Luke Zhang (Talk | contribs) |
|||
| (15 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 62: | Line 62: | ||
float: left; | float: left; | ||
width: 100%; | width: 100%; | ||
| − | padding: | + | padding: 23px 0%; |
margin: 0 0px !important; | margin: 0 0px !important; | ||
} | } | ||
| Line 72: | Line 72: | ||
display: block !important; | display: block !important; | ||
} | } | ||
| − | #logo img { width:150px; margin-top: | + | #logo img { width:150px; margin-top:5px;} /*???*/ |
#menu a { text-decoration: none; } | #menu a { text-decoration: none; } | ||
| Line 249: | Line 249: | ||
.paragraphs{ | .paragraphs{ | ||
| − | padding: 0 | + | padding: 0 150px 0 150px; |
font-family: sans-serif; | font-family: sans-serif; | ||
text-align: center; | text-align: center; | ||
| Line 289: | Line 289: | ||
<ul> | <ul> | ||
<!--links--> | <!--links--> | ||
| − | <li><a href=" | + | <li><a href="https://2018.igem.org/Team:SDU-CHINA/Experiments">Protocols</a></li> |
<li><a href="https://2018.igem.org/Team:SDU-CHINA/Notebook">Notebook</a></li> | <li><a href="https://2018.igem.org/Team:SDU-CHINA/Notebook">Notebook</a></li> | ||
<li><a href="https://2018.igem.org/Team:SDU-CHINA/Safety">Safety</a></li> | <li><a href="https://2018.igem.org/Team:SDU-CHINA/Safety">Safety</a></li> | ||
| Line 339: | Line 339: | ||
<div class="paragraphs"> | <div class="paragraphs"> | ||
| − | <h1 id="main-title"> | + | <h1 id="main-title">Description</h1> |
| − | <p>As one of the foundations of sustainable development, metabolic engineering rebuilds and optimizes metabolic network as well as regulatory pathways within cells to enhance production of native metabolites or to endow cells with the ability to produce new products. These products include fuels, chemicals, foods, feeds, and pharmaceuticals | + | <p>As one of the foundations of sustainable development, metabolic engineering rebuilds and optimizes metabolic network as well as regulatory pathways within cells to enhance production of native metabolites or to endow cells with the ability to produce new products. These products include fuels, chemicals, foods, feeds, and pharmaceuticals<sup>[1,2]</sup>. In order to improve the titer and yield of the target product, both the over-expression of genes responsible for target compound production <sup>[3,4,5]</sup> and the deletion of genes responsible for by-product synthesis <sup>[6,7,8,9]</sup> are required.</p> |
| − | < | + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2018/3/35/T--SDU-CHINA--description.jpg" height="350"><br> |
| − | < | + | <br> |
| − | <p> | + | <p>However, some of these deleted genes are responsible for the synthesis of intermediates of important metabolic pathways. The deletion of these genes can influence bacterial growth and cell maintenance. Deletion of these genes would increase the titer and yield of the desired product per cell but decrease the growth rate and final cell density, perhaps resulting in cell death. After all, the final cell density is important for the total titer and yield during fermentation.</p> |
| − | < | + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2018/f/fa/T--SDU-China--TRAIN_GROW.gif" height="250"><br> |
| + | <p>An alternative approach is to keep the expression of these genes high until an adequate cell mass is achieved, then turn these genes off. For example, instead of permanently knocking out a gene from the chromosome, a novel gene expression control system could conditionally inhibit the expression of a specific gene<sup>[10]</sup>.</p> | ||
| − | <p> | + | <p>A common choice is using commercially available induction systems, for instance, based on L-arabinose and isopropyl-b-D- thiogalactoside (IPTG) for the expression of enzymatic pathways. The use of artificial chemical inducers like L-arabinose and IPTG, although effective, less favourable because of the high cost of inducers, toxicity of inducer, and incompatibilities with industrial scale-up<sup>[11]</sup>. Recently, biological chemical inducer systems have been applied in metabolic engineering, mainly including two types: intermediate metabolite-induced system and quorum sensing (QS) system. In former, the special biosensor (e.g., the activator) detects the corresponding class of intermediate metabolites like NADPH/NADP<sup>+</sup><sup>[12]</sup>, and then promotes the expression of genes downstream. Different with the former, what the latter detects are the quorum sensing molecules like N-acyl homoserine lactones (AHL)<sup>[13]</sup>. However, intermediate metabolite-induced systems have poor generality and selectivity, and QS systems are difficult to regulate.</p> |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | [ | + | |
