Leagrssmff (Talk | contribs) |
Leagrssmff (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 162: | Line 162: | ||
<div class="block title"> | <div class="block title"> | ||
<h1>Data analysis</h1></div> | <h1>Data analysis</h1></div> | ||
| + | <div class= "block full"> <p> See all your data in this Excel file. </p> | ||
<div class="block title"> | <div class="block title"> | ||
<h2>Population</h2></div> | <h2>Population</h2></div> | ||
Revision as of 17:11, 13 October 2018

Gold & Integrated HP

Developing a Project Idea
After assembling our team, we spent the first two months in brainstorming sessions, researching potential topics for this year’s competition. A team member presented us the field of bionic prosthesis, and we were all shocked by the number of people who were suffering from an amputation. His first idea was to use the capacity of bacteria to drive an electrical current to amplify the signal between the patient’s nerves and electrical sensors linked to a prosthesis. This way, redirection of nerves wouldn’t be necessary and the patient would be able to accomplish more natural actions.
When we started to look more in details the field of prosthesis and implant, we realized that along with device loosening or malfunctions and foreign-material reactions, infection remains the most serious problems encountered with surgical implants. We quickly learned that biofilm formation is common to all types of implanted foreign-body infections. Indeed, the high susceptibility of implanted devices to infection is due to a locally acquired host defense deficiency. Thus, this persistence at a specific site is mainly because of the rapid formation of a biofilm, which is resistant to host defense and antimicrobial agents as a result of reduced access and diffusion characteristics within it. We then decided to integrate this aspect inside our project: while favoring the growth of the nerve and the conduction of a signal through a bacterial interface, we could also diminish the risk of infection. At first, we wanted to find a system to directly kill the S. aureus, but after talking with Dr. Jean-Marc Ghigo (Genetics of Biofilm Unit, Institut Pasteur), we realized that the biofilm configuration would give us some hard time and require extra steps to manipulate. We decided to shift our goal, and rather than killing S. aureus, we would limit the virulence of the bacteria and restrict its ability to form a biofilm. This could be achieved by subverting the quorum sensing of the pathogenic bacteria and blocking the signal. In this way, S. aureus could be handled by the host’s immune system and by the patient’s doctor with a normal dosage of antibiotics.
In order to learn more about the significance of these issues in the medical field, we interviewed many professionals working either directly with patients, industries working on high tech metallic or ceramic implants, and amputees through the contact of ADEPA « Association for the Defense and Study of Amputated People ». Through all this work, we were invited for many tours, first at the European Hospital George-Pompidou where we had the chance to observe Dr. Benjamin Bouyer M.D., a lumbar rachis surgeon, during surgery to see the procedures put in place to diminish the risk of infection during the integration of an implant inside the body.
Targeted pathogenic bacteria and Chassis
The first thing we needed to do was to narrow down the pathogenic bacteria we would work on. After researching in the literature and talking with experts in the fields of prosthetics, we found out that Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis are the two most frequently found bacterial infectious agents on implants. We decided to use the biobrick designed by the iGEM team LMU_Munich 2014, who worked on a genetic circuit enabling Bacillus subtilis to actively detect Staphylococcus aureus.
Our bacterial chassis of choice, which would inhibit the quorum sensing of Staphylococcus aureus, needed to be a bacterium naturally occurring inside the human body. Indeed, we didn’t want to introduce a new strain inside the human body. The chassis also needed to have a good secretion system, as well as a good tolerance for the immune system. We narrowed down our choices between Bacillus subtilis, which the iGEM LMU_Munich 2014 worked on, and Escherichia coli, naturally living inside the gastrointestinal tract of humans with mostly no problem except for some strains. Because we wanted to improve their construction and because of convenience inside our lab, since we already had competent E. coli cells, we decided to use this strain. We optimized our sequences for an E. coli expression, and adapted them to its secretion system by adding export signals. This way, our construction could be broadened and used in a different type of bacterium. To replicate our plasmids, we used Escherichia coli DH5 alpha and to secrete our proteins, Escherichia coli BL21De3 pLys S.
Conceptualizing our Proof of Concept
