one half of maximum expression.
From our curve-fit data, we found our Kstimulus value to be 0.2784 uM. This implies that our promoter construct is approximately 23 times more sensitive to the chemical than the threshold of the cytotoxicological limit defined in literature. From our curve fit, we also found that Vmax value occurs at a copper sulfate concentration of 5 uM. As defined by the EPA, the relevant dose is 6.25 uM. Because our Vmax is very close to the EPA defined value, it implies that our promoter operates within the range defined by the EPA to be of interest.
The data that is displayed on the wiki is data that was found twelve hours after induction in the cell line, CHO-DG44.


We also conducted an analysis of our data for our MT2 construct. However, we found that the error was too high, and therefore we determined that it wasn’t sensitive enough at this time, and further experiments are required.
Our transgenic (MT1) mammalian cells proved to be much more sensitive to copper sulfate than the defined EPA range of concern. This indicates that the metallothionein 1 gene is being expressed in the cell when exposed to these concentrations of copper sulfate. This gene is typically activated as part of heavy metal induced stress pathways and has been implicated as a chelator of heavy metals in yeast. This suggests it is possible that similar stress pathways are stimulated in human cells at similar concentrations-- concentrations approximately 400 times lower than the EPA cytotoxicological level. Further experiments are required to examine this finding, and investigate what it means for human health.
Figure 2. Chemicals of Concern
| Chemical name | Klamath Environmental concentration | Cytotoxicology(In micromoles per liter) | Measured Kstim MT1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen Peroxide[1] | -- | Relevant dose is 60 uM[3] | 0.9546 uM |
| Copper sulfate[2] | Copper measured at concentration of 19-67 ppm (112uM - 420uM)[4] | Relavant dode is <1.3ppm (6.25uM)[4] | 0.2784 uM |
References
[1] “Copper Fact Sheet.” Archive.epa.gov, US EPA, archive.epa.gov/pesticides/reregistration/web/pdf/copper_red_fs.pdf.
“Copper Sulfate.” Copper Sulfate, EXTOXNET, pmep.cce.cornell.edu/profiles/extoxnet/carbaryl-dicrotophos/copper-sulfate-ext.html.
“CDC - COPPER SULFATE (Anhydrous) - International Chemical Safety Cards - NIOSH.” Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, www.cdc.gov/niosh/ipcsneng/neng0751.html.
Nakamura, Jun, et al. “Micromolar Concentrations of Hydrogen Peroxide Induce Oxidative DNA Lesions More Efficiently than Millimolar Concentrations in Mammalian Cells.” Nucleic Acids Research, Oxford University Press, 15 Mar. 2003, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC152865/.
“Hydrogen Peroxide.” Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 11 Apr. 2016, www.cdc.gov/niosh/npg/npgd0335.html.
Eagles-Smith, C.A., and B.L. Johnson, 2012, Contaminants in the Klamath Basin: Historical patterns, current distribution, and data gap identification: U.S. Geological Survey Administrative Report, 88 p.
Santos, Anderson K. et al. "Expression System Based on An MtIIa Promoter to Produce Hpsa In Mammalian Cell Cultures". Frontiers in Microbiology, vol 7, 2016. Frontiers Media SA, doi:10.3389/fmicb.2016.01280.
Peterson CW, Narula SS, Armitage IM. "3D solution structure of copper and silver-substituted yeast metallothioneins". FEBS Lett. 379 (1): 85–93, 1996. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(95)01492-6. PMID 8566237.

 Cenozoic
Cenozoic