| − | [ | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | [13] | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2018/3/3a/T--SDU-China--TRAIN_production.gif" height="250"><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p>In recent years, with the development of optogenetics in synthetic biology, precisely, a variety of light sensors provide a powerful piece of kit that can control cellular processes spatially and temporally<sup>[14-18]</sup>. On the one hand, as the inducer, light is not only cheaper and no-toxic, but also regulates the gene expression rapidly. On the other hand, using light as the inducer can avoid tedious genetic manipulation because conditions such as light duration, light intensity can be optimized from outside. Moreover, light has the other properties such as invertibility, spatial and temporal precision, and it can be the interface between electricity and organisms. Thus, light can be an ideal tool, which properties matches with metabolic pathways regulation<sup>[19]</sup>. We intend to take advantage of light as exogenous signal controlling the metabolic flux to balance the growth and production phase.</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p>With rapid development of industry, petrochemical plastics have spread worldwide due to their low cost, with ease of manufacture, versatility, and imperviousness to water<sup>[20]</sup>. Plastic bags, plastic bottles, Plastic greenhouses, etc. have become part of our daily life. And so much convenience plastic products bring to our life, which we can’t imagine the life without them.</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p>However, it seems that every coin has two sides. Petrochemical plastics are so hard to be degraded that they can neither be diluted by pouring into the ocean nor be completely degraded in years by being buried underground. And as more and more plastic products are produced, the total amount of plastic waste increases in a terrible rate within years. It seems that the only way to solve the plastic pollution nowadays, is burning them, which however, will release toxic chemicals and do harm to ourselves, probably causing nausea, headaches, damages in the nervous system, etc<sup>[21]</sup>. Hence, it’s our emergency to develop another convenient and low-cost material to replace the traditional plastics.</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p>Polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) is one of the promising bio-materials as a replacement, which can be naturally synthesized by a wide range of microorganisms as an intracellular carbon source. In addition, products made of PHB possess the outstanding physical properties similar to traditional plastics. It is accessible and more importantly bio-degradable. Even through it is thrown into the environment by mistake, it can still be degraded within years causing no pollution. Besides, PHB is also a renewable resource as it can be produced by microorganisms sustainably. Thus, for its broad market prospects, we would like to use PHB production as an example of our growth-production switching system, hoping that we can improve the production rate of PHB to reduce the cost.</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <h4 id="main-title">References</h4> | ||
| + | <p>[1] Keasling, Jay D. "Manufacturing Molecules Through Metabolic Engineering." Science 330.6009(2010):1355-1358.<br> | ||
| + | [2] Rabinovitchdeere, C. A., et al. "Synthetic biology and metabolic engineering approaches to produce biofuels. " Chemical Reviews 113.7(2013):4611-4632.<br> | ||
