Engagement
WeChat subscription
We established a WeChat subscription, launching introductions, questionnaires, and declaring feedbacks.




Report on Questionnaire
To investigate public’s cognition state and acceptance level on genetically modified food(referred as GM food in parts of the article below), we set up this questionnaire. It includes twenty questions, of which consist the sample's age, occupation and educational background, as well as a series of surveys on genetically modified food. A total of 675 questionnaires were collected in this survey.
The following questions are not in exactly the same order as those in the questionnaire, but are rather sorted by relevancy.
1. Basic information statistics
Question 1: age statistics
Question 2: occupation statistics
Question 3: educational background statistics

From these chart, we could see that our responders are distributed in various ages, industries and educational backgrounds, and the sample size is relatively large, reaching 675 people. Therefore, this survey has certain universality and representativeness.
Question 4: the most common way to acquire knowledge/information

The purpose of question 4 is to investigate the ways the public obtain information. It can be seen from the figure above that people mainly obtain information through search engines, WeChat subscriptions and other network methods. In order to reach a more effective and efficient way to spread information, these ways are our best choice list.
2. Public awareness and opinions on genetically modified food
Question 5: Will you pay attention to the topic of "safety of genetically modified food”?

The results showed that 243 people were generally concerned. 236 people were more concerned. Ninety-eight were very concerned and 83 were less concerned; Fifteen people don't pay any attention.
Question 6: Whether or not it is considered appropriate to label food packaging as genetically modified food?

We could see that almost everyone states that they had the rights to know what their food consist of, and only about thirty person do not care about this topic.
From our data related to the two questions, we could reach the conclusion that most people are actually concerned about the safety of genetically modified food, and they care about whether their food have been genetically modified, which makes our research and future movements more meaningful. And we could assume that this is a hot topic, and we could raise public’s attention if we engage with them via this theme.
To get more detailed information on public opinion and awareness, we added a few more questions.
Question 7: Among theses statements, which best fits your understanding of genetically modified food?

From our figures above, we could see that most people have fair awareness and their own proper thinking towards genetically modified food, whether it is negative or positive, at least they are aware of the principle/basic theory of genetically modified food and the process before they appear on the market. But still, about thirteen percent of people thought GM food might as well change our genes and cause us to transform into alternative creatures, which means they need more detailed information on this technology.
If you put another question in mind and consider the two questions together, things become fairly interesting.
Question 8: In your consideration, what drawbacks does genetically modified food have?

In all responses, number of people thinking that GM food could increase incidence of various diseases comes first. Since this is actually a fairly possible hypothesis that we are all concerned about, we were really glad to see this result. But people thinking it might be harmful to our genes comes second. Although it is not an impossible hypothesis, it contradicts the results from the previous question, in which only a small percent of person chose"They modified genes of food, and might produce some unknown poisonous matters”. This leads us to assume that there is a number of people who do not really understand what gene engineering is, so they see harm our genes” and “cause variations” as two different options, proving that we need more education about this.
To form a complete set, we also set up a question discussing advantages of GM food.
Question 9: In your consideration, what advantages does genetically modified food have?
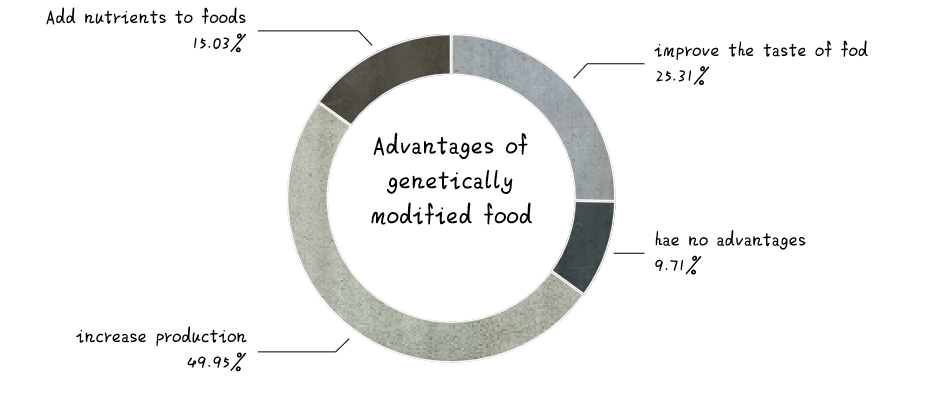
And we had another similar questions, which we could consider together.
Question 10: In your consideration, Why is there such a thing as genetically modified food?