When conceptualizing our proof of concept device, we decided to design a microfluidic chip to simulate the actions that would occur inside the patient’s body. The chip would be capable of measuring the neuronal signal as well as the conductivity of the biofilm, letting us know whether our system would work correctly inside a prosthetic. After talking with many professionals such as Dr. Heng Lu (ESPCI) and Dr Ayako Yamada (ENS, Ecole Normale Supérieure, Paris), we first designed a PDMS microfluidic chip with a vitreous carbon electrode to measure the signals. After talking with Dr. Catherine Villard (Institut Curie, Paris) and Dr. Frederic Khanoufi (University Paris Diderot—ITODYS), an electrochemist, we realized this type of electrode was highly sensitive, perhaps too sensitive for our type of device, and not adaptable to the size of our microfluidic chip. Guided by their advice, we switched to gold electrodes and started the fabrication process of the different type of chips at the Pierre Gilles de Gennes Institute. After attending the iCOE 2018, we learned about PEDOT (poly(3,4-ethylene dioxythiophene) polystyrene sulfonate ), and its conductive properties. As we also wanted to confine our bacteria so they would not harm our neuronal cells, we partnered with Sterlitech, and tested nanoporous polycarbonate membranes coated in gold as well as nanoporous alumina oxide membrane coated in PEDOT: PSS, PEDOT: CL and PEDOT: TS. This way, we could still measure the neuronal signal and the conductivity of the biofilm while protecting the cells from getting eaten by the bacteria.
Designing the interface between the tissues and the prosthetis
When we started to think about the scientific aspect of our project, we also started to design and think about how our biofilm would integrate into a physical medical device. First, we wanted to design a full prosthesis. We realized that it wasn’t the core of the problem. Indeed, the technology missing in this field was the actual interface between the prosthesis and the osseointegrated steel/titanium/ceramic stem inside the human body, limiting the field of bionic prosthesis. We decided to focus on this interface and started to talk with Dr. Benjamin Bouyer, a Lumbar rachis surgeon, on how we could deposit the biofilm on or in the osseointegrated stem. We realized that the stem would be in direct contact with the surgeon meaning that if we coated the whole structure with our biofilm, it would probably be stripped off, and get deposited on the gloves and contaminate other areas. We also spoke with one member of the board of directors of ADEPA, “Association de Défense et d’Etude des Personnes Amputés », which translates to « Association for the Defense and Study of Amputated Persons” who is himself an amputee. He gave us great advice on the designing phase of this interface and raised the issue of the socket causing excessive sudation and discomfort for the patient. After meeting with experts from I-CERAM (Ceramic medical devices company, Limoges, France) and the CERAH (Center for Studies and Research on the Equipment for the Handicapped), we learned more and more about the different materials used in the making of prostheses. At this point, we realized that doing a full stainless-steel interface would stimulate the growth of bacteria in a biofilm structure. Therefore, we decided to switch and do the part in direct contact with the patient in ceramic, knowing that we still have the same problem that I-CERAM and the CERAH were facing currently. Indeed, steel doesn’t last as much as ceramic, which could be a problem when creating an interface composed of both materials. We knew then that the patient would probably need corrective surgeries to fix his osseointegrated stem. Having considered these parameters, we then decided to start modeling our prototype by integrating those different aspects as much as possible. Because we wanted it to be cost-effective and injection-moldable, we built our current prototype in ABS, a thermoplastic polymer that could be 3D-printed. We ordered the electronic parts composed of a charger, battery, and amplifier, and assembled it into its current state as our POC.
Addressing law issues
While we were doing adjustments to our design in the lab, our team of jurists also researched how our device could be integrated into society given the current political and economic landscape in France. The use of GMOs, for the environment, food industry or medicine, is highly regulated in France and Europe. It is limited to design animal models of diseases and to produce large quantities of molecules for the pharmaceutical industry. The use of genetically modified bacteria inside the human body is not the subject of specific laws, which made our research on the subject difficult. We focused our research on medical device’s regulation in order to see if our project could be marketed. At first, it appeared almost naturally that our project was a medical device, but as it has to be understood as a legal term, it responds to a specific definition. Working on medical devices’ regulations helped us to better define our project, classify it and analyze our project in the scope of European regulations. We also tried to cover some legal questions related to our project and tried to find answers and other legal system such as the American one.
All these feedback from scientific experts, association members representing patients, and physicians/surgeons, allowed us to develop our project NeuronArch to what it is today. Without them, our project would not have been the same, and we really want to thank them for that.
Silver