| + | [3] Wang, C. W., M. K. Oh, and J. C. Liao. "Engineered isoprenoid pathway enhances astaxanthin production in Escherichia coli. " Biotechnology & Bioengineering 62.2(2015):235-241.<br> | ||
| + | [4] Lee, Kwang Ho, et al. "Systems metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for L‐threonine production." Molecular systems biology 3.1 (2007): 149.<br> | ||
| + | [5] Lütke-Eversloh, Tina, and Gregory Stephanopoulos. "Combinatorial pathway analysis for improved L-tyrosine production in Escherichia coli: identification of enzymatic bottlenecks by systematic gene overexpression." Metabolic engineering 10.2 (2008): 69-77.<br> | ||
| + | [6] Clomburg, J. M, and R. Gonzalez. "Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for the production of 1,2-propanediol from glycerol. " Biotechnology & Bioengineering 108.4(2015):867-879.<br> | ||
| + | [7] Qian, Z. G., X. X. Xia, and S. Y. Lee. "Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for the production of putrescine: a four carbon diamine." Biotechnology & Bioengineering 104.4(2010):651-662.<br> | ||
| + | [8] Atsumi, S, et al. "Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for 1-butanol production. " Metabolic Engineering 10.6(2007):305-311.<br> | ||
| + | [9] Balzer, Grant J., et al. "Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli to minimize byproduct formate and improving succinate productivity through increasing NADH availability by heterologous expression of NAD+-dependent formate dehydrogenase." Metabolic engineering 20 (2013): 1-8.<br> | ||
| + | [10] Soma, Y, et al. "Metabolic flux redirection from a central metabolic pathway toward a synthetic pathway using a metabolic toggle switch." Metabolic Engineering 23.5(2014):175-184.<br> | ||
| + | [11] Lo, T. M., et al. "A Two-Layer Gene Circuit for Decoupling Cell Growth from Metabolite Production." Cell Systems 3.2(2016):133-143.<br> | ||
| + | [12] Zhang, J., et al. "Engineering an NADPH/NADP+ redox biosensor in yeast." Acs Synthetic Biology 5.12(2016):1546.<br> | ||
| + | [13] Galloway, W. R., et al. "Quorum sensing in Gram-negative bacteria: small-molecule modulation of AHL and AI-2 quorum sensing pathways." Chemical Reviews 111.1(2011):28. | ||
| + | [14] Baumschlager, A, S. K. Aoki, and M. Khammash. "Dynamic Blue Light-Inducible T7 RNA Polymerases (Opto-T7RNAPs) for Precise Spatiotemporal Gene Expression Control." Acs Synthetic Biology 6.11(2017).<br> | ||
| + | [15] Han, Tiyun, C. Quan, and H. Liu. "Engineered photoactivatable genetic switches based on the bacterium phage T7 RNA polymerase." Acs Synthetic Biology 6.2(2016).<br> | ||
| + | [16] Levskaya, A, et al. "Synthetic biology: engineering Escherichia coli to see light. " Nature 438.7067(2005):441-442.<br> | ||
| + | [17] Tabor, Jeffrey J., A. Levskaya, and C. A. Voigt. "Multichromatic Control of Gene Expression in Escherichia coli." Journal of Molecular Biology 405.2(2011):315-324.<br> | ||
| + | [18] Fernandez-Rodriguez, J, et al. "Engineering RGB color vision into Escherichia coli." Nature Chemical Biology 13.7(2017):706-708.<br> | ||
| + | [19] Zhao, E. M., et al. "Optogenetic regulation of engineered cellular metabolism for microbial chemical production. " Nature 555.7698(2018).<br> | ||
| + | [20] Wikipedia contributors. (2018, October 14). Plastic. In Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia. Retrieved 18:31, October 17, 2018, from https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Plastic&oldid=864042427<br> | ||
| + | [21] Guest Bloggers.(July 15, 2014).But can’t you just burn plastic? plastic-free tuesday.<br> | ||
</p> | </p> | ||
Latest revision as of 02:44, 18 October 2018
Description
As one of the foundations of sustainable development, metabolic engineering rebuilds and optimizes metabolic network as well as regulatory pathways within cells to enhance production of native metabolites or to endow cells with the ability to produce new products. These products include fuels, chemicals, foods, feeds, and pharmaceuticals[1,2]. In order to improve the titer and yield of the target product, both the over-expression of genes responsible for target compound production [3,4,5] and the deletion of genes responsible for by-product synthesis [6,7,8,9] are required.