From the figures above, we shall see that most people thought genetically modified food are produced because of the food shortage we may face, and they mostly agree that this is an advantage that could not be ignored. We believe this is a representation of reasonable thinking, since most people do not denial and do not refuse to admit the good influences GM food bring to us. But there is still about 10 percent of people, resisting this technology strongly and failed to see it in a more considerable way. This is what future education might be aiming at.
Besides surveying on public’s opinions of advantages and disadvantages of genetically modified food separately, we also set question asking their total attitude to genetically modified food as whole.
Question 11: Integrating all factors, what’s your opinion towards genetically modified food?

From our data, we could see about half of the people engaged in our questionnaire stay neutral on the topic, and after reading some of their written feedbacks, we found that many people are still waiting for an accurate research result on this, and they stated:”Before any experiment results prove the certainties of those disadvantages, they would just wait and see, and would just stay neutral about this.” About 30 percent of people hold a negative attitude towards GM food another 12 percent do not have a precise description for their position and only less than ten percent of people are positive about this. We have no rights to say which attitude is right or wrong, but for our team only, we surely agree most on a neutral or positive attitude, because till now, no actual experiments have proven the GM food very harmful to human beings.
Related to this, we surveyed how much people would buy genetically modified food.
Question 12: Would you buy genetically engineered food yourself?

We could see that people who would not buy genetically modified food are more than people who would, occupying 57percent. But if we form a connection between this question and our previous question, we could see an interesting phenomenon. People who chose neutral would also chose”sides" when asked whether they would buy GM food, and if our data are correct, we could see slightly more neutral people would not buy GM food. This could be our flaws when setting up the answers, but this is truly a vital question which everyone might face when shopping in the supermarket, so we thought this might be more accurate and representative on showing people’s attitude than the previous question. And for the answer to that, is more people are still negative and concerned about genetically modified food, while on the other hand there are a large number of people chasing to buy it.
Speaking of buying genetically modified food, we also installed a set of questions to penetrate into this.
Question 13: In your point of view, can we find genetically modified food in the market?

About 99 percent of people believe we could buy genetically modified food in the market, which is actually a correct cognition of the current situation. But there is still one percent of person unaware of the present market status, and it’s a direction we could walk towards—to eliminate that last one percent of people.
Question 14: Which kinds food do you think genetically modified technology mainly exists in?

Question 15: List these genetically modified food by the sequence of high acceptance to low acceptance.

From these figures, we could see that people are more likely to know modified soy products, vegetables/fruits and grain, and when milk and meat are mentioned, there is a big drop down, inferring a large number of decrease. Also, as dairies are only indirect product of genetically modification technology, thus compared with other types of modified food, it should be safer theoretically. In other words, public acceptance shall be high. But the results show milk products ranked second to last, meaning fairly low acceptance. Both conclusion indicate a lack of knowledge about genetically modified food.
Question 16: Generally, how do you distinguish genetically modified food and regular food when shopping?

Many people are not capable of distinguishing GM food and regular food, people thinking strange vegetables and fruits are genetically modified and people looking at the label come second and third in the figure. Since labels mainly appeared on processed food, and not so commonly seen on fruits or vegetables, we could say that most people can not tell whether they are eating genetically modified fresh food, and the government and food-producing companies shall be aware of this and provide a more transparent and comforting marketing environment.
When we come across the topic of genetically modified food in the market, we think of the experiment and process it have to undergo before it appears in the market. Therefore leading to our next series of questions.
Question 17: What restrictions do you think there should be on genetically modified foods?

About half of the responders think full and transparent animal experiment is enough, though this is still something not so easy to achieve. Another half holds a rather negative position in this question.
Question 18: Do you know the process genetically modified food undergo before coming in the market?