Our Project in Society
One of the main concerns we had while developing our synthetic biology project was to determine in which way our biofilm could be used and who would be using it, in order to evaluate its impact on society. The field which would benefit the most of a nerves redirection while reducing the risk of infection, was orthopedic surgery, targeting patients suffering amputation.
Survey

Introduction
The project NeuronArch is also based on the survey that gives us information to orientate and improve our ideas. This survey has three main goals. Those goals concern both our project and synthetic biology in a general way:
- Vulgarize synthetic biology - Introduce our project to general public - Obtain opinion about our project from health professional
To achieve those goals, we had to reflex on the survey’s framework. For that, we decided to distinguish two types of public: general public (children, students, parents…) and health professional. Then, we realized a little “map” of our survey which respects our goals and our different publics.

As is shown by the the map above, there are two common sections : one at the beginning talking about general questions, synthetic biology and biofilms for all publics and one at the end of the survey to gather feedbacks and opinion. Then, a section about infections in prosthesis, just for health professional who are working in relation with prosthesis. Indeed, we decided to limit health professional to those who are in contact with prosthesis: orthopaedist, physiotherapist, nurse, student in medicine… This choice enabled us to collect relevant information concerning the project NeuronArch and to achieve the third goal of this survey. Besides the distinction between general public and medical professional, we wanted to make out the different levels of biology . For that, we asked a question concerning science education level. This question helped us to analyse answers about synthetic biology for example. After defining goals, publics and framework of our survey, we had to reflex on the analysis process.
Approach though trial and error
This approach was adopted just after collecting first answers. The last section of the survey is dedicated to public’s opinion and feedbacks about the survey. With this section, we can gather all critics and advices to improve the survey (and the project too!).

We adapted our explanatory content making it more readable. We added some questions: for example, we decided to ask biology level to improve our analysis and to well understand comments and feedbacks. We also modified some questions: - About the age fork - About the infection rate in prosthesis: we discussed with the team and we had comments that mentioned that the question was too confused. Moreover, we received comments question about the project and the scientific part. Further to a suggestion in the comments, we thought about developing a way to re-answer making the survey even more interactive. This process through trial and error enabled us to improve the survey and obtain relevant answers. Also, this approach helped us for the different analysis: quantitative and qualitative.
Data analysis
See all your data in this Excel file.
Population
Our survey was launched on August 21st, 2018 on the platform Google Form and was destined to the French public. We received 205 answers from 80 men and 125 women.

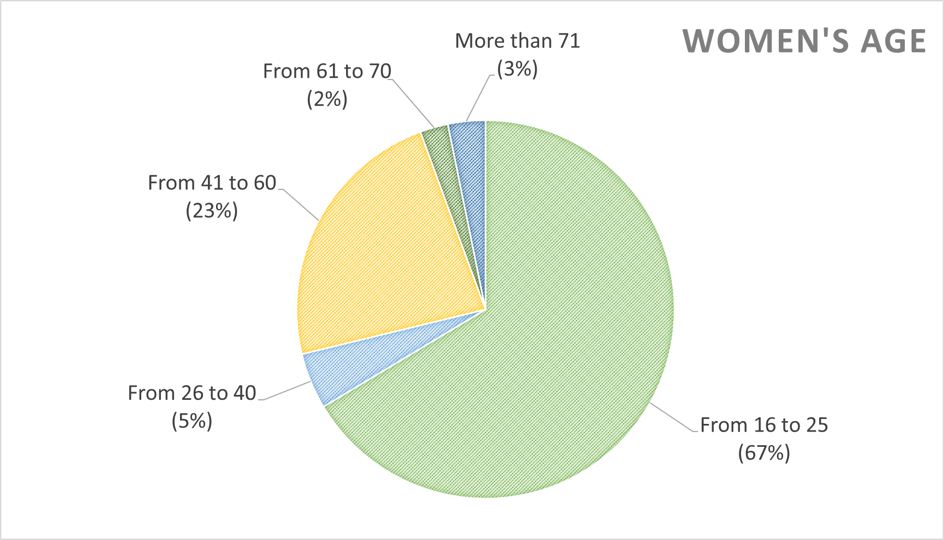
We tried to diffuse our survey on the internet, trying to reach as much people as possible. At the beginning we noticed that most of the answers were from the young population, between 16 and 25, mostly people from the age of the team members. We then tried to reach an older population, from 26 to more than 71.