However, some of these deleted genes are responsible for the synthesis of intermediates of important metabolic pathways. The deletion of these genes can influence bacterial growth and cell maintenance. Deletion of these genes would increase the titer and yield of the desired product per cell but decrease the growth rate and final cell density, perhaps resulting in cell death. After all, the final cell density is important for the total titer and yield during fermentation.
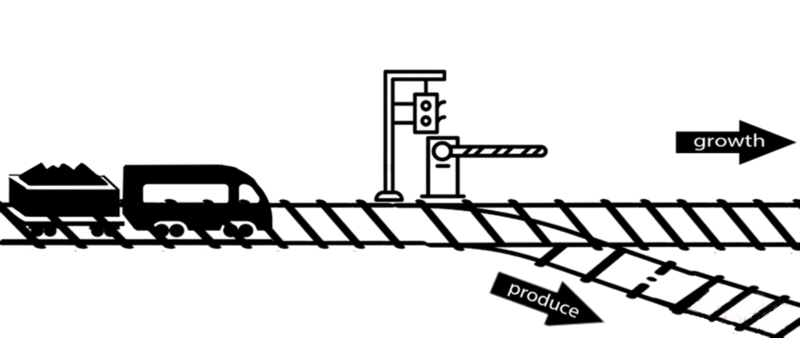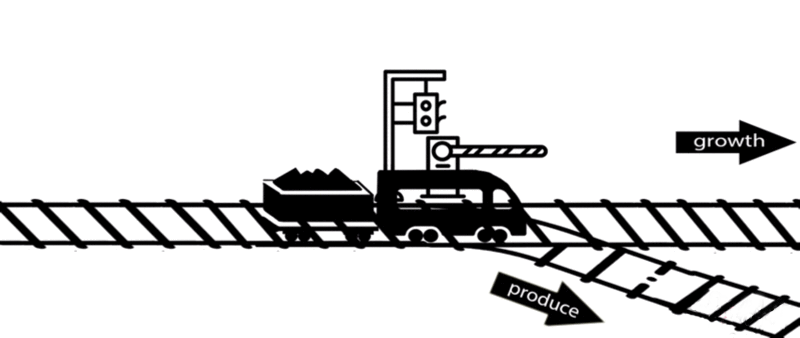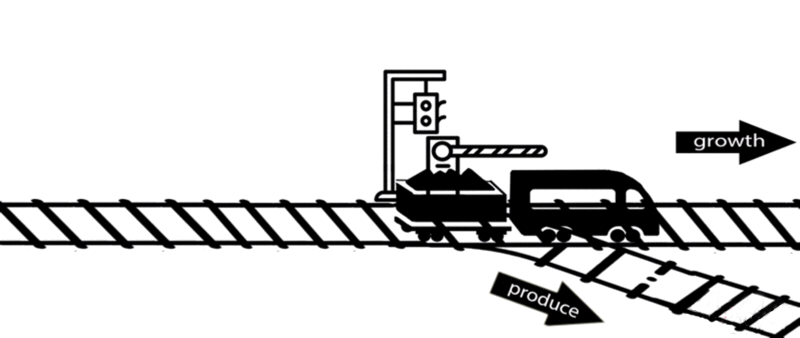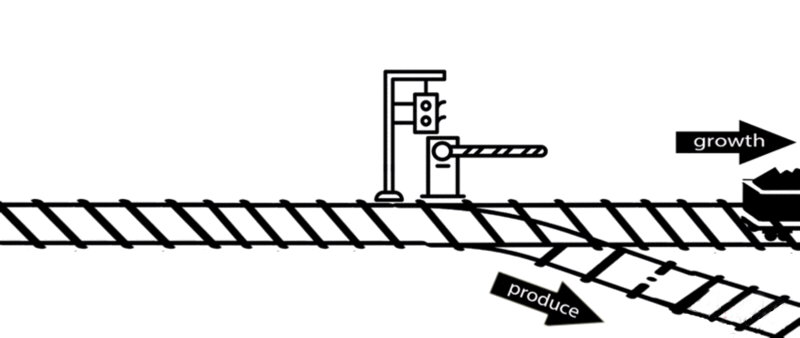
An alternative approach is to keep the expression of these genes high until an adequate cell mass is achieved, then turn these genes off. For example, instead of permanently knocking out a gene from the chromosome, a novel gene expression control system could conditionally inhibit the expression of a specific gene[10].
A common choice is using commercially available induction systems, for instance, based on L-arabinose and isopropyl-b-D- thiogalactoside (IPTG) for the expression of enzymatic pathways. The use of artificial chemical inducers like L-arabinose and IPTG, although effective, less favourable because of the high cost of inducers, toxicity of inducer, and incompatibilities with industrial scale-up[11]. Recently, biological chemical inducer systems have been applied in metabolic engineering, mainly including two types: intermediate metabolite-induced system and quorum sensing (QS) system. In former, the special biosensor (e.g., the activator) detects the corresponding class of intermediate metabolites like NADPH/NADP+[12], and then promotes the expression of genes downstream. Different with the former, what the latter detects are the quorum sensing molecules like N-acyl homoserine lactones (AHL)[13]. However, intermediate metabolite-induced systems have poor generality and selectivity, and QS systems are difficult to regulate.

In recent years, with the development of optogenetics in synthetic biology, precisely, a variety of light sensors provide a powerful piece of kit that can control cellular processes spatially and temporally[14-18]. On the one hand, as the inducer, light is not only cheaper and no-toxic, but also regulates the gene expression rapidly. On the other hand, using light as the inducer can avoid tedious genetic manipulation because conditions such as light duration, light intensity can be optimized from outside. Moreover, light has the other properties such as invertibility, spatial and temporal precision, and it can be the interface between electricity and organisms. Thus, light can be an ideal tool, which properties matches with metabolic pathways regulation[19]. We intend to take advantage of light as exogenous signal controlling the metabolic flux to balance the growth and production phase.
With rapid development of industry, petrochemical plastics have spread worldwide due to their low cost, with ease of manufacture, versatility, and imperviousness to water[20]. Plastic bags, plastic bottles, Plastic greenhouses, etc. have become part of our daily life. And so much convenience plastic products bring to our life, which we can’t imagine the life without them.
However, it seems that every coin has two sides. Petrochemical plastics are so hard to be degraded that they can neither be diluted by pouring into the ocean nor be completely degraded in years by being buried underground. And as more and more plastic products are produced, the total amount of plastic waste increases in a terrible rate within years. It seems that the only way to solve the plastic pollution nowadays, is burning them, which however, will release toxic chemicals and do harm to ourselves, probably causing nausea, headaches, damages in the nervous system, etc[21]. Hence, it’s our emergency to develop another convenient and low-cost material to replace the traditional plastics.
Polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) is one of the promising bio-materials as a replacement, which can be naturally synthesized by a wide range of microorganisms as an intracellular carbon source. In addition, products made of PHB possess the outstanding physical properties similar to traditional plastics. It is accessible and more importantly bio-degradable. Even through it is thrown into the environment by mistake, it can still be degraded within years causing no pollution. Besides, PHB is also a renewable resource as it can be produced by microorganisms sustainably. Thus, for its broad market prospects, we would like to use PHB production as an example of our growth-production switching system, hoping that we can improve the production rate of PHB to reduce the cost.
References
[1] Keasling, Jay D. "Manufacturing Molecules Through Metabolic Engineering." Science 330.6009(2010):1355-1358.
[2] Rabinovitchdeere, C. A., et al. "Synthetic biology and metabolic engineering approaches to produce biofuels. " Chemical Reviews 113.7(2013):4611-4632.
[3] Wang, C. W., M. K. Oh, and J. C. Liao. "Engineered isoprenoid pathway enhances astaxanthin production in Escherichia coli. " Biotechnology & Bioengineering 62.2(2015):235-241.
[4] Lee, Kwang Ho, et al. "Systems metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for L‐threonine production." Molecular systems biology 3.1 (2007): 149.
[5] Lütke-Eversloh, Tina, and Gregory Stephanopoulos. "Combinatorial pathway analysis for improved L-tyrosine production in Escherichia coli: identification of enzymatic bottlenecks by systematic gene overexpression." Metabolic engineering 10.2 (2008): 69-77.
[6] Clomburg, J. M, and R. Gonzalez. "Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for the production of 1,2-propanediol from glycerol. " Biotechnology & Bioengineering 108.4(2015):867-879.
[7] Qian, Z. G., X. X. Xia, and S. Y. Lee. "Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for the production of putrescine: a four carbon diamine." Biotechnology & Bioengineering 104.4(2010):651-662.
[8] Atsumi, S, et al. "Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for 1-butanol production. " Metabolic Engineering 10.6(2007):305-311.
[9] Balzer, Grant J., et al. "Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli to minimize byproduct formate and improving succinate productivity through increasing NADH availability by heterologous expression of NAD+-dependent formate dehydrogenase." Metabolic engineering 20 (2013): 1-8.
[10] Soma, Y, et al. "Metabolic flux redirection from a central metabolic pathway toward a synthetic pathway using a metabolic toggle switch." Metabolic Engineering 23.5(2014):175-184.
[11] Lo, T. M., et al. "A Two-Layer Gene Circuit for Decoupling Cell Growth from Metabolite Production." Cell Systems 3.2(2016):133-143.
[12] Zhang, J., et al. "Engineering an NADPH/NADP+ redox biosensor in yeast." Acs Synthetic Biology 5.12(2016):1546.
[13] Galloway, W. R., et al. "Quorum sensing in Gram-negative bacteria: small-molecule modulation of AHL and AI-2 quorum sensing pathways." Chemical Reviews 111.1(2011):28.
[14] Baumschlager, A, S. K. Aoki, and M. Khammash. "Dynamic Blue Light-Inducible T7 RNA Polymerases (Opto-T7RNAPs) for Precise Spatiotemporal Gene Expression Control." Acs Synthetic Biology 6.11(2017).
[15] Han, Tiyun, C. Quan, and H. Liu. "Engineered photoactivatable genetic switches based on the bacterium phage T7 RNA polymerase." Acs Synthetic Biology 6.2(2016).
[16] Levskaya, A, et al. "Synthetic biology: engineering Escherichia coli to see light. " Nature 438.7067(2005):441-442.
[17] Tabor, Jeffrey J., A. Levskaya, and C. A. Voigt. "Multichromatic Control of Gene Expression in Escherichia coli." Journal of Molecular Biology 405.2(2011):315-324.
[18] Fernandez-Rodriguez, J, et al. "Engineering RGB color vision into Escherichia coli." Nature Chemical Biology 13.7(2017):706-708.
[19] Zhao, E. M., et al. "Optogenetic regulation of engineered cellular metabolism for microbial chemical production. " Nature 555.7698(2018).
[20] Wikipedia contributors. (2018, October 14). Plastic. In Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia. Retrieved 18:31, October 17, 2018, from https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Plastic&oldid=864042427
[21] Guest Bloggers.(July 15, 2014).But can’t you just burn plastic? plastic-free tuesday.