Most people know there is going to be a series of animal experiment before genetically modified food come into market, but the process are completely unknown to them. This could actually cause people’s unnecessary fear and concern, just because of human’s nature of being afraid to unknown. Therefore it is very important to build a more transparent and assuring system of producing and monitoring genetically modified food, and this could also help eliminate prejudice on this technology.
Meanwhile , we peaked into the future gene modification might holds in the eyes of publics.
Question 19: Do you support the generalization of genetically modified food ?

Question 20: Which sentence most describes your thought on the future of gene modification?

From the two questions above, we could see that more people are against and passive about gene modification, whether it is the product of it or the technology itself. We have no evidence to say these concerns are impossible, but till now, they at least haven’t been proved possible. Thinking this way ,we believe that there are a number off people who have bias on this topic.
3. Conclusion
Though opinions could not be simply judged, it is true that many people engaged with this research are lack of knowledge in gene modification, not to mention the synthetic biology as a whole subject. From this, we believe, it’s better to give lectures or write articles based on this topic to spread necessary knowledge, and this is partly why we held a school lecture, which would be mentioned in our next part of Human Practice.
Feedback on school presentations
Through our questionnaire feedback, we found that the public still had some misunderstandings about synthetic biology and genetically modified methods, so we decided to conduct a school lecture. The original idea was to popularize the basic knowledge of synthetic biology through this lecture, and contribute to the popularization of synthetic biology and the transformation of public opinion.
Our instructor and three teams mates lectured on different subjects, which mainly includes three topics. First on all, is THEORY, which is the basic knowledge on molecular and synthetic biology, along with some interesting and controversial news and problems in the field that is meaningful to be discussed. Secondly, is PRACTICE, which stands for the methods we used in our experiments and the significance behind them. Last, is COMPETITION, representing a introduction on iGEM and our team project, hoping to raise the public’s attention and interests in participating in synthetic biology and being an experimenter themselves.

Since recycling the public’s ideas can broaden our own thinking, therefore preventing us from getting stuck in a situation where a lot of energy is invested in a certain direction, but the general trend of the whole discipline is ignored. In this case, we should take the current situation of development and popularization into account and make corresponding changes and efforts. Thus we collected the feedbacks and analyzed them respectfully.

About the harvest
In the feedback we collected, 25% of those who had a lot of harvest, 39% of those who had a certain harvest, 22% of those who had some harvest, 10% of those who had a little harvest, and 4% of those who had no harvest. The presentation involves students and teachers of all grades and levels in the school, so the difficulty of the presentation is a key issue. More people are concentrated in the area where there is harvest, which indicates that the difficulty and difficulty of our publicity is more appropriate, which basically reaches our original intention of popularizing popular science.

About the idea
The audience's thoughts on the application field are concentrated in the related fields of medicine, biology, pharmacy and so on, which is also what the scientists are aiming at. There have been some successful applications in medicine, such as the synthesis of artemisinin and the precursor of the anticancer drug Paclitaxel. Synthetic biology is also closely related to sociology and social production, although the public is less involved, and there are already studies and partial production of bioenergy and biological products. In general, the field of synthetic biology development is more in line with public expectations.
In fact, philosophy is a very broad subject. Specific science is the foundation of philosophy. The progress of specific science promotes the development of philosophy. The specific science that we are doing is important for philosophy, but it is not limited to the field of synthetic biology.
The answer to the field of synthetic biology is more diverse, broadly grouped into health care, academic research, industrial production, life and society. Academic research contains paleontology research, genetic modification, human cloning, biological weapons, etc., of course there are also many disputes, sometimes technical level can achieve, but the moral and ethical will limit its reality, so in the process of the application of synthetic biology, still have many difficulties to be overcome, is not only a technical, there are some social factors, involves many interdisciplinary areas. The idea of a health care orientation that treats cancer, produces organs, evolves immune systems, synthetic antibiotics and other drugs, as well as in-vitro fertilization, needs to be based on a lot of academic research and ethical discussion. The application of production has been mature, such as cell factories and other technologies. Obviously, industrial production is also closely related to the development of academic research. Life and society, for example, will contribute to the development of medical ethics. To sum up, the development of synthetic biology is more in line with the public expectation and faces some problems. People who study synthetic biology need to make efforts to bring it into public view, eliminate misunderstandings and provide more possible choices in the future.