In the end, we still have a majority of young people between 16 and 25, however almost 1/3 of the answers are from other range.

With the first version of our survey, we did not ask details about the scientific background, and especially the background in biology. However, we quickly realize, reading some comments and seeing the first results, that feedback on the survey and on what people understood or already knew was highly related to their background in biology. For example, at we were surprised that some people answered that the survey did not help them to better understand synthetic biology, but in the end, we discovered that some of them had a Ph.D. or were College student in biology.

Opinion about synthetic biology
One of the goals of our survey was to vulgarize synthetic biology by asking questions on it and explaining what it is and what it is for. We wanted to know whether people knew what is was and whether they had interest in it. We can see that a few people are not interested in synthetic biology or GMOs at all.


As there are people interested in synthetic biology and GMOs, it appears that a lot of them have some apprehensions, which could explain their interest in it.

In general people have apprehensions concerning synthetic biology, even though, we can also observe that 100% of those polled have a good opinion about synthetic biology’s utility. Indeed, even though 75% of those polled thinks synthetic biology needs an ethical framework, it is still a field of study that could have a great role in driving the science forward.

Opinion about our project
As our product is meant to be a medical device and inserted in the human body, an important question would: would people accept to wear our prosthesis? As we wanted to have the most honest answer to this question, we paid attention to the formulation. The question was « If necessary and in if a NeuronArch prosthesis were available on the market, would you be ready to integrate to your body or recommend such a medical device, integrating genetically modified organisms? ». We wanted to remind them that we were talking about a medical device that would insert GMOs in the human body. We were surprised by the rate a positive answer to this question. Indeed, only 11% of those polled answered they would not accept to wear our device.

Our survey was also a way to present our project to health professionals. Indeed, our survey was made of 2 parts, on with general questions about synthetic biology and a second one dedicated to health professional in contact with amputees. Even though this part was hard to fill, as it requires 2 characteristics (working in the field of health; being in contact with amputees), it was very interesting to analyze the answers of persons working in the medical fields and to read their comments. We discovered that there was a real interest in our project. We asked for example, whether they thought our project was feasible and what they were thinking of our project. On 8 answers, 6 answers were « Yes », 1 answer was « Maybe » and the last comment was a comment on our project « Project that tries to improve a real current problem » We also gathered some information on the percentage of implant related infections, the ways to improve the comfort of the patients who are wearing a prothesis and information on how implant-related infections are treated.

Feedback on our survey
A last part of our survey was a feedback of our survey. We wanted to know if it had helped people to understand what synthetic biology is and if our explanations were sufficient. We asked questions about the whether or not our survey helped them understanding what synthetic biology is, on the clarity of our explanations and the relevance of our questions. In order to better evaluate the impact of our survey, we wanted people to evaluate their knowledge of synthetic biology before and after answering our survey.

What is the most important aspect is that, among those who did not know synthetic biology at all, more than the half of this 14% of people, have a positive evaluation of their knowledge of synthetic biology. Indeed, more than the half gave 4/5 or 5/5 as a grade to the question: Did our survey help you to better understand what synthetic biology is? Concerning the clarity of our explanations, we asked people to rate it, thanks to a scale going from 1 to 5 (1: explanations lack of clarity; 5: explanations are very clear).

We also asked people to explain their answers. Three main types of comment stood out: in one hand, people said that our survey was clear and well explained with a good point for illustrations and photos, but in the other hand, it also appeared that it was too long and repetitive. It also appears for 6 people that our survey was not vulgarize enough and was difficult to understand when having no background in biology.

Some comments: « Je suis de tout coeur avec vous dans ce projet ! » (“I am with you in this project with all my heart!”) « J'ai appris beaucoup d'informations sur le sujet que je ne connaissais pas » (“I have learned a lot of information on a subject I did not know before”) « Merci de m'avoir fait connaître votre projet et j'espère qu'il sera couronné de succès et qu'il pourra servir dans d'autres circonstances (éviter la multirésistance de certains germes, proposer d'autres thérapies ...) » (“Thanks for making me discover your project and I hope it will be successful and that it will useful in other circumstances (avoid multiresistance to some germs, offer other kind of therapies…)”) « Sujet intéressant, qui pourra, et j'espère améliorer la vie des personnes amputées. Et surtout bon courage et bonne chance à vous. » (“Interesting subject, that will, and I hope, improve life of amputees. Above all good luck”)